Technology
Why Hackers Hack: Motives Behind Cyberattacks
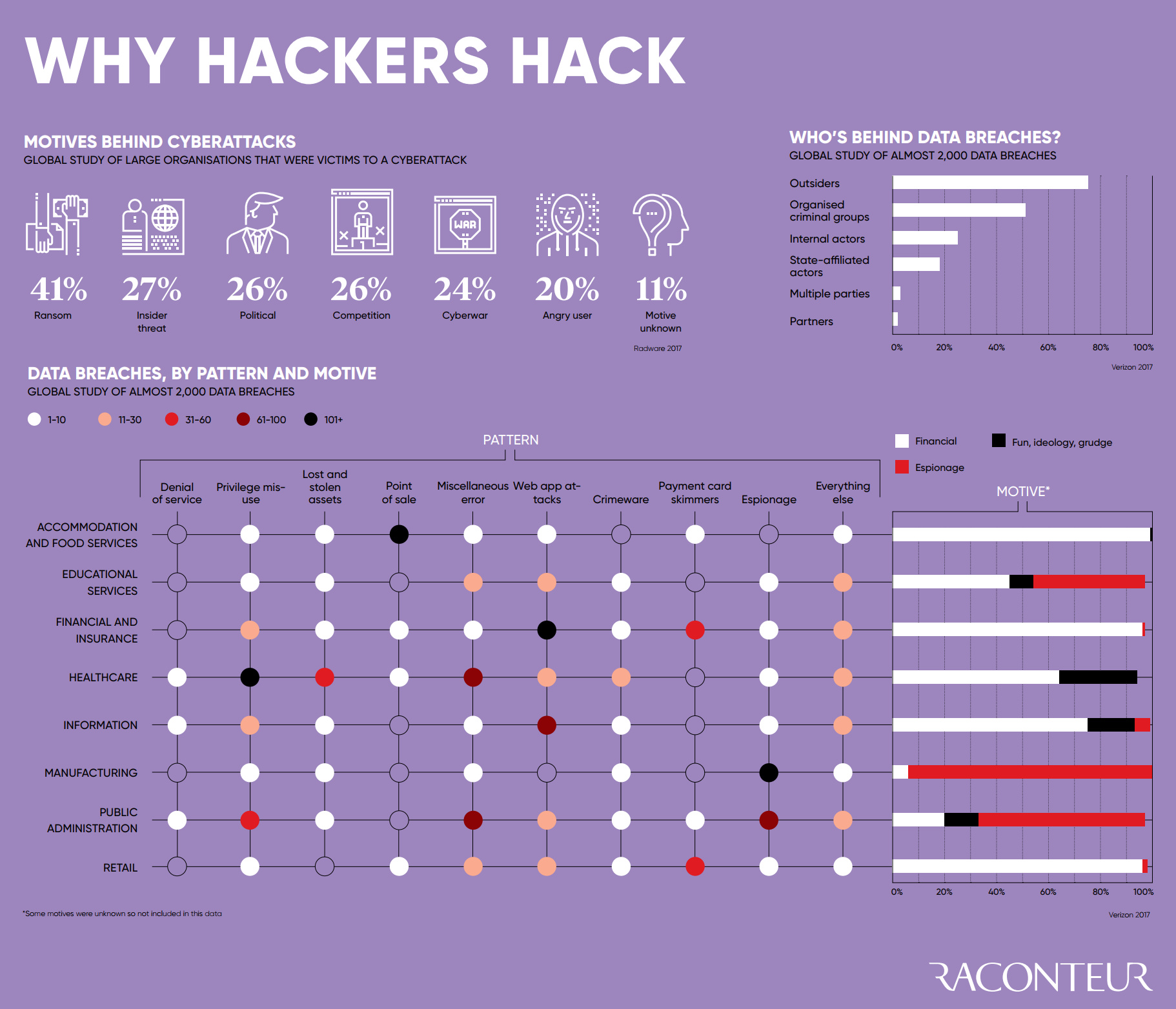
Why Hackers Hack: The Motives Behind Cyberattacks
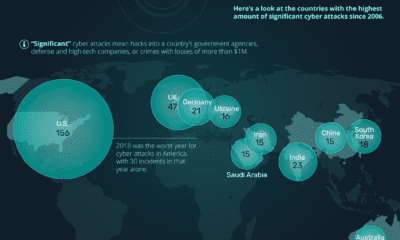
Cyberattacks caused $450 billion of damage to the global economy in 2016, and this number is predicted to keep rising as we keep adding more connected devices to the mix.
The magnitude of this impact should not be understated. It’s bigger than the size of notable economies like the UAE ($371B) or Norway ($370B) – which is why it’s no surprise to see organizations putting major resources to shore up their internal defenses and to reduce the risk of threats.
But while the origins of this cybersecurity boom may be clear, what is less obvious is why all of this hacking is happening in the first place.
Why do hackers hack, and what are the motives behind these powerful cyberattacks?
Why Hackers Hack
Today’s infographic comes to us from Raconteur, and it breaks down the statistics from a couple of large global studies on cybersecurity.
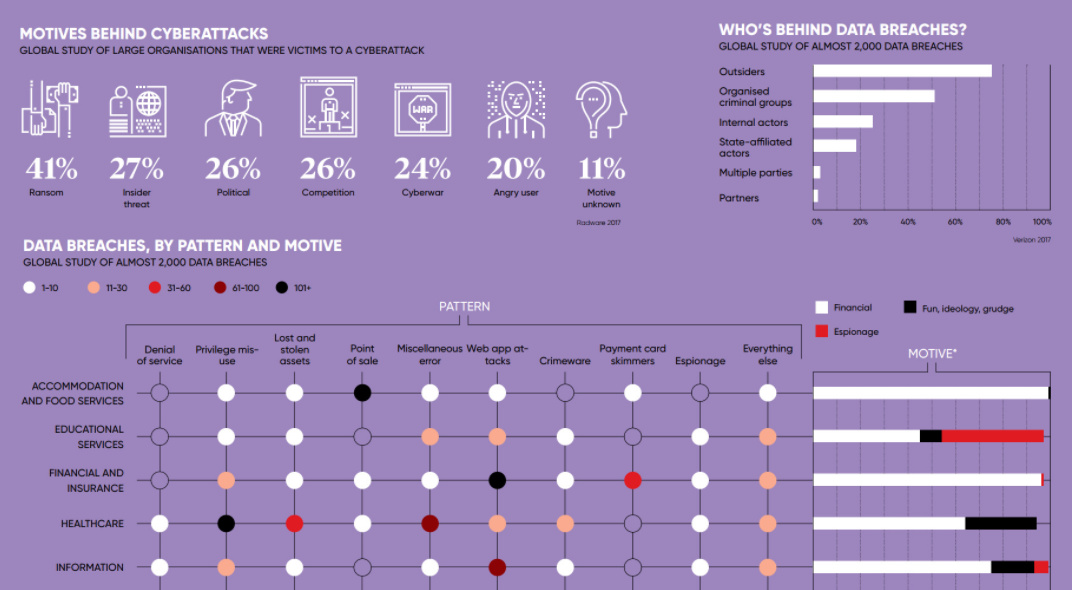
One of the first datasets shown comes from Radware, showing the motives behind why hackers hack:
- Ransom (41%)
- Insider threat (27%)
- Political reasons (26%)
- Competition (26%)
- Cyberwar (24%)
- Angry user (20%)
- Motive unknown (11%)
Interestingly, ransom is a top motive at 41% – but other reasons like politics, competition, and cyberwar were pretty evenly distributed in the mix as well.
Verizon, in their 2017 Data Breach Investigations Report, break down the motives of hackers in a different way. Using the three wider categories of “Financial”, “Espionage” and “Fun, Ideology, or Grudge (FIG)”, here is how cyberattacks look over time:
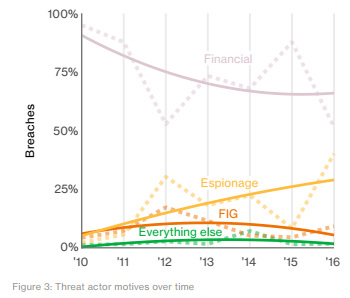
Most notably, espionage appears to be on the rise.
That’s significant, because over 50% of hacks already come from organized criminal groups, and close to 20% originate from state-affiliated actors. With espionage becoming a more common motive, it suggests that cyberattacks will continue getting more sophisticated and deliberate, and that specialized teams of hackers are executing a growing percentage of the attacks.
(For a real-time view of this espionage in action, make sure to watch cyberwarfare happening in real-time.)
Who and Why?
Hackers hack for a multitude of different reasons.
However, it does seem that the actors and motives for hacking are gradually shifting over time. Fewer cyberattacks today have FIG motives (fun, ideology, grudge), and more attacks are increasingly tied to espionage.
With more deliberate, determined, sophisticated, and team-based attackers – it’s no wonder that the cybersecurity industry is growing at a 9.5% annual clip.
Technology
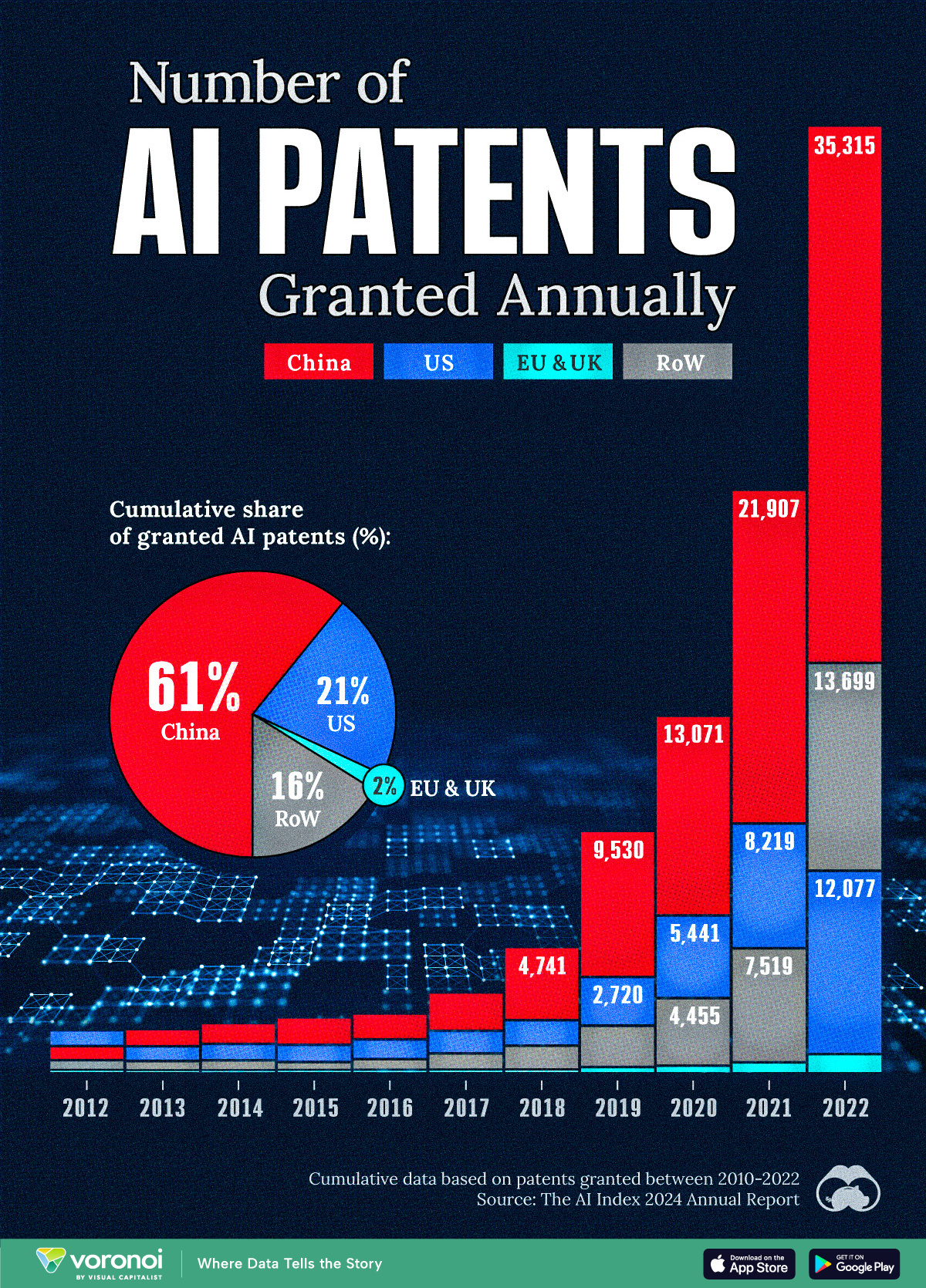
Visualizing AI Patents by Country
See which countries have been granted the most AI patents each year, from 2012 to 2022.
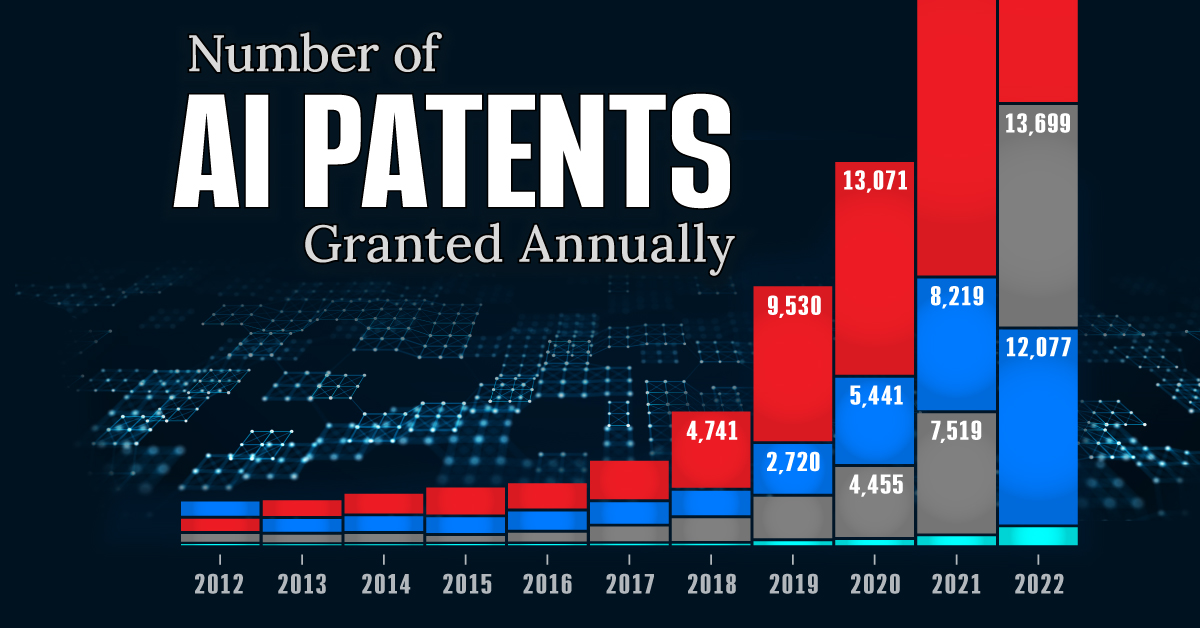
Visualizing AI Patents by Country
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This infographic shows the number of AI-related patents granted each year from 2010 to 2022 (latest data available). These figures come from the Center for Security and Emerging Technology (CSET), accessed via Stanford University’s 2024 AI Index Report.
From this data, we can see that China first overtook the U.S. in 2013. Since then, the country has seen enormous growth in the number of AI patents granted each year.
| Year | China | EU and UK | U.S. | RoW | Global Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 307 | 137 | 984 | 571 | 1,999 |
| 2011 | 516 | 129 | 980 | 581 | 2,206 |
| 2012 | 926 | 112 | 950 | 660 | 2,648 |
| 2013 | 1,035 | 91 | 970 | 627 | 2,723 |
| 2014 | 1,278 | 97 | 1,078 | 667 | 3,120 |
| 2015 | 1,721 | 110 | 1,135 | 539 | 3,505 |
| 2016 | 1,621 | 128 | 1,298 | 714 | 3,761 |
| 2017 | 2,428 | 144 | 1,489 | 1,075 | 5,136 |
| 2018 | 4,741 | 155 | 1,674 | 1,574 | 8,144 |
| 2019 | 9,530 | 322 | 3,211 | 2,720 | 15,783 |
| 2020 | 13,071 | 406 | 5,441 | 4,455 | 23,373 |
| 2021 | 21,907 | 623 | 8,219 | 7,519 | 38,268 |
| 2022 | 35,315 | 1,173 | 12,077 | 13,699 | 62,264 |
In 2022, China was granted more patents than every other country combined.
While this suggests that the country is very active in researching the field of artificial intelligence, it doesn’t necessarily mean that China is the farthest in terms of capability.
Key Facts About AI Patents
According to CSET, AI patents relate to mathematical relationships and algorithms, which are considered abstract ideas under patent law. They can also have different meaning, depending on where they are filed.
In the U.S., AI patenting is concentrated amongst large companies including IBM, Microsoft, and Google. On the other hand, AI patenting in China is more distributed across government organizations, universities, and tech firms (e.g. Tencent).
In terms of focus area, China’s patents are typically related to computer vision, a field of AI that enables computers and systems to interpret visual data and inputs. Meanwhile America’s efforts are more evenly distributed across research fields.
Learn More About AI From Visual Capitalist
If you want to see more data visualizations on artificial intelligence, check out this graphic that shows which job departments will be impacted by AI the most.
-

 Mining1 week ago
Mining1 week agoGold vs. S&P 500: Which Has Grown More Over Five Years?
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries