Visualized: How Much Metal is Used in Clean Energy Technology?
How Much Metal is Used in Clean Energy?
In 2022, a record 12% of all global power was harnessed from solar and wind, up from 10% in 2021, underscoring the growth of clean energy sources.
Essential minerals that form the foundation of clean energy technologies are at the heart of this transition. But what makes these minerals so indispensable?
This infographic, sponsored by Teck, looks at how much, and what types of metals are used in clean energy.
Clean Energy Uses More Metal
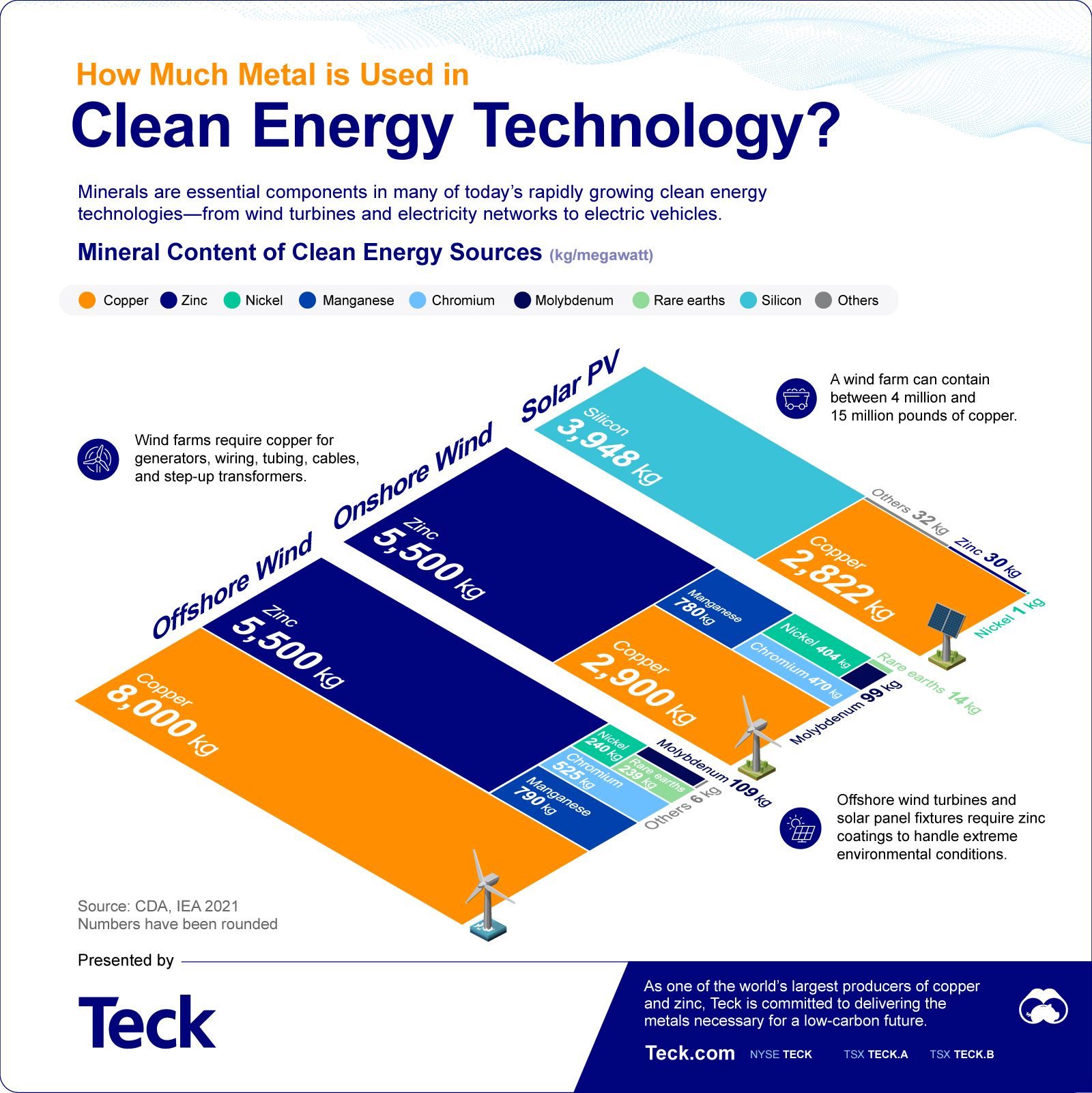
Clean energy systems, on average, require more minerals to build. Let’s take a look at the amount needed for wind and solar applications.
| Offshore wind | Onshore wind | Solar PV | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | 8,000 kg/MW | 2,900 kg/MW | 2,822 kg/MW |
| Zinc | 5,500 kg/MW | 5,500 kg/MW | 30 kg/MW |
| Manganese | 790 kg/MW | 780 kg/MW | - |
| Chromium | 525 kg/MW | 470 kg/MW | - |
| Nickel | 240 kg/MW | 404 kg/MW | 1 kg/MW |
| Rare Earths | 239 kg/MW | 14 kg/MW | - |
| Molybdenum | 109 kg/MW | 99 kg/MW | - |
| Silicon | - | - | 3,948 kg/MW |
| Others | 6 kg/MW | - | 32 kg/MW |
Offshore wind uses the largest amount of metals here, with its copper demand alone reaching around 8,000 kilograms per megawatt of energy.
A Closer Look at Copper
Copper is the world’s third most used industrial metal and is essential for clean energy technologies due to its outstanding conductivity, versatility, and superior heat dissipation capabilities compared to other metals.
Copper’s sustainability credentials are also firmly established. This is due to its recyclability rate of 100%, meaning it can be reused multiple times without any decline in performance.
Growing clean energy infrastructure will place even more significant demands on copper. A wind farm can contain between 4 million and 15 million pounds of copper.
A Closer Look at Zinc
Zinc is renowned as one of the most versatile and vital elements in human applications. It stands as the fourth most used metal worldwide, following iron, aluminum, and copper.
Its primary application is in the galvanization process, where it acts as a protective layer for iron and steel against corrosion.
Zinc coatings play a crucial role in public transportation and infrastructure by extending the life of steel used in bridge rails, support structures, railway tracks, and more.
The construction of solar panels and wind turbines has resulted in additional demand for zinc because these assets are always exposed to the elements.
A 100MWh solar panel park—capable of powering 110,000 homes—needs 240 tonnes of zinc.
Metals for the Future
As the world moves towards renewable energy sources, copper, and zinc will remain in high demand.
Teck, being one of the world’s largest producers of copper and zinc, is dedicated to providing the metals essential for a low-carbon future.

-

 Mining14 hours ago
Mining14 hours agoVisualizing Global Gold Production in 2023
Gold production in 2023 was led by China, Australia, and Russia, with each outputting over 300 tonnes.
-

 Energy1 week ago
Energy1 week agoRanked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2023
Asia dominates this ranking of the world’s largest EV battery manufacturers in 2023.
-

 Mining2 weeks ago
Mining2 weeks agoGold vs. S&P 500: Which Has Grown More Over Five Years?
The price of gold has set record highs in 2024, but how has this precious metal performed relative to the S&P 500?
-

 Mining4 weeks ago
Mining4 weeks agoCharted: The Value Gap Between the Gold Price and Gold Miners
While the price of gold has reached new record highs in 2024, gold mining stocks are still far from their 2011 peaks.
-
 Mining3 months ago
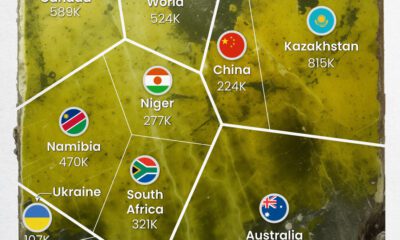
Mining3 months agoCharted: Global Uranium Reserves, by Country
We visualize the distribution of the world’s uranium reserves by country, with 3 countries accounting for more than half of total reserves.
-
 Energy4 months ago
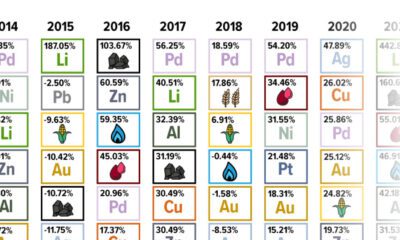
Energy4 months agoThe Periodic Table of Commodity Returns (2014-2023)
Commodity returns in 2023 took a hit. This graphic shows the performance of commodities like gold, oil, nickel, and corn over the last decade.



