Money
Mapped: A Snapshot of Wealth in Africa
Mapped: A Snapshot of Wealth in Africa
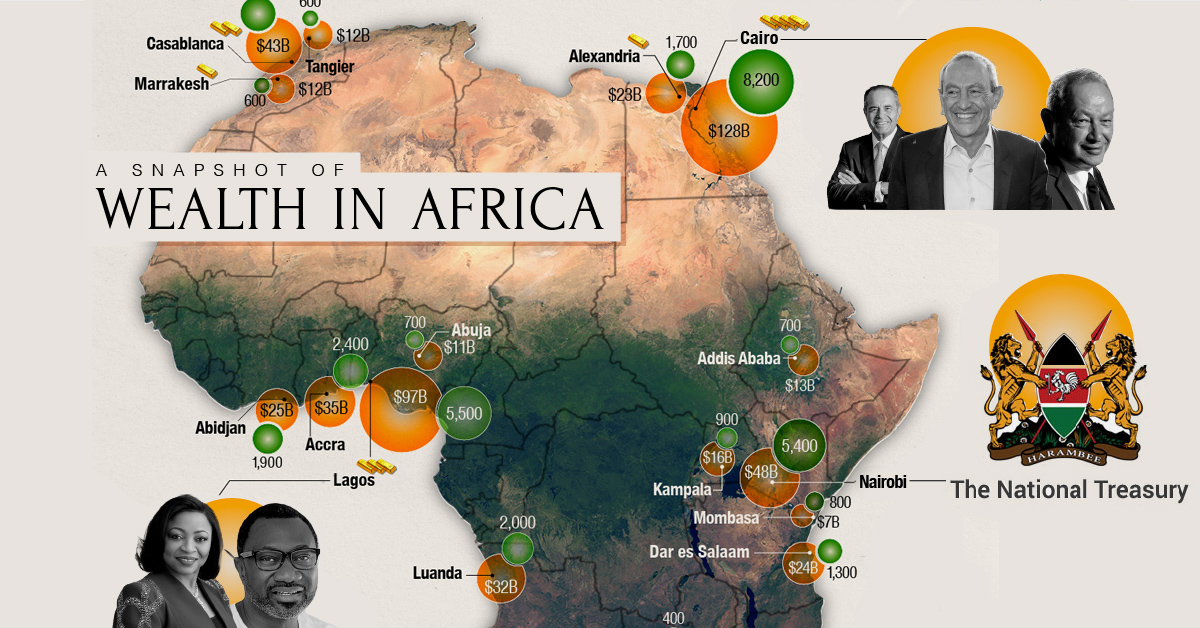
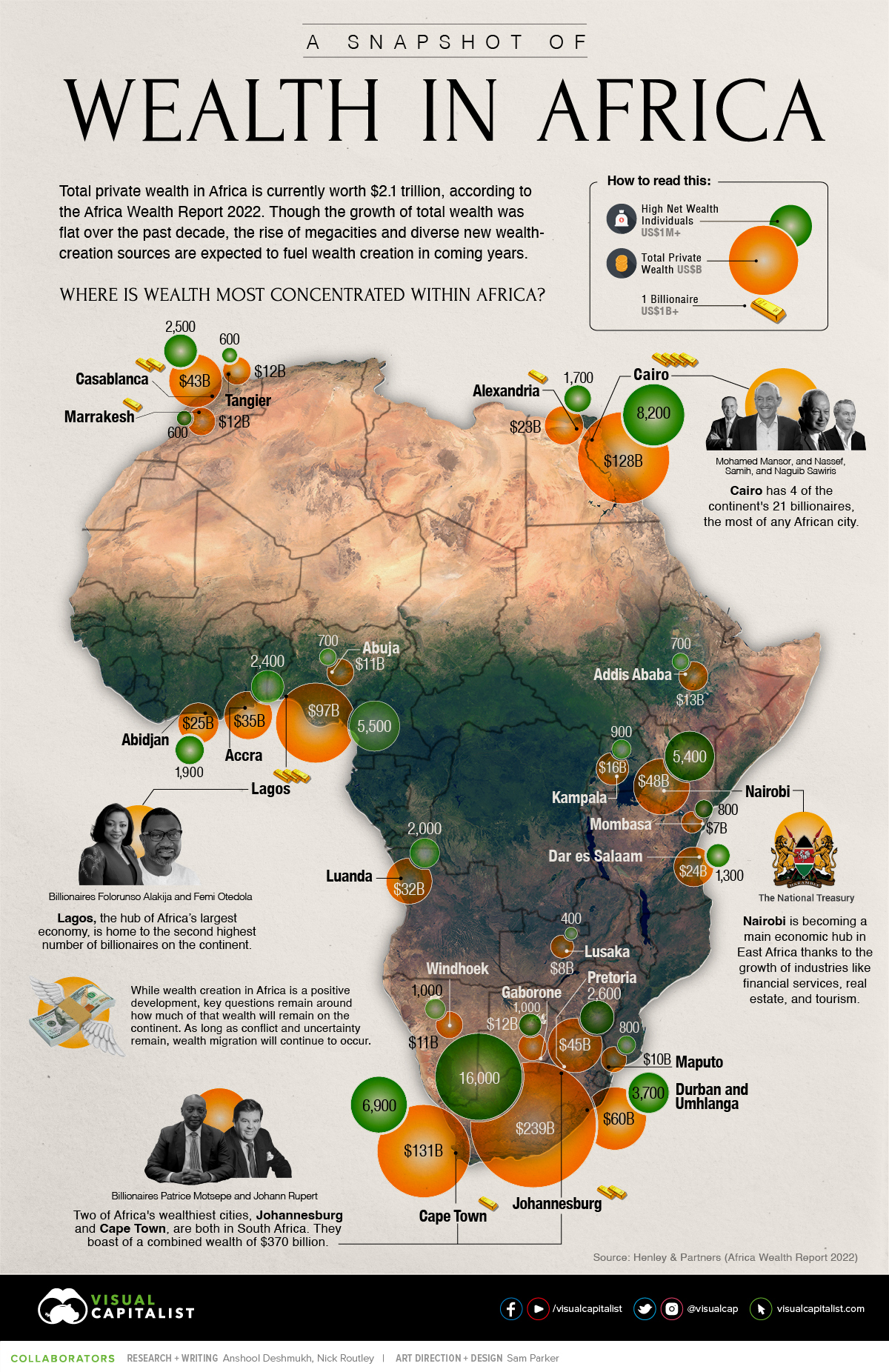
The continent of Africa contains more than 50 countries, but just five account for more than half of total wealth on the continent: South Africa, Egypt, Nigeria, Morocco, and Kenya.
Despite recent setbacks in Africa’s largest economies, wealth creation has been strong in a number of areas, and total private wealth is now estimated to be US$2.1 trillion. There also an estimated 21 billionaires in Africa today.
Drawing from the latest Africa Wealth Report, here’s a look at where all that wealth is concentrated around the continent.
A Country-Level Look at Wealth in Africa
South Africa is a still a major stronghold of wealth in Africa, with a robust luxury real estate market and ample wealth management services. The country is also ranked second on the continent in per capita wealth. That said, the country has faced challenges in recent years.
An estimated 4,500 high net worth individuals (wealth of US$1 million or more) have left South Africa over the past decade, migrating to places like the UK, Australia, and the United States. In one stark data point, the report points out that “there are 15 South African born billionaires in the world, but only 5 of them still live in South Africa.”
Here is how major African countries compare in terms of per capita wealth.
| Rank | Country | Wealth per Capita (US$) |
|---|---|---|
| #1 | 🇲🇺 Mauritius | $34,000 |
| #2 | 🇿🇦 South Africa | $10,970 |
| #3 | 🇳🇦 Namibia | $9,320 |
| #4 | 🇧🇼 Botswana | $7,880 |
| #5 | 🇲🇦 Morocco | $3,380 |
| #6 | 🇪🇬 Egypt | $3,000 |
| #7 | 🇬🇭 Ghana | $1,890 |
| #8 | 🇰🇪 Kenya | $1,700 |
| #9 | 🇦🇴 Angola | $1,620 |
| #10 | 🇨🇮 Côte d'Ivoire | $1,610 |
| #11 | 🇳🇬 Nigeria | $1,100 |
| #12 | 🇹🇿 Tanzania | $940 |
| #13 | 🇷🇼 Rwanda | $850 |
| #14 | 🇺🇬 Uganda | $820 |
| #15 | 🇿🇲 Zambia | $760 |
| #16 | 🇲🇿 Mozambique | $650 |
| #17 | 🇪🇹 Ethiopia | $540 |
Mauritius is Africa’s wealthiest nation on a per capita basis. Here are a few reasons why the island nation comes out on top:
- HNWI growth – Wealthy individuals have flocked to Mauritius in recent years
- Ease of doing business – Mauritius ranked 13th worldwide in World Bank’s Doing Business Report
- Low taxes – There is no inheritance tax or capital gains tax in the country
- Safety – Mauritius was recently rated by New World Wealth as the safest country in Africa
- Financial sector – A growing local financial services sector and stock market (SEMDEX)
As a result, Mauritius has seen the strongest growth in total private wealth over the past decade, followed by Rwanda and Ethiopia.
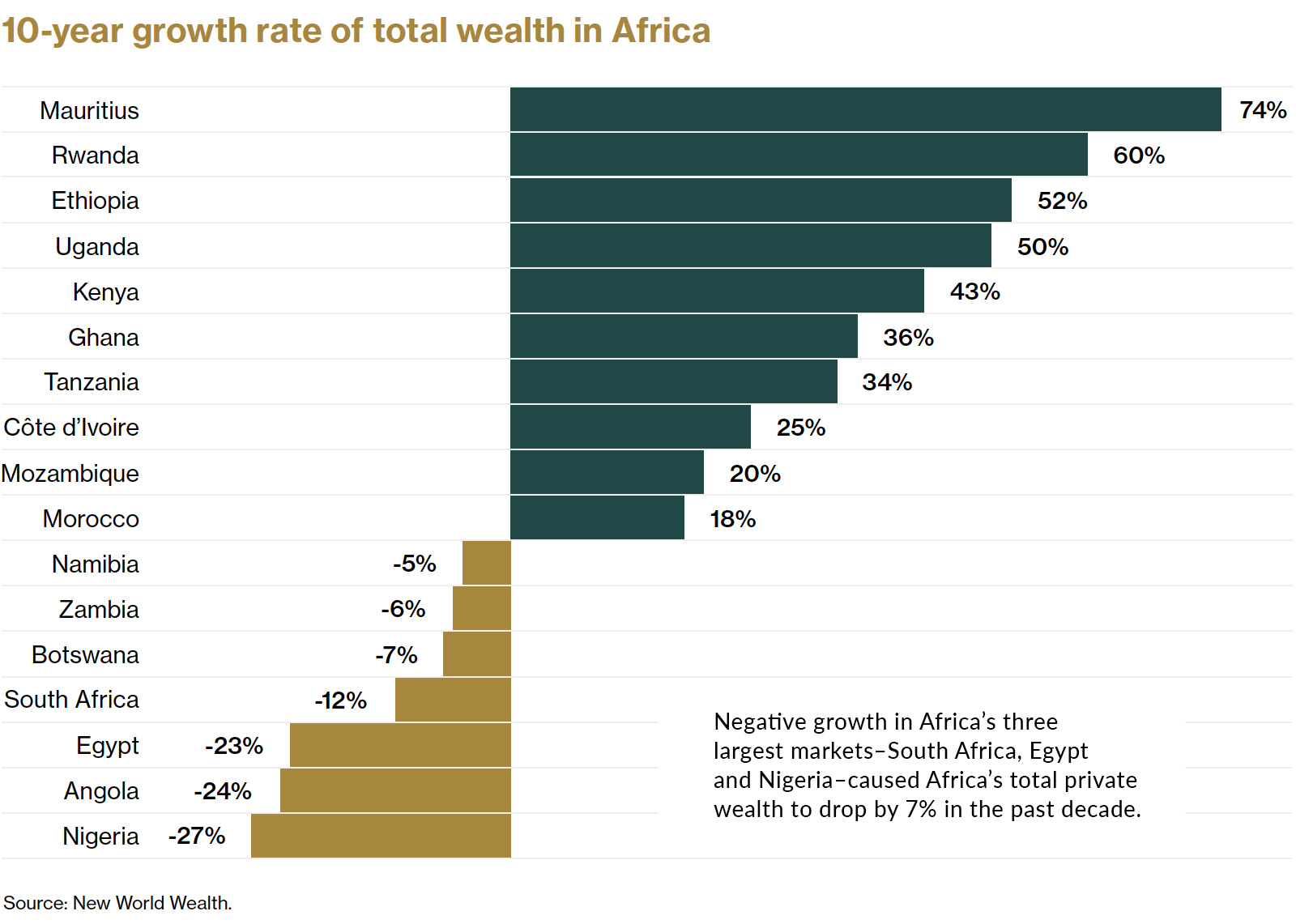
On the flip side of the equation, Nigeria—which is Africa’s largest economy—saw a steep drop in total wealth. The country has struggled in recent years with high unemployment, corruption, and an over-reliance on crude oil.
The Big Picture
Over time, African countries are becoming less dependent on extractive industries, and business conditions are continuing to improve nearly across the board. These tailwinds, combined with the continent’s favorable demographics, point to a bright economic future for Africa.
The outlook for private wealth on the continent is largely positive as well. Total private wealth held in Africa is expected to reach US$3 trillion by 2031, an increase of close to 40%.
Money
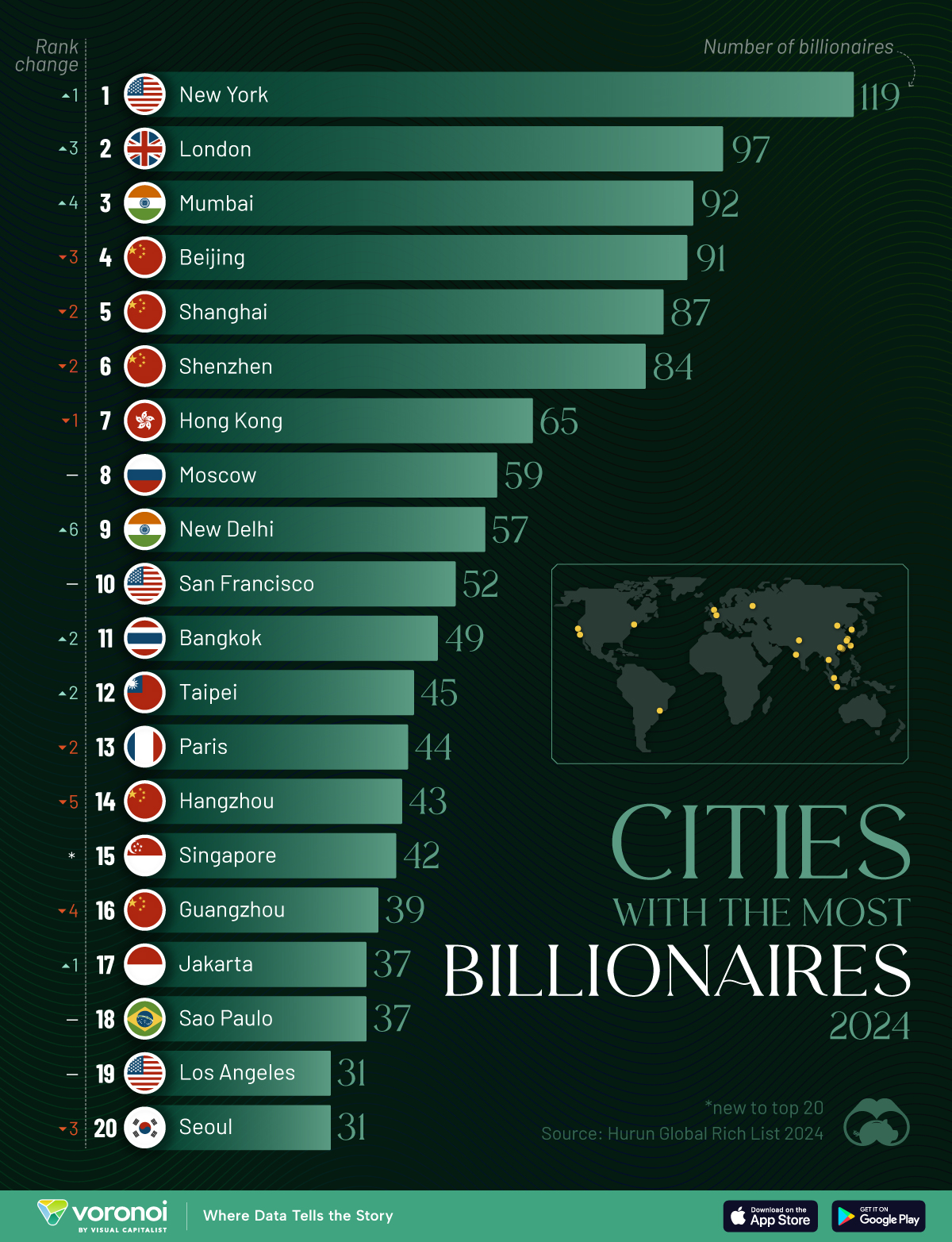
Charted: Which City Has the Most Billionaires in 2024?
Just two countries account for half of the top 20 cities with the most billionaires. And the majority of the other half are found in Asia.
Charted: Which Country Has the Most Billionaires in 2024?
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Some cities seem to attract the rich. Take New York City for example, which has 340,000 high-net-worth residents with investable assets of more than $1 million.
But there’s a vast difference between being a millionaire and a billionaire. So where do the richest of them all live?
Using data from the Hurun Global Rich List 2024, we rank the top 20 cities with the highest number of billionaires in 2024.
A caveat to these rich lists: sources often vary on figures and exact rankings. For example, in last year’s reports, Forbes had New York as the city with the most billionaires, while the Hurun Global Rich List placed Beijing at the top spot.
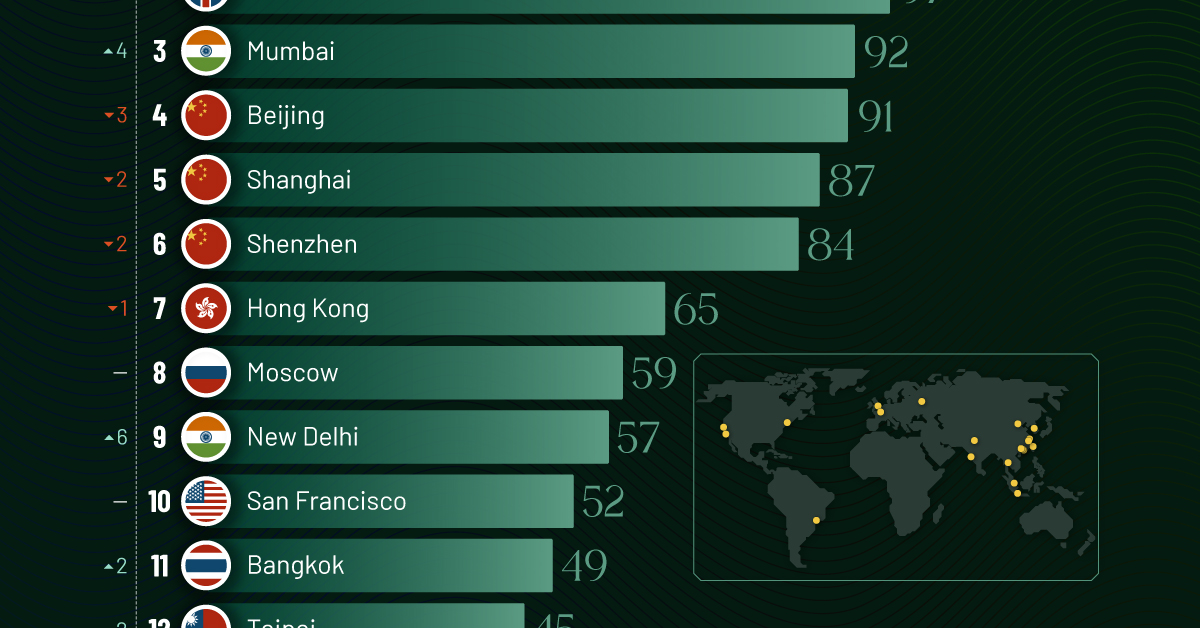
Ranked: Top 20 Cities with the Most Billionaires in 2024
The Chinese economy’s doldrums over the course of the past year have affected its ultra-wealthy residents in key cities.
Beijing, the city with the most billionaires in 2023, has not only ceded its spot to New York, but has dropped to #4, overtaken by London and Mumbai.
| Rank | City | Billionaires | Rank Change YoY |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇺🇸 New York | 119 | +1 |
| 2 | 🇬🇧 London | 97 | +3 |
| 3 | 🇮🇳 Mumbai | 92 | +4 |
| 4 | 🇨🇳 Beijing | 91 | -3 |
| 5 | 🇨🇳 Shanghai | 87 | -2 |
| 6 | 🇨🇳 Shenzhen | 84 | -2 |
| 7 | 🇭🇰 Hong Kong | 65 | -1 |
| 8 | 🇷🇺 Moscow | 59 | No Change |
| 9 | 🇮🇳 New Delhi | 57 | +6 |
| 10 | 🇺🇸 San Francisco | 52 | No Change |
| 11 | 🇹🇭 Bangkok | 49 | +2 |
| 12 | 🇹🇼 Taipei | 45 | +2 |
| 13 | 🇫🇷 Paris | 44 | -2 |
| 14 | 🇨🇳 Hangzhou | 43 | -5 |
| 15 | 🇸🇬 Singapore | 42 | New to Top 20 |
| 16 | 🇨🇳 Guangzhou | 39 | -4 |
| 17T | 🇮🇩 Jakarta | 37 | +1 |
| 17T | 🇧🇷 Sao Paulo | 37 | No Change |
| 19T | 🇺🇸 Los Angeles | 31 | No Change |
| 19T | 🇰🇷 Seoul | 31 | -3 |
In fact all Chinese cities on the top 20 list have lost billionaires between 2023–24. Consequently, they’ve all lost ranking spots as well, with Hangzhou seeing the biggest slide (-5) in the top 20.
Where China lost, all other Asian cities—except Seoul—in the top 20 have gained ranks. Indian cities lead the way, with New Delhi (+6) and Mumbai (+3) having climbed the most.
At a country level, China and the U.S combine to make up half of the cities in the top 20. They are also home to about half of the world’s 3,200 billionaire population.
In other news of note: Hurun officially counts Taylor Swift as a billionaire, estimating her net worth at $1.2 billion.
-

 Debt1 week ago
Debt1 week agoHow Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees