Markets
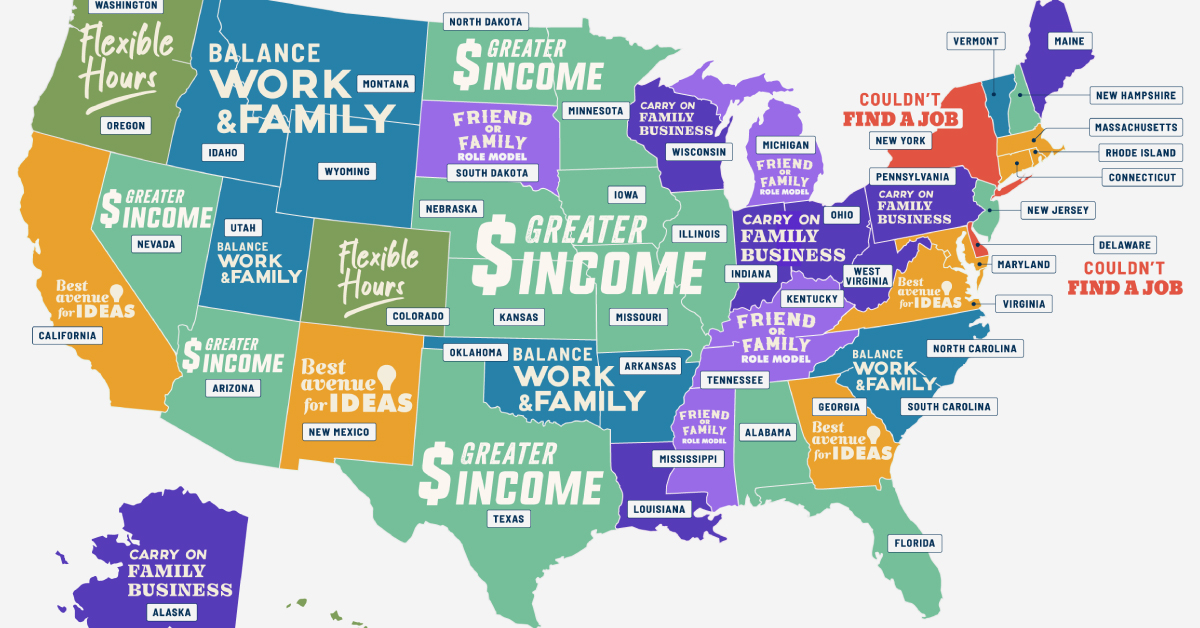
Why Do People Start Businesses in Every U.S. State?
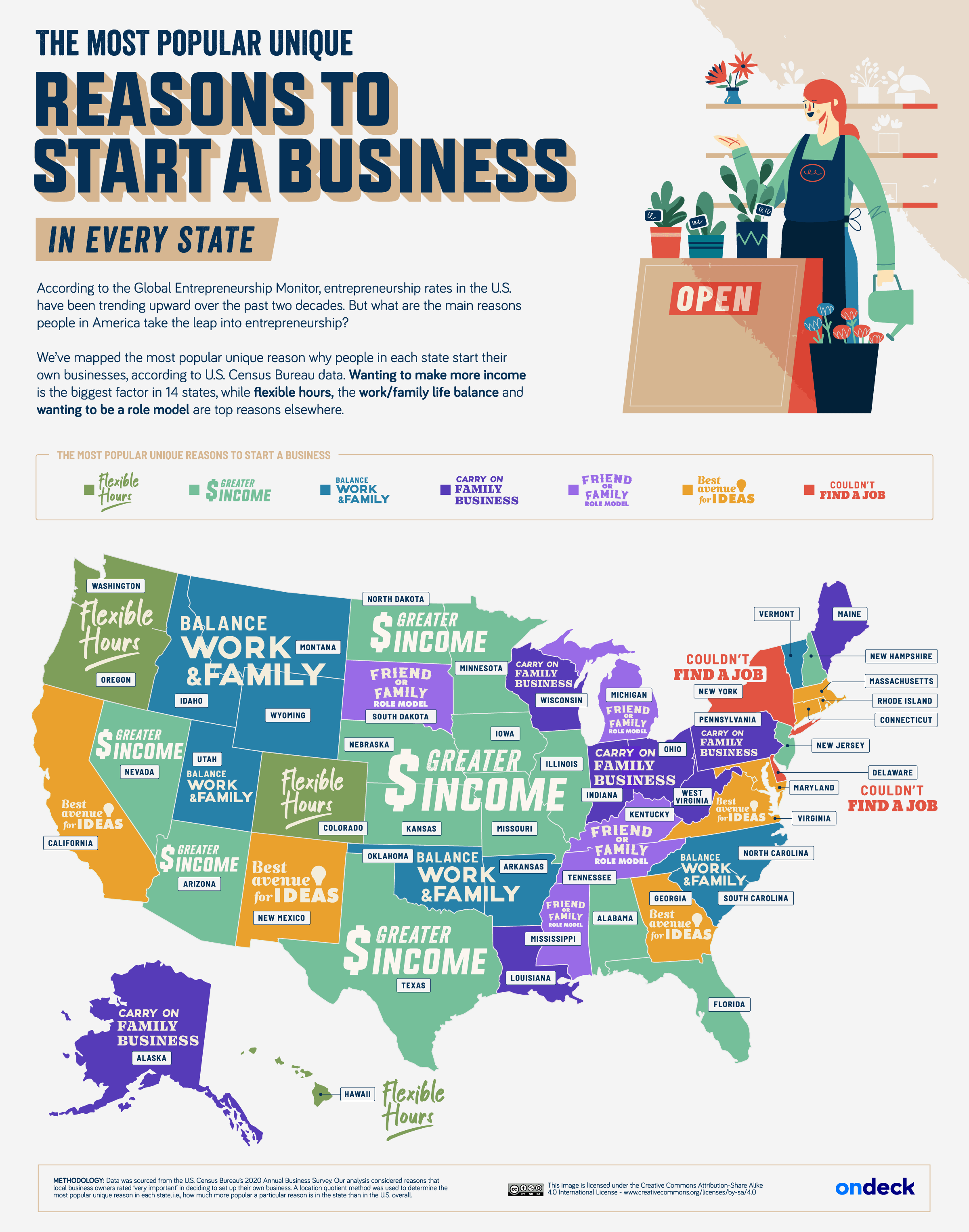
Why Do People Start Businesses in Every U.S. State?
People have various motivations for starting their businesses.
Some seek higher income. Others are looking for a balance between family life and career. In some situations, entrepreneurship may be the only way to fight unemployment.
In this infographic, OnDeck uses data from the U.S. Census Bureau’s 2020 Annual Business Survey to highlight the most unique reasons for why people start businesses in each U.S. state.
Editor’s note: The map tracks the most popular unique reasons to start a business. In this case, “unique” is defined by how much a particular reason stands out from the U.S. average across all states. For example, in Delaware, more respondents said they started businesses because they “couldn’t find jobs” (11.6%) than in any other state (U.S. average: 7.3%). So, even though it’s not numerically the most popular reason overall, it is the unique reason that stands out the most for that state.
The Most Popular Unique Reasons to Start a Business
According to the Global Entrepreneurship Monitor, entrepreneurship rates in the U.S. have been trending upward over the past two decades.
In fact, despite multi-billion dollar companies getting the spotlight, 99.9% of businesses across the U.S. are small businesses, employing over 60 million people.
Wanting to make more income is the biggest unique factor in starting a business in 14 states, including some of the states with the highest unemployment rates, like New Hampshire, North Dakota, and Alabama.

In Utah, a higher percentage (65.4%) of entrepreneurs start businesses to achieve a work-life balance than in any other state. Notably, Utah is known for having the largest average family size, as reported by the U.S. Census Bureau, and has a strong religious presence.
On the other hand, in Florida, more business founders (69.2%) start their businesses to become their own bosses than anywhere else.
New York and California are states where entrepreneurs mentioned that they couldn’t find a job as a key unique reason to start a business. In fact, both states lead as the worst for job seekers, as shown in another Visual Capitalist graphic.
Small Businesses to Remain Vital
Despite all the different reasons to start a business, the fact is that entrepreneurship is still crucial for the U.S. economy.
Over the last 25 years, small businesses have added over 12.9 million jobs. For perspective, that’s about two-thirds of the jobs added to the economy.
In 2021, a record-breaking 5.4 million new business applications were filed in the U.S.

This article was published as a part of Visual Capitalist's Creator Program, which features data-driven visuals from some of our favorite Creators around the world.
Economy
Economic Growth Forecasts for G7 and BRICS Countries in 2024
The IMF has released its economic growth forecasts for 2024. How do the G7 and BRICS countries compare?

G7 & BRICS Real GDP Growth Forecasts for 2024
The International Monetary Fund’s (IMF) has released its real gross domestic product (GDP) growth forecasts for 2024, and while global growth is projected to stay steady at 3.2%, various major nations are seeing declining forecasts.
This chart visualizes the 2024 real GDP growth forecasts using data from the IMF’s 2024 World Economic Outlook for G7 and BRICS member nations along with Saudi Arabia, which is still considering an invitation to join the bloc.
Get the Key Insights of the IMF’s World Economic Outlook
Want a visual breakdown of the insights from the IMF’s 2024 World Economic Outlook report?
This visual is part of a special dispatch of the key takeaways exclusively for VC+ members.
Get the full dispatch of charts by signing up to VC+.
Mixed Economic Growth Prospects for Major Nations in 2024
Economic growth projections by the IMF for major nations are mixed, with the majority of G7 and BRICS countries forecasted to have slower growth in 2024 compared to 2023.
Only three BRICS-invited or member countries, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and South Africa, have higher projected real GDP growth rates in 2024 than last year.
| Group | Country | Real GDP Growth (2023) | Real GDP Growth (2024P) |
|---|---|---|---|
| G7 | 🇺🇸 U.S. | 2.5% | 2.7% |
| G7 | 🇨🇦 Canada | 1.1% | 1.2% |
| G7 | 🇯🇵 Japan | 1.9% | 0.9% |
| G7 | 🇫🇷 France | 0.9% | 0.7% |
| G7 | 🇮🇹 Italy | 0.9% | 0.7% |
| G7 | 🇬🇧 UK | 0.1% | 0.5% |
| G7 | 🇩🇪 Germany | -0.3% | 0.2% |
| BRICS | 🇮🇳 India | 7.8% | 6.8% |
| BRICS | 🇨🇳 China | 5.2% | 4.6% |
| BRICS | 🇦🇪 UAE | 3.4% | 3.5% |
| BRICS | 🇮🇷 Iran | 4.7% | 3.3% |
| BRICS | 🇷🇺 Russia | 3.6% | 3.2% |
| BRICS | 🇪🇬 Egypt | 3.8% | 3.0% |
| BRICS-invited | 🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia | -0.8% | 2.6% |
| BRICS | 🇧🇷 Brazil | 2.9% | 2.2% |
| BRICS | 🇿🇦 South Africa | 0.6% | 0.9% |
| BRICS | 🇪🇹 Ethiopia | 7.2% | 6.2% |
| 🌍 World | 3.2% | 3.2% |
China and India are forecasted to maintain relatively high growth rates in 2024 at 4.6% and 6.8% respectively, but compared to the previous year, China is growing 0.6 percentage points slower while India is an entire percentage point slower.
On the other hand, four G7 nations are set to grow faster than last year, which includes Germany making its comeback from its negative real GDP growth of -0.3% in 2023.
Faster Growth for BRICS than G7 Nations
Despite mostly lower growth forecasts in 2024 compared to 2023, BRICS nations still have a significantly higher average growth forecast at 3.6% compared to the G7 average of 1%.
While the G7 countries’ combined GDP is around $15 trillion greater than the BRICS nations, with continued higher growth rates and the potential to add more members, BRICS looks likely to overtake the G7 in economic size within two decades.
BRICS Expansion Stutters Before October 2024 Summit
BRICS’ recent expansion has stuttered slightly, as Argentina’s newly-elected president Javier Milei declined its invitation and Saudi Arabia clarified that the country is still considering its invitation and has not joined BRICS yet.
Even with these initial growing pains, South Africa’s Foreign Minister Naledi Pandor told reporters in February that 34 different countries have submitted applications to join the growing BRICS bloc.
Any changes to the group are likely to be announced leading up to or at the 2024 BRICS summit which takes place October 22-24 in Kazan, Russia.
Get the Full Analysis of the IMF’s Outlook on VC+
This visual is part of an exclusive special dispatch for VC+ members which breaks down the key takeaways from the IMF’s 2024 World Economic Outlook.
For the full set of charts and analysis, sign up for VC+.
-

 Lithium6 days ago
Lithium6 days agoRanked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2023
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoThe Largest Earthquakes in the New York Area (1970-2024)
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: The Countries With the Most Air Pollution in 2023
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanking the Top 15 Countries by Carbon Tax Revenue
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
-

 Mining2 weeks ago
Mining2 weeks agoGold vs. S&P 500: Which Has Grown More Over Five Years?