Misc
Ranked: Most Popular U.S. Undergraduate Degrees (2011–2021)
Ranked: Most Popular U.S. Undergraduate Degrees (2011–2021)
In an era of soaring tuition fees and mounting student debt, choosing which undergraduate degree to pursue has become a crucial decision for any aspiring college student. And it always helps to see which way the winds are blowing.
This visualization by Kashish Rastogi, based on data from the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES), examines the changing landscape of undergraduate degrees awarded between the 2010–2011 and 2020–2021 academic years.
Undergraduate Degrees Growing in Popularity
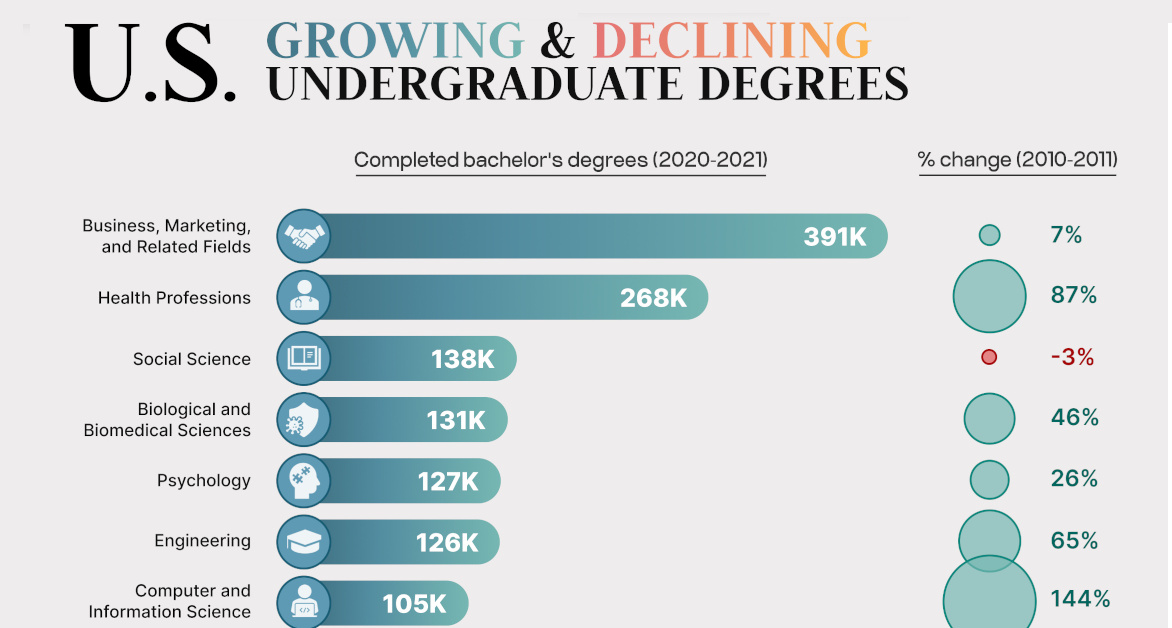
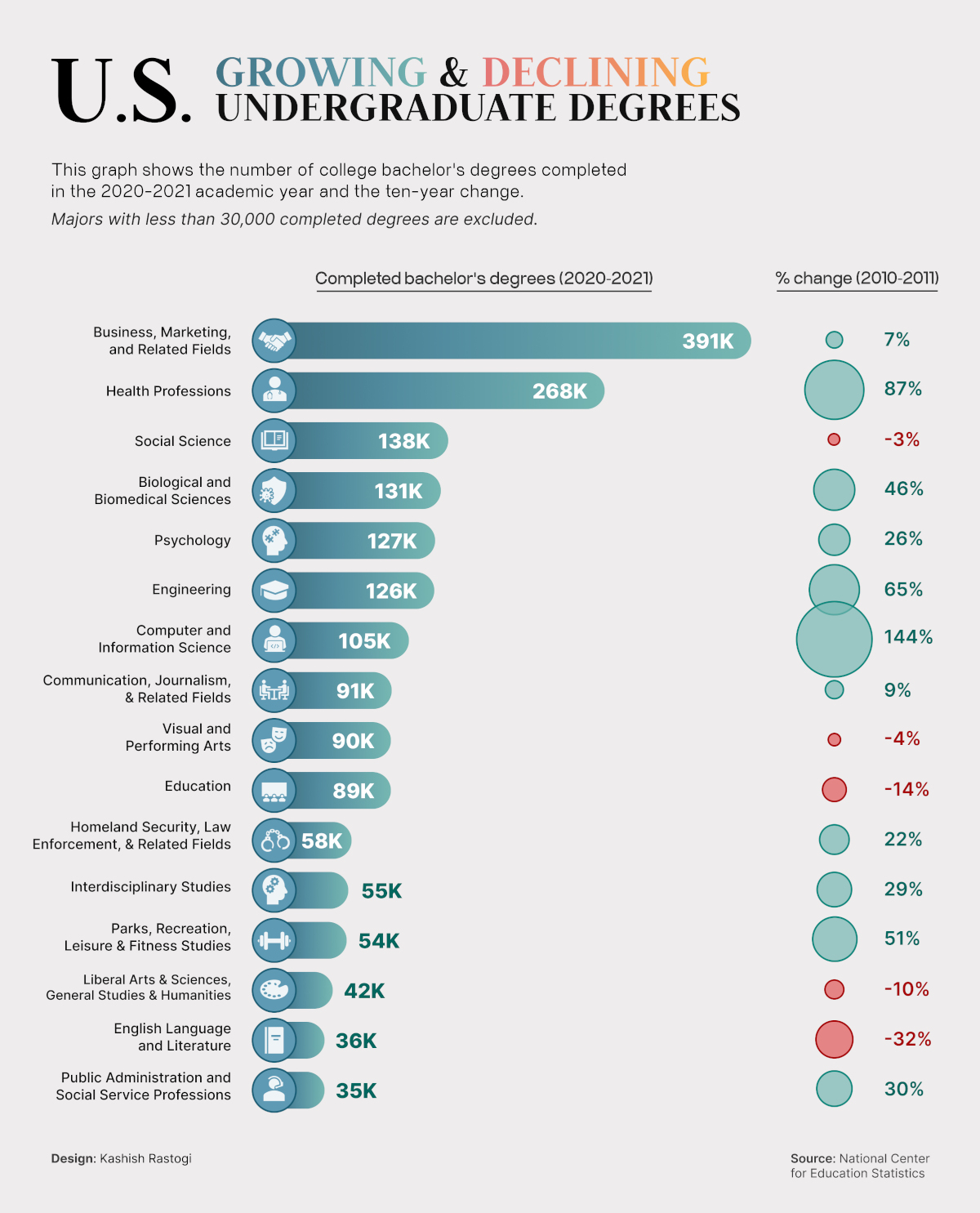
The NCES classifies all four-year bachelor degrees into 38 fields of study. Of these fields, 21 saw an increase in graduates in 2020–2021 compared to 2010–2011.
While only those with more than 30,000 graduates have been shown in the graphic (to prevent overrepresentation of large changes in small pools of graduates), the full list is available below.
| Rank | Field of Study | 2010–2011 | 2020–2021 | % Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Business | 363,919 | 390,781 | +7% |
| 2 | Health Professions | 143,463 | 268,018 | +87% |
| 3 | Biomedical Sciences | 89,984 | 131,499 | +46% |
| 4 | Psychology | 100,906 | 126,944 | +26% |
| 5 | Engineering | 76,356 | 126,037 | +65% |
| 6 | Computer Sciences | 43,066 | 104,874 | +144% |
| 7 | Communication | 83,231 | 90,775 | +9% |
| 8 | Security & Law Enforcement | 47,600 | 58,009 | +22% |
| 9 | Interdisciplinary Studies | 42,473 | 54,584 | +29% |
| 10 | Leisure & Fitness Studies | 35,934 | 54,294 | +51% |
| 11 | Public Administration | 26,799 | 34,817 | +30% |
| 12 | Physical Sciences | 24,338 | 28,706 | +18% |
| 13 | Mathematics | 17,182 | 27,092 | +58% |
| 14 | Agriculture Sciences | 15,851 | 21,418 | +35% |
| 15 | Natural Resources & Conservation | 12,779 | 20,507 | +61% |
| 16 | Engineering Technologies | 16,187 | 18,562 | +15% |
| 17 | Transportation | 4,941 | 5,993 | +21% |
| 18 | Legal | 4,429 | 4,589 | +4% |
| 19 | Military Technologies | 64 | 1,524 | +2,281% |
| 20 | Science Technologies | 367 | 532 | +45% |
| 21 | Library Science | 96 | 119 | +24% |
Let’s take a look at the areas of study that were most popular, as well as some of the fastest growing fields:
Computer and Information Sciences
Bachelor’s degrees in this discipline have grown by 144% since 2010–2011, with over 100,000 graduates in 2020–2021. The allure of the tech sector’s explosive growth likely contributed to its popularity among students.
Health Professions
Undergraduate degrees in health professions saw an 87% increase, attracting nearly 260,000 graduates in 2020–2021. This field accounted for 13% of the total graduating class, reflecting the growing appeal of the healthcare sector.
Engineering
There were 50,000 more engineering graduates in the U.S. in 2021, up 65% from 2011. With a median income over $100,000 per year, engineering graduates can usually rely on good wages as well as versatility in future careers, capable of finding jobs in tech, design, and communication fields, and of course, becoming future entrepreneurs.
Biomedical Sciences
University graduates in this field, which focuses on the integration of the study of biology with health and medicine, grew by 46%. A subset of this category—epidemiology—has been in the limelight recently thanks to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Business
While this category recorded a modest 7% growth in graduates, its popularity has been indisputable in the last decade, representing the largest proportion of the graduating class in both 2011 and 2021.
Fields with Declining University Graduates (2011‒2021)
Meanwhile, 17 areas of study experienced declines in the number of completed university degrees. We explore some of the notable ones below:
| Rank | Field of Study | 2010–2011 | 2020–2021 | % Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Social Sciences | 142,161 | 137,908 | -3% |
| 2 | Visual & Performing Arts | 93,939 | 90,022 | -4% |
| 3 | Education | 104,008 | 89,398 | -14% |
| 4 | Liberal Arts | 46,717 | 41,909 | -10% |
| 5 | English | 52,754 | 35,762 | -32% |
| 6 | History | 35,008 | 22,919 | -35% |
| 7 | Human Sciences | 22,438 | 22,319 | -1% |
| 8 | Foreign Languages | 21,705 | 15,518 | -29% |
| 9 | Philosophy & Religion | 12,830 | 11,988 | -7% |
| 10 | Architecture | 9,831 | 9,296 | -5% |
| 11 | Ethnic, Cultural & Gender Studies | 8,955 | 7,374 | -18% |
| 12 | Theology | 9,073 | 6,737 | -26% |
| 13 | Communications Tech | 4,858 | 4,557 | -6% |
| 14 | Personal & Culinary Services | 1,214 | 594 | -51% |
| 15 | Construction Trades | 328 | 221 | -33% |
| 16 | Mechanic & Repair | 226 | 221 | -2% |
| 17 | Precision Production | 43 | 28 | -35% |
English
Popular in the 1970s, the English undergraduate degree has gone through peaks (80s and 90s) and troughs (2000s and 10s) of popularity in the last 50 years. Between 2010–2011 and 2020–2021, the number of students with an English degree has fallen by a third.
The state of English’s woes are even making its way to pop culture, like in Netflix’s The Chair, which follows the head of a struggling English department at a major university.
Education
The existing teacher shortage in the United States does not seem to be getting fixed by a burgeoning supply of new grads. In fact, the number of university graduates in Education fell 14% between 2011 and 2021. With concerns around stagnant wages, burnout, and little to no support for supplies, many teachers are seeing an already demanding job becoming harder.
Liberal Arts
In the classic era, the liberal arts covered seven fields of study: rhetoric, grammar, logic, astronomy, mathematics, geometry, and music. Now, liberal art degrees include several other subjects: history, political science, and even philosophy—but students are meant to primarily walk away with critical thinking skills.
The modern world rewards specialization however, and a wider-scope liberal arts degree is seeing fewer takers, with a 10% drop in graduating students.
Where Does This Data Come From?
Source: The National Center for Education’s statistics from their Integrated Postsecondary Education Data System surveys. Numbers for both 2010–2011 and 2020–2021 academic years can be found from their summary tables by changing the award level code (bachelor degrees) and the year on the left-hand toolbar.

This article was published as a part of Visual Capitalist's Creator Program, which features data-driven visuals from some of our favorite Creators around the world.
VC+
VC+: Get Our Key Takeaways From the IMF’s World Economic Outlook
A sneak preview of the exclusive VC+ Special Dispatch—your shortcut to understanding IMF’s World Economic Outlook report.

Have you read IMF’s latest World Economic Outlook yet? At a daunting 202 pages, we don’t blame you if it’s still on your to-do list.
But don’t worry, you don’t need to read the whole April release, because we’ve already done the hard work for you.
To save you time and effort, the Visual Capitalist team has compiled a visual analysis of everything you need to know from the report—and our VC+ Special Dispatch is available exclusively to VC+ members. All you need to do is log into the VC+ Archive.
If you’re not already subscribed to VC+, make sure you sign up now to access the full analysis of the IMF report, and more (we release similar deep dives every week).
For now, here’s what VC+ members get to see.
Your Shortcut to Understanding IMF’s World Economic Outlook
With long and short-term growth prospects declining for many countries around the world, this Special Dispatch offers a visual analysis of the key figures and takeaways from the IMF’s report including:
- The global decline in economic growth forecasts
- Real GDP growth and inflation forecasts for major nations in 2024
- When interest rate cuts will happen and interest rate forecasts
- How debt-to-GDP ratios have changed since 2000
- And much more!
Get the Full Breakdown in the Next VC+ Special Dispatch
VC+ members can access the full Special Dispatch by logging into the VC+ Archive, where you can also check out previous releases.
Make sure you join VC+ now to see exclusive charts and the full analysis of key takeaways from IMF’s World Economic Outlook.
Don’t miss out. Become a VC+ member today.
What You Get When You Become a VC+ Member
VC+ is Visual Capitalist’s premium subscription. As a member, you’ll get the following:
- Special Dispatches: Deep dive visual briefings on crucial reports and global trends
- Markets This Month: A snappy summary of the state of the markets and what to look out for
- The Trendline: Weekly curation of the best visualizations from across the globe
- Global Forecast Series: Our flagship annual report that covers everything you need to know related to the economy, markets, geopolitics, and the latest tech trends
- VC+ Archive: Hundreds of previously released VC+ briefings and reports that you’ve been missing out on, all in one dedicated hub
You can get all of the above, and more, by joining VC+ today.
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoHow Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Environment2 weeks ago
Environment2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001