Politics
Arms Sales: USA vs. Russia (1950-2017)
Arms Sales: USA vs. Russia (1950-2017)
Between countless proxy wars and the growing threat of nuclear catastrophe, the Cold War created an unprecedented geopolitical climate.
For nearly half a century, the world’s two biggest superpowers were scrambling to top one another by any means necessary. It was a tension that ignited everything from the space race to sports rivalries, with the impact often spilling over to neighboring nations.
Not only did the U.S. and Soviet Union duke it out in the mother of all arms races – they also extended their influence by selling arms outside of their borders. Interestingly, this latter race continues on until today, almost three decades after the fall of the Iron Curtain.
Visualizing Arms Sales
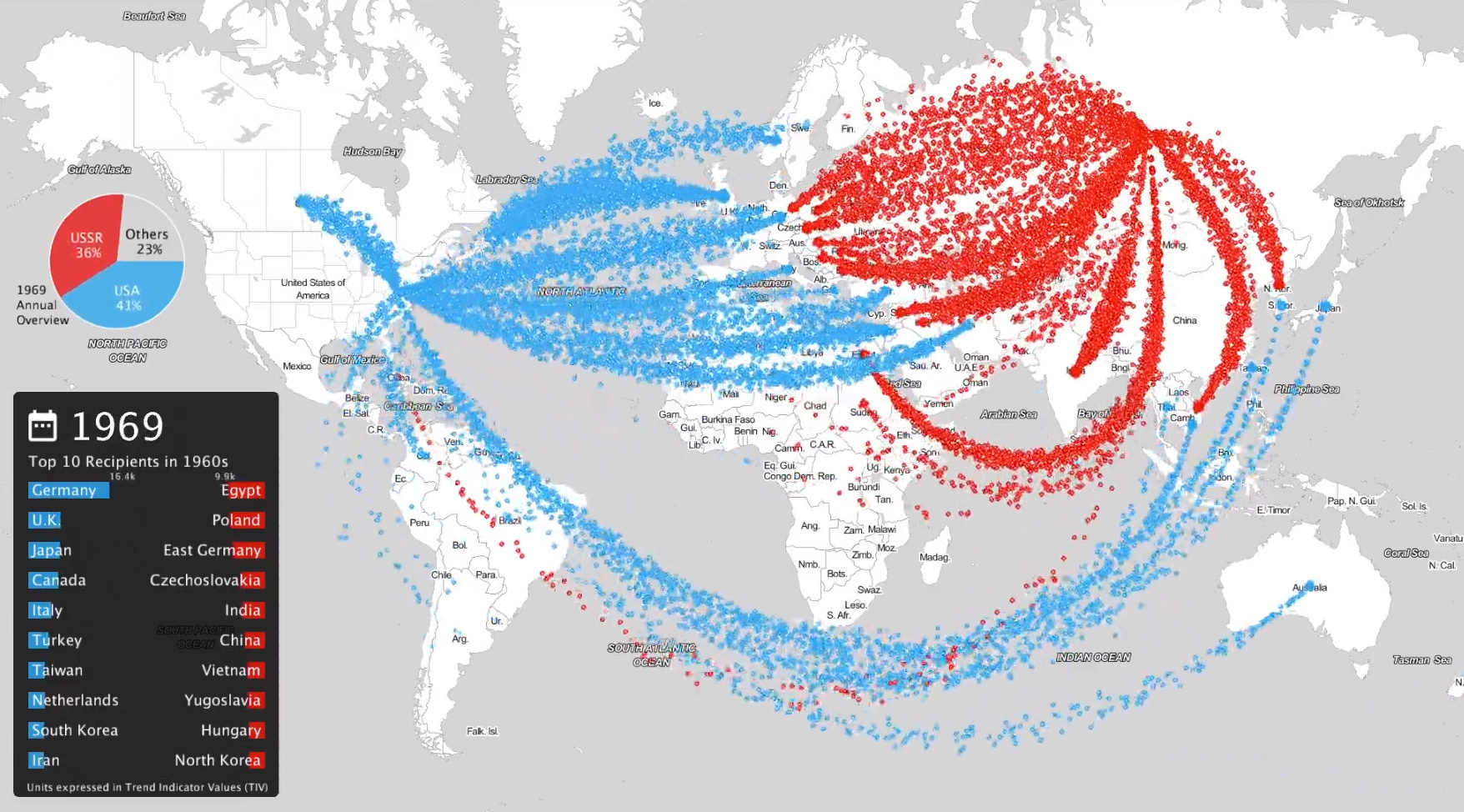
Today’s animation comes from data scientist Will Geary, and it shows the history of international arms sales originating from the U.S. and the Soviet Union (later Russia) from 1950 to 2017.
More specifically, using data from the SIPRI Arms Transfers Database, the animation shows the geographic movement of arms from country to country as well as the evolving share of the arms trade held by the respective countries. The video is also pleasantly backed by audio that represents music from each decade, ranging from Buffalo Springfield to The Clash.
Peak Arms Dominance
If you watch the pie chart in the upper left corner of the animation, you’ll see that the early-1960s is the peak of U.S. and Soviet arm dominance – at this point, around the same time as the Cuban Missile Crisis and then the JFK assassination, the two superpowers combined for 80% of global arms sales.
In the 1960s, the biggest customers of U.S. arms were Germany, the United Kingdom, and Japan – while the Soviets sent the most weapons to Egypt, Poland, and East Germany.
Fall of the Wall
By the 1980s, the global arms trade started dying down as Soviet leaders like Gorbachev focused on domestic reforms, and eventually perestroika.
Later, the Soviet Union dissolved, and arms sales continued to plunge all the way to 2001:
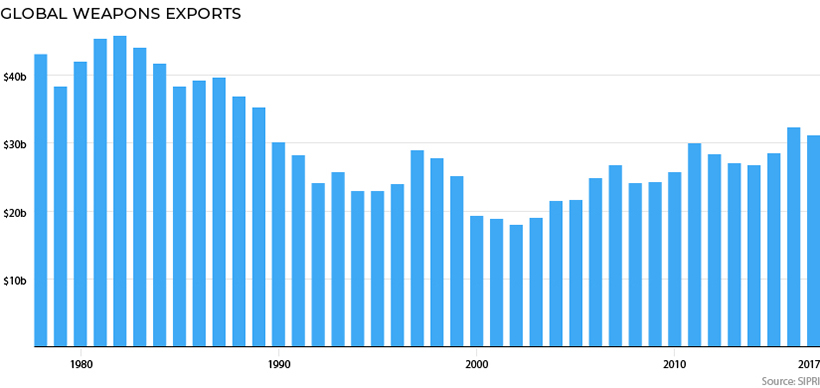
Since then, arms sales have been ramping up again – and today, they are back at levels last seen before the Berlin Wall came down.
The Modern Era
Who is selling the most arms, according to the last 10 years of data?
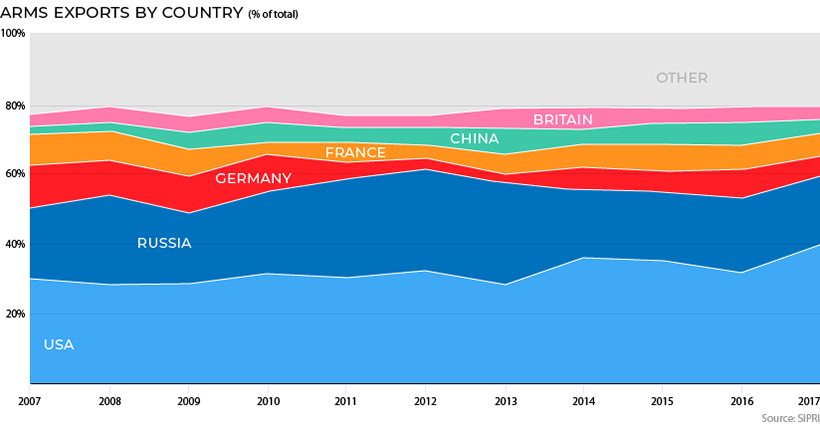
Even though the Cold War is now long gone, the U.S. and Russia have kept their legacy of international arms sales going well into the 21st century.
And today, the two nations combine for roughly 60% of arms sales, with top U.S. weapons manufacturers like Lockheed Martin and Raytheon getting a big slice of that pie.
United States
Charted: What Southeast Asia Thinks About China & the U.S.
A significant share of respondents from an ASEAN-focused survey are not happy about rising American and Chinese influence in the region.
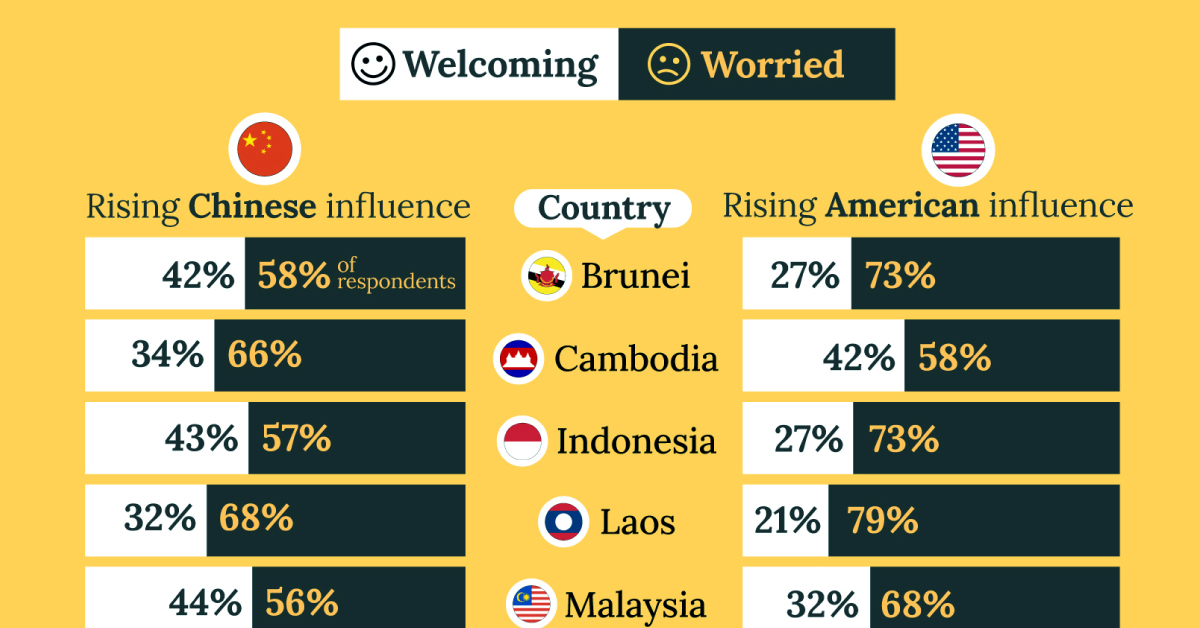
What Southeast Asia Thinks About China & the U.S.
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
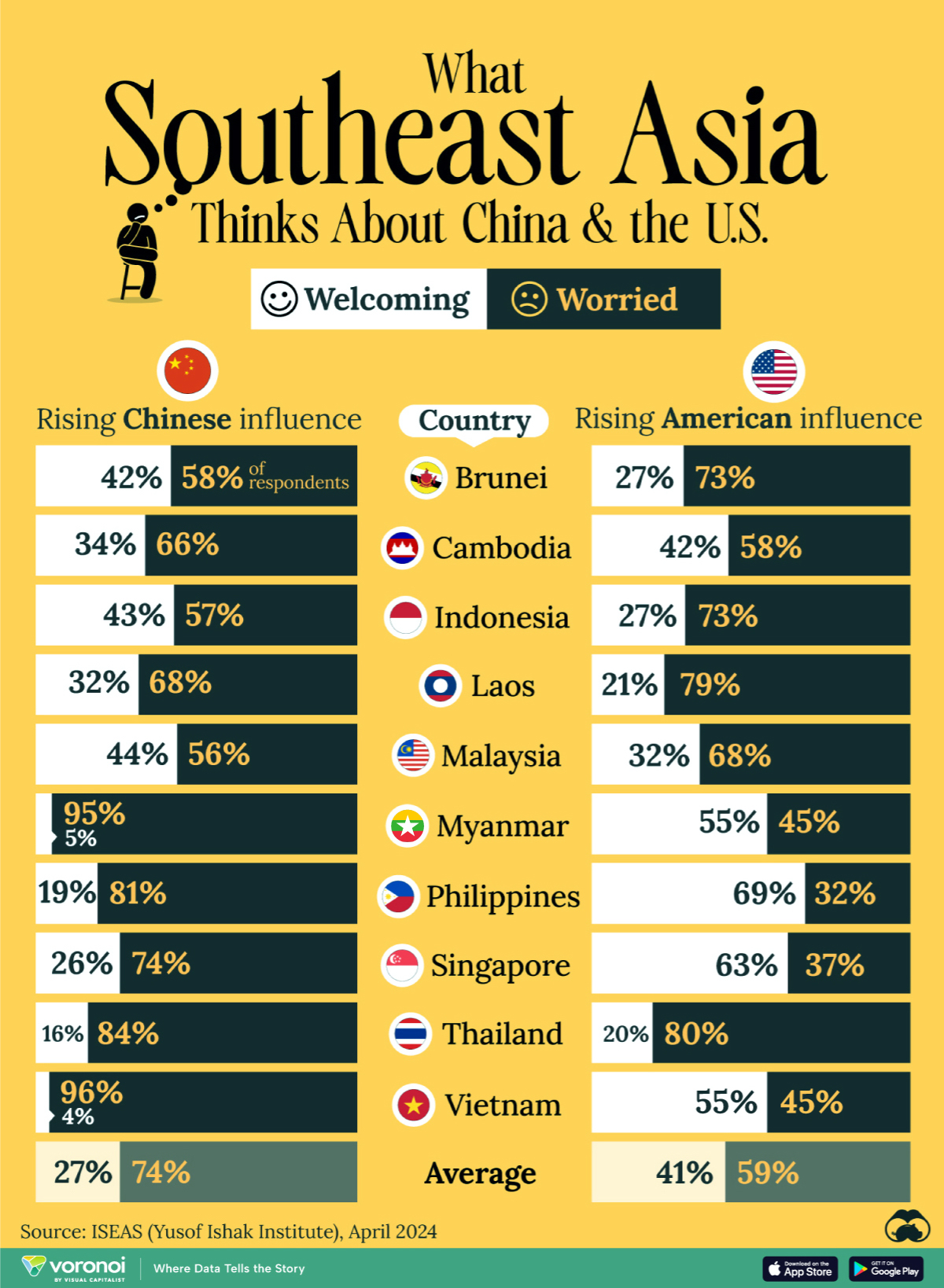
This chart visualizes the results of a 2024 survey conducted by the ASEAN Studies Centre at the ISEAS-Yusof Ishak Institute. Nearly 2,000 respondents were asked if they were worried or welcoming of rising Chinese and American geopolitical influence in their country.
The countries surveyed all belong to the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), a political and economic union of 10 states in Southeast Asia.
Feelings Towards China
On average, a significant share of respondents from all 10 countries are worried about rising influence from both the U.S. and China.
However, overall skepticism is higher for China, at 74% (versus 59% for U.S.).
| Country | Worried About Growing 🇨🇳 Influence | Welcome Growing 🇨🇳 Influence |
|---|---|---|
| 🇧🇳 Brunei | 58% | 42% |
| 🇰🇭 Cambodia | 66% | 34% |
| 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 57% | 43% |
| 🇱🇦 Laos | 68% | 32% |
| 🇲🇾 Malaysia | 56% | 44% |
| 🇲🇲 Myanmar | 95% | 5% |
| 🇵🇭 Philippines | 81% | 19% |
| 🇸🇬 Singapore | 74% | 26% |
| 🇹🇭 Thailand | 84% | 16% |
| 🇻🇳 Vietnam | 96% | 4% |
| Average | 74% | 27% |
The recently-cooled but still active territorial concerns over the South China Sea may play a significant role in these responses, especially in countries which are also claimants over the sea.
For example, in Vietnam over 95% of respondents said they were worried about China’s growing influence.
Feelings Towards America
Conversely, rising American influence is welcomed in two countries with competing claims in the South China Sea, the Philippines (69%) and Vietnam (55%).
| Country | Worried About Growing 🇺🇸 Influence | Welcome Growing 🇺🇸 Influence |
|---|---|---|
| 🇧🇳 Brunei | 73% | 27% |
| 🇰🇭 Cambodia | 58% | 42% |
| 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 73% | 27% |
| 🇱🇦 Laos | 79% | 21% |
| 🇲🇾 Malaysia | 68% | 32% |
| 🇲🇲 Myanmar | 45% | 55% |
| 🇵🇭 Philippines | 32% | 69% |
| 🇸🇬 Singapore | 37% | 63% |
| 🇹🇭 Thailand | 80% | 20% |
| 🇻🇳 Vietnam | 45% | 55% |
| Average | 59% | 41% |
Despite this, on a regional average, more respondents worry about growing American influence (59%) than they welcome it (41%).
Interestingly, it seems almost every ASEAN nation has a clear preference for one superpower over the other.
The only exception is Thailand, where those surveyed were not a fan of either option, with 84% worried about China, and 80% worried about the U.S.
-

 Economy7 days ago
Economy7 days agoThe Most Valuable Companies in Major EU Economies
-

 Wealth2 weeks ago
Wealth2 weeks agoCharted: Which City Has the Most Billionaires in 2024?
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoAll of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoThe Carbon Footprint of Major Travel Methods
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoVisualizing the Most Common Pets in the U.S.
-

 Culture2 weeks ago
Culture2 weeks agoThe World’s Top Media Franchises by All-Time Revenue
-

 voronoi1 week ago
voronoi1 week agoBest Visualizations of April on the Voronoi App
-

 Wealth1 week ago
Wealth1 week agoCharted: Which Country Has the Most Billionaires in 2024?