Technology
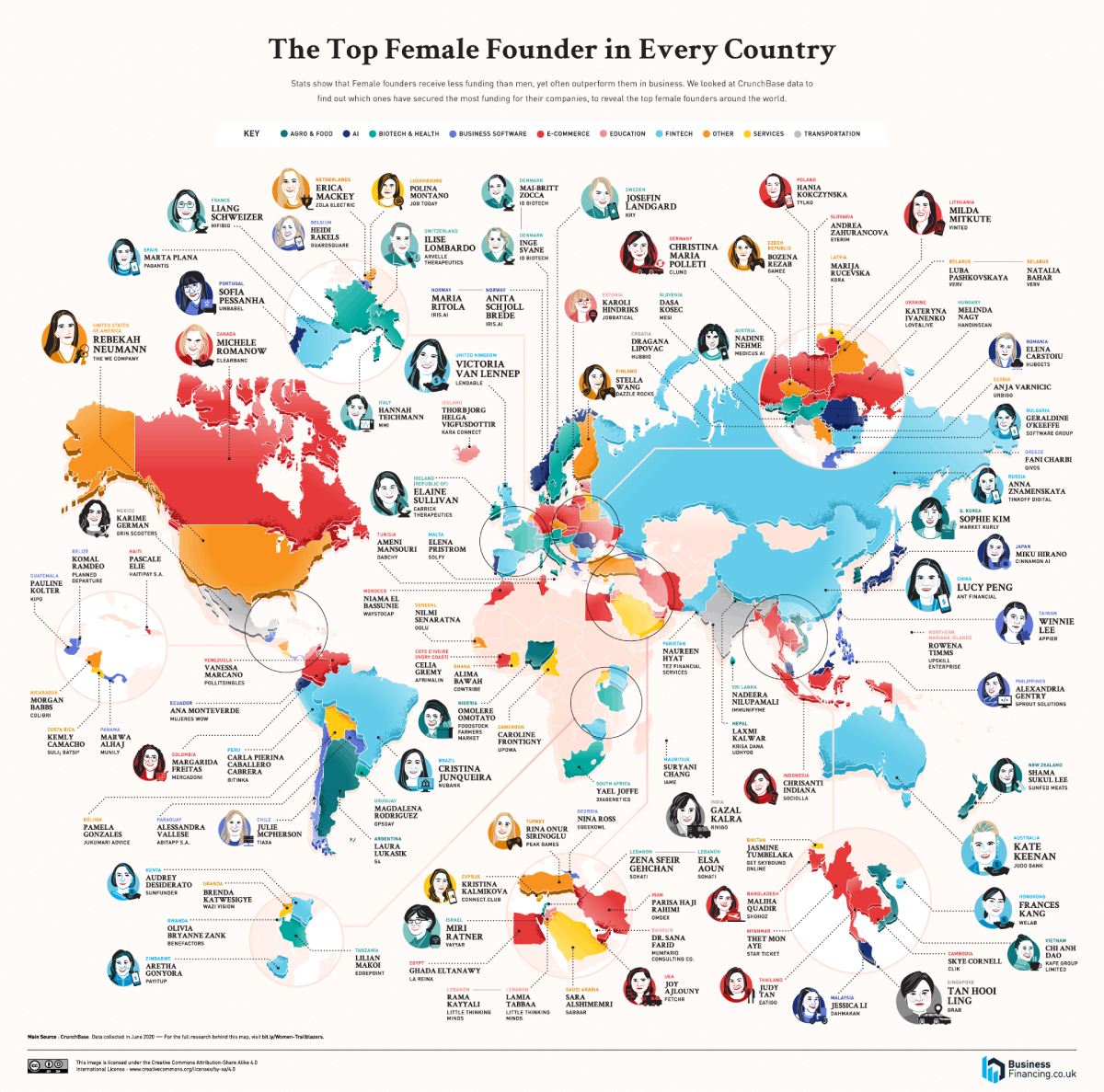
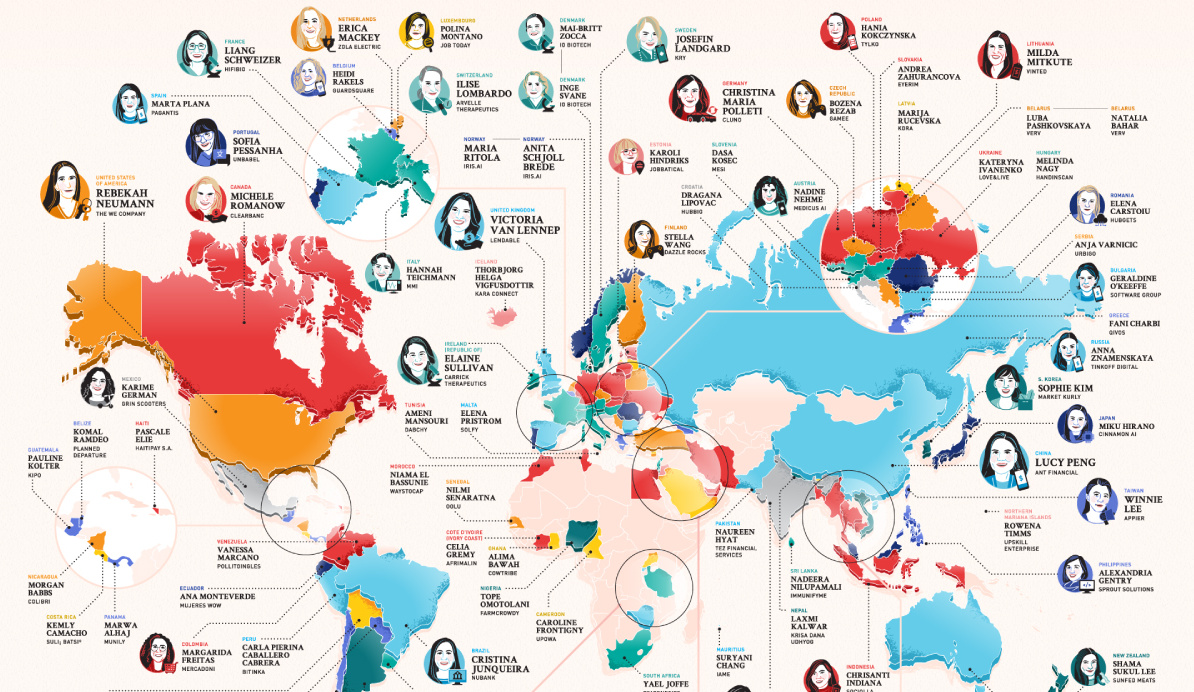
Mapped: The Top Female Founder in Each Country
View the full-size version of this infographic.
Mapped: The Top Female Founder in Each Country
View the high resolution of this infographic by clicking here.
Companies with at least one female founder generate 78 cents of revenue for every dollar of venture funding, while male-led startups generate roughly 31 cents.
Yet, startups with only female founders receive just 3% of total invested dollars globally.
The above infographic from Business Financing explores the global landscape of female-led startups. It shows the top female founders according to the highest amount of capital raised, in each country profiled.
Global Rankings: The Top 10 Female Founders
Which female founders have received the most funding worldwide?
Based on data from Crunchbase, individuals were selected across 102 countries if they were a founder or co-founder of an active company as of May 21, 2020. Companies were selected depending on their status in seed, early stage venture, or late stage venture funding.
With $22 billion in funding, Lucy Peng, co-founder of Ant Group and Alibaba tops the list. Peng taught economics for five years before co-founding Alibaba with 18 others in 1999. Today, she is worth over $1 billion.
Peng’s 2.1% stake in Ant Group is estimated to be worth roughly $4.8 billion. Ant Group filed for an IPO worth an estimated $225 billion valuation in August 2020.
| Female Founder | Funding | Company | Industry | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lucy Peng | $22B | Ant | Financial | China |
| Rebekah Neumann | $19.5B | The We Company | Real Estate | U.S. |
| Tan Hooi Ling | $9.9B | Grab | Transportation | Singapore |
| Kate Keenan | $1.4B | Judo Bank | FinTech | Australia |
| Victoria van Lennep | $1.2B | Lendable | FinTech | United Kingdom |
| Cristina Junqueira | $1.1B | Nubank | FinTech | Brazil |
| Frances Kang | $581M | WeLab | FinTech | Hong Kong |
| Sophie Kim | $282M | Market Kurly | Agro & Food | South Korea |
| Ilise Lombardo | $278M | Arvelle Therapeutics | Biotech & Health | Switzerland |
| Milda Mitkute | $260M | Vinted | Ecommerce | Lithuania |
Following Peng is Rebekah Neumann, who has raised $19.5 billion with The We Company. Neumann studied business with a minor in Buddhism at Cornell, and later co-founded the gig-focused firm in 2010 with her husband Adam Neumann and Miguel McKelvey. Following the notoriously disastrous IPO of WeWork, she and her husband have since left the company.
Coming in third is Tan Hooi Ling who founded Grab in Singapore. The ride-hailing app is a major competitor of Uber in Asian markets.
Cristina Junqueira, who co-founded digital banking firm NuBank, also makes it into the top 10 list. Currently, NuBank operates as the largest fintech firm in South America, with over 20 million users. Meanwhile, Lithuania’s first tech unicorn, Vinted was co-founded by Milda Mitkute and serves as the largest secondhand clothing platform worldwide.
Unicorns Bucking the Trend
While funding for female-led startups has been disproportionately low over the years, the number of unicorns—private companies valued in excess of $1 billion—headed by women has grown over fivefold.
Since 2013, women-led unicorns have jumped from just four to 21 in 2019. While these numbers are still objectively quite small, they continue to climb.
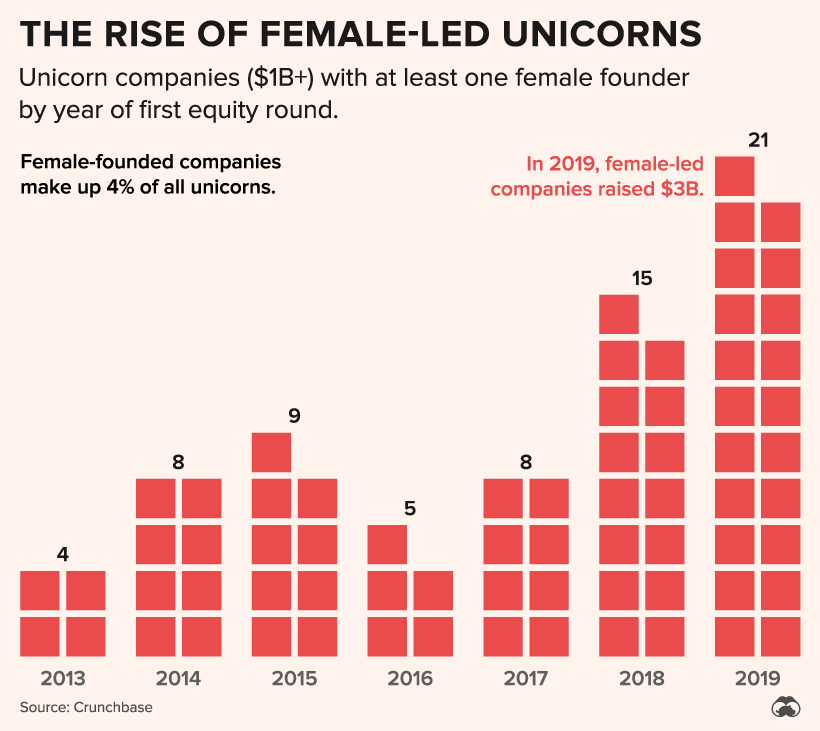
Among the newly minted unicorns in 2019 was Airwallex, a company that allows businesses to track cross-border revenues. In April, the startup raised $160 million, valuing it at $1.8 billion.
Along with Airwallex, Scale, Glossier and The RealReal are also found on the list.
New Waves of Venture Capital
In 2019, 2,300 venture deal rounds included startups with at least one female founder. Of these, a number of startups raised over $100 million in funding in 2019 on a worldwide level.
| Startup | Funding Amount | Country |
|---|---|---|
| Guild Education | $157 million | U.S. |
| Luckin Coffee | $150 million | China |
| Northern Arc | $130 million | India |
| Kuaikan Manhua | $125 million | China |
| SpringWorks Therapeutics | $125 million | U.S. |
| Rent the Runway | $125 million | U.S. |
| Genera Energy | $118 million | U.S. |
| Tala | $110 million | U.S. |
| Kronos Bio | $105 million | U.S. |
| Insitro | $100 million | U.S. |
| Talaris | $100 million | U.S. |
| Away | $100 million | U.S. |
| Glossier | $100 million | U.S. |
Interestingly, funding data shows that women VCs are three times more likely than men to invest in women. This, coupled with the growing number of female partners at venture capital firms, is bringing a new perspective to tech financing.
At the same time, it’s opening up new markets. For instance, the $57 billion child care industry is largely overlooked by the VC world. San Francisco-based Winnie raised $9 million in funding in 2019, capitalizing on a marketplace specifically for parents.
Consumer products and markets focusing on solutions for women present areas of significant growth, particularly on a global level.
What’s Next For Female Founders?
While just a fraction of all venture funding is allocated to women-led companies, trends illustrate clear resilience.
Female-founded firms continually outperform—and shareholder returns are only getting better every year. As both startup and venture capital ecosystems continue to evolve, the future of women-led entrepreneurship is as bright as ever.
Technology
All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
Intel, TSMC, and more have received billions in subsidies from the U.S. CHIPS Act in 2024.

All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This visualization shows which companies are receiving grants from the U.S. CHIPS Act, as of April 25, 2024. The CHIPS Act is a federal statute signed into law by President Joe Biden that authorizes $280 billion in new funding to boost domestic research and manufacturing of semiconductors.
The grant amounts visualized in this graphic are intended to accelerate the production of semiconductor fabrication plants (fabs) across the United States.
Data and Company Highlights
The figures we used to create this graphic were collected from a variety of public news sources. The Semiconductor Industry Association (SIA) also maintains a tracker for CHIPS Act recipients, though at the time of writing it does not have the latest details for Micron.
| Company | Federal Grant Amount | Anticipated Investment From Company |
|---|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 Intel | $8,500,000,000 | $100,000,000,000 |
| 🇹🇼 TSMC | $6,600,000,000 | $65,000,000,000 |
| 🇰🇷 Samsung | $6,400,000,000 | $45,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Micron | $6,100,000,000 | $50,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 GlobalFoundries | $1,500,000,000 | $12,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Microchip | $162,000,000 | N/A |
| 🇬🇧 BAE Systems | $35,000,000 | N/A |
BAE Systems was not included in the graphic due to size limitations
Intel’s Massive Plans
Intel is receiving the largest share of the pie, with $8.5 billion in grants (plus an additional $11 billion in government loans). This grant accounts for 22% of the CHIPS Act’s total subsidies for chip production.
From Intel’s side, the company is expected to invest $100 billion to construct new fabs in Arizona and Ohio, while modernizing and/or expanding existing fabs in Oregon and New Mexico. Intel could also claim another $25 billion in credits through the U.S. Treasury Department’s Investment Tax Credit.
TSMC Expands its U.S. Presence
TSMC, the world’s largest semiconductor foundry company, is receiving a hefty $6.6 billion to construct a new chip plant with three fabs in Arizona. The Taiwanese chipmaker is expected to invest $65 billion into the project.
The plant’s first fab will be up and running in the first half of 2025, leveraging 4 nm (nanometer) technology. According to TrendForce, the other fabs will produce chips on more advanced 3 nm and 2 nm processes.
The Latest Grant Goes to Micron
Micron, the only U.S.-based manufacturer of memory chips, is set to receive $6.1 billion in grants to support its plans of investing $50 billion through 2030. This investment will be used to construct new fabs in Idaho and New York.
-

 Debt1 week ago
Debt1 week agoHow Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees