Technology
The Multi-Billion Dollar Industry That Makes Its Living From Your Data
The Multi-Billion Dollar Industry That Makes Its Living From Your Data
In the ocean ecosystem, plankton is the raw material that fuels an entire food chain. These tiny organisms on their own aren’t that remarkable, but en masse, they have a huge impact on the world.
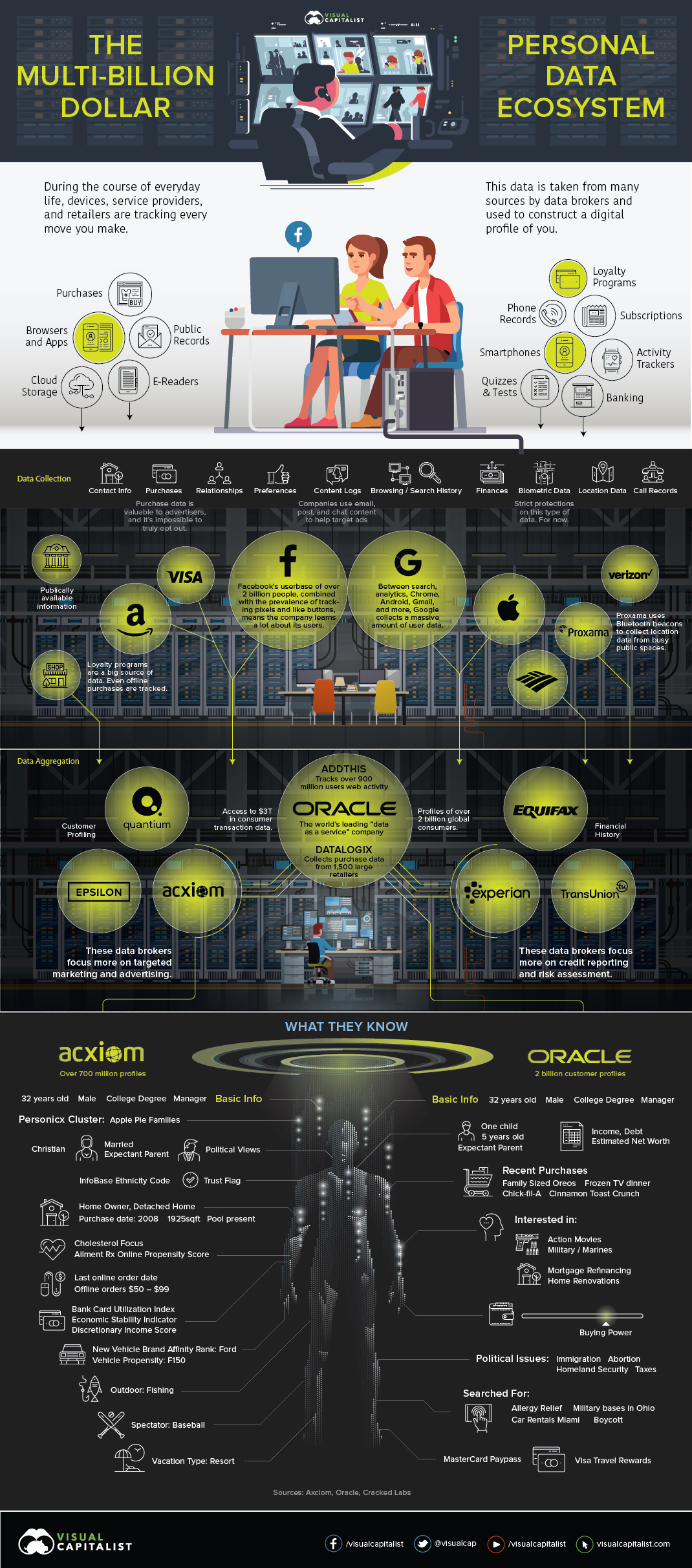
Here on dry land, the massive volume of content and meta data we produce fuels a marketing research industry that is worth nearly $50 billion. Every instant message, page click, and step you take now produces a data point that can be used to build a detailed profile of who you are.
Every breath you take, Every move you make
The coarse-grained demographics and contact information of yesteryear seems quaint compared to today’s sophisticated data collection battleground. In the past, marketers would make judgement calls on your likely income and family structure based on where you lived, and you’d receive “targeted” mail and calls from telemarketers. Loyalty programs and the emergence of web analytics pushed things a little further.
Today, the steady march of technological advancement has created a vast data collection empire that measures every aspect of your digital life and, increasingly, your offline life as well. Facebook alone uses nearly one hundred data points to target ads to you – everything from your marital status to whether you’ve been on vacation lately or not. Telecoms have access to extremely detailed information on your location. Apple has biometric data.
Also watching your every move are web trackers. “Cookie-syncing” is one of the sneaky ways advertisers can follow you around the internet. Basically, cookie-syncing allows third parties to share browsing information at such a large scale that even the NSA “piggybacks” off them for surveillance purposes.
The recent sales growth of smart speakers will only increase the breadth of data companies collect and analyze. Amazon and Google have both filed patents for technology that would essentially allow them to mine audio recordings for keywords. Advertisers could potentially target you with diapers before your family and friends even know you’re expecting a baby.
Following the ones and zeros
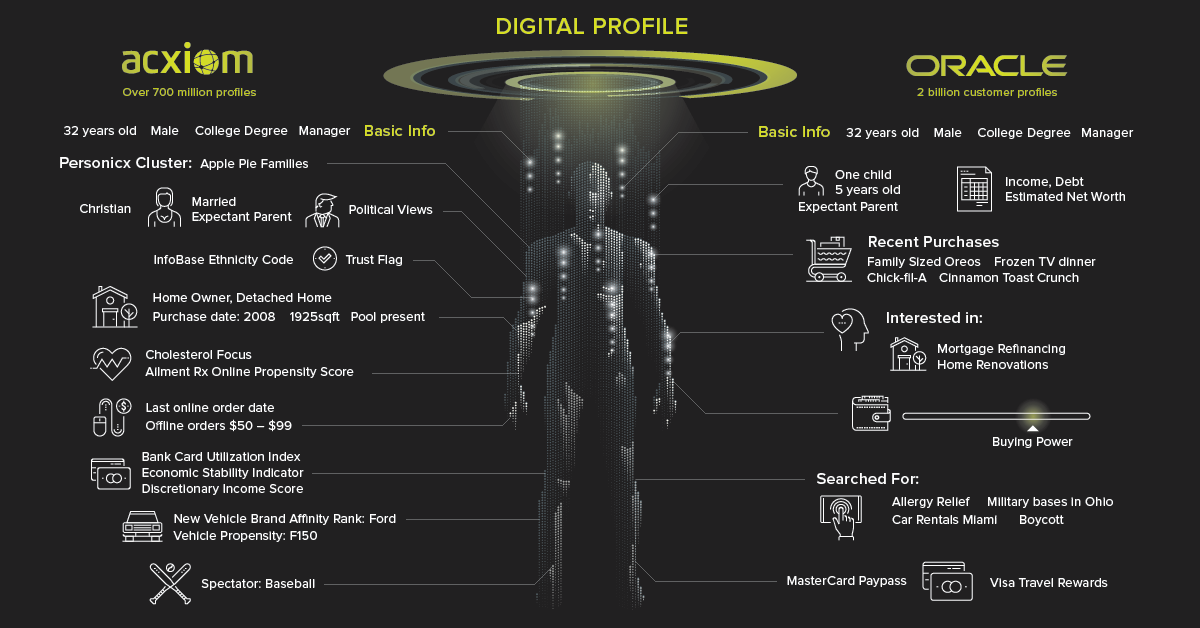
While web trackers and companies like Apple and Google are collecting a lot of personal and behavioral data, it’s the whales of the data ecosystem – data brokers – who are creating increasingly detailed profiles on almost everyone.
Data brokers trade on the privacy of consumers and operate in the shadows.
– Senator Al Franken (D-Minn)
The goal of data brokers, such as Experian or Acxiom, is to siphon up as much personal data as possible and apply it to profiles. This data comes from a wide variety of sources. Your purchases, financial history, internet activity, and even psychographic attributes are mixed with information from public records to create a robust dossier. Digital profiles are then sorted into one of thousands of categories to help optimize advertising efforts.
Fear the shadow profile?
According to Pew Research, 91% of Americans “agree” or “strongly agree” that people have lost control over how personal information is collected and used.
Though optimizing clickthroughs is a big business, companies are increasingly moving beyond advertising to extract value from their growing data pipeline. Amalgamated data is increasingly being viewed as a clever way to assess risk in the decision-making process (e.g. hiring, insurance, loan or housing applications), and the stakes for consumers are going up in the process.
For example, a man may feel comfortable sharing their HIV status on Grindr (for practical reasons), but may not want that information going to a third party. (Unfortunately, that really happened.)
In 2015, Facebook filed a patent for a service that would help insurance companies vet people based on the credit ratings of their social network.
The More You Know
Below the surface of our screens, our digital profiles continue to take shape.
Measures like adjusting website privacy controls and clearing cookies are a good start, but that’s only a fraction of the data companies are collecting. Not only do data brokers make it hard to officially opt out, their partnerships with corporations and advanced data collection methods cast such a wide net, that it’s almost impossible to exclude individual people.
Data brokers have operated with very little scrutiny or oversight, but that may be changing. Under intense public and governmental pressure, Facebook recently cut ties with data brokers. For a company that has bullishly pursued monetization of user data at every turn, the move is a sign that the public sentiment is changing.
The more information on the personal data industry, visit Cracked Labs’ report on the issue.
Technology
Visualizing AI Patents by Country
See which countries have been granted the most AI patents each year, from 2012 to 2022.
Visualizing AI Patents by Country
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
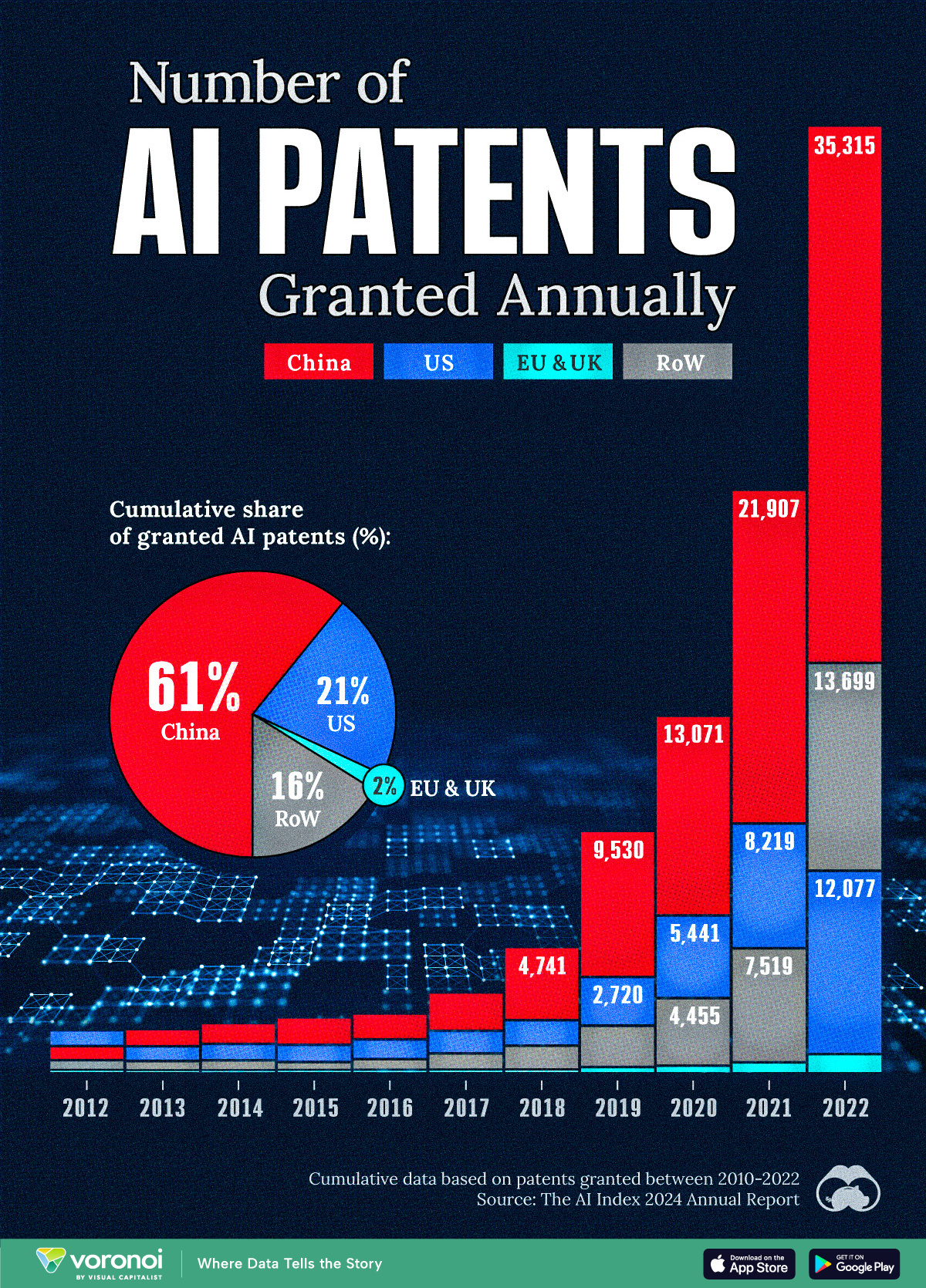
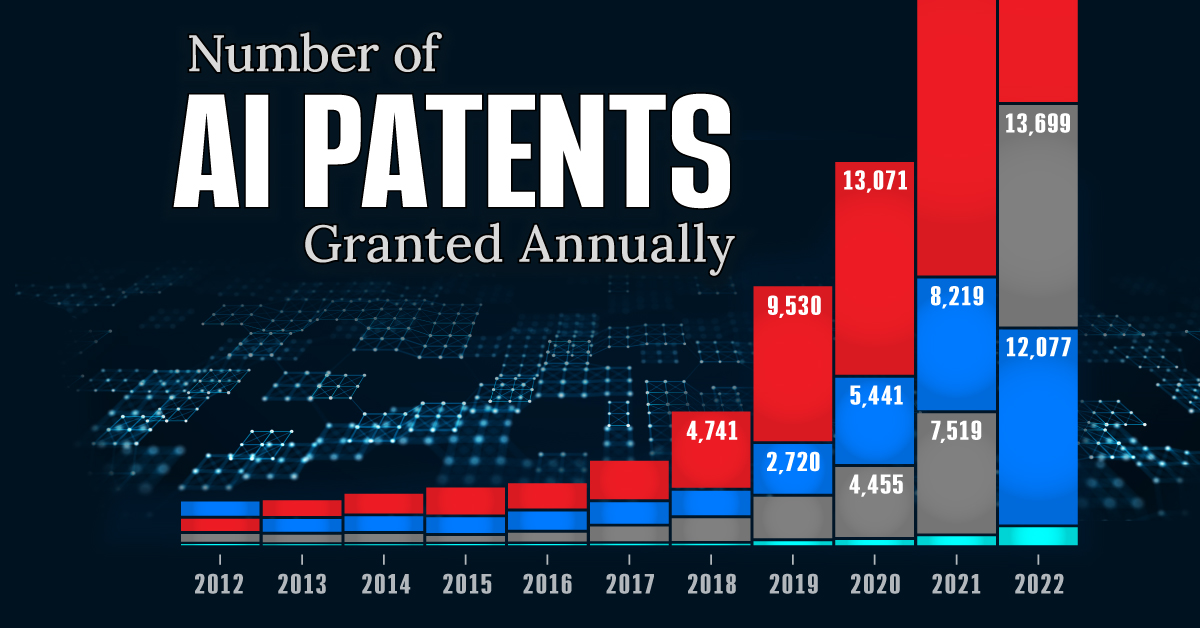
This infographic shows the number of AI-related patents granted each year from 2010 to 2022 (latest data available). These figures come from the Center for Security and Emerging Technology (CSET), accessed via Stanford University’s 2024 AI Index Report.
From this data, we can see that China first overtook the U.S. in 2013. Since then, the country has seen enormous growth in the number of AI patents granted each year.
| Year | China | EU and UK | U.S. | RoW | Global Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 307 | 137 | 984 | 571 | 1,999 |
| 2011 | 516 | 129 | 980 | 581 | 2,206 |
| 2012 | 926 | 112 | 950 | 660 | 2,648 |
| 2013 | 1,035 | 91 | 970 | 627 | 2,723 |
| 2014 | 1,278 | 97 | 1,078 | 667 | 3,120 |
| 2015 | 1,721 | 110 | 1,135 | 539 | 3,505 |
| 2016 | 1,621 | 128 | 1,298 | 714 | 3,761 |
| 2017 | 2,428 | 144 | 1,489 | 1,075 | 5,136 |
| 2018 | 4,741 | 155 | 1,674 | 1,574 | 8,144 |
| 2019 | 9,530 | 322 | 3,211 | 2,720 | 15,783 |
| 2020 | 13,071 | 406 | 5,441 | 4,455 | 23,373 |
| 2021 | 21,907 | 623 | 8,219 | 7,519 | 38,268 |
| 2022 | 35,315 | 1,173 | 12,077 | 13,699 | 62,264 |
In 2022, China was granted more patents than every other country combined.
While this suggests that the country is very active in researching the field of artificial intelligence, it doesn’t necessarily mean that China is the farthest in terms of capability.
Key Facts About AI Patents
According to CSET, AI patents relate to mathematical relationships and algorithms, which are considered abstract ideas under patent law. They can also have different meaning, depending on where they are filed.
In the U.S., AI patenting is concentrated amongst large companies including IBM, Microsoft, and Google. On the other hand, AI patenting in China is more distributed across government organizations, universities, and tech firms (e.g. Tencent).
In terms of focus area, China’s patents are typically related to computer vision, a field of AI that enables computers and systems to interpret visual data and inputs. Meanwhile America’s efforts are more evenly distributed across research fields.
Learn More About AI From Visual Capitalist
If you want to see more data visualizations on artificial intelligence, check out this graphic that shows which job departments will be impacted by AI the most.
-

 Mining1 week ago
Mining1 week agoGold vs. S&P 500: Which Has Grown More Over Five Years?
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries