Technology
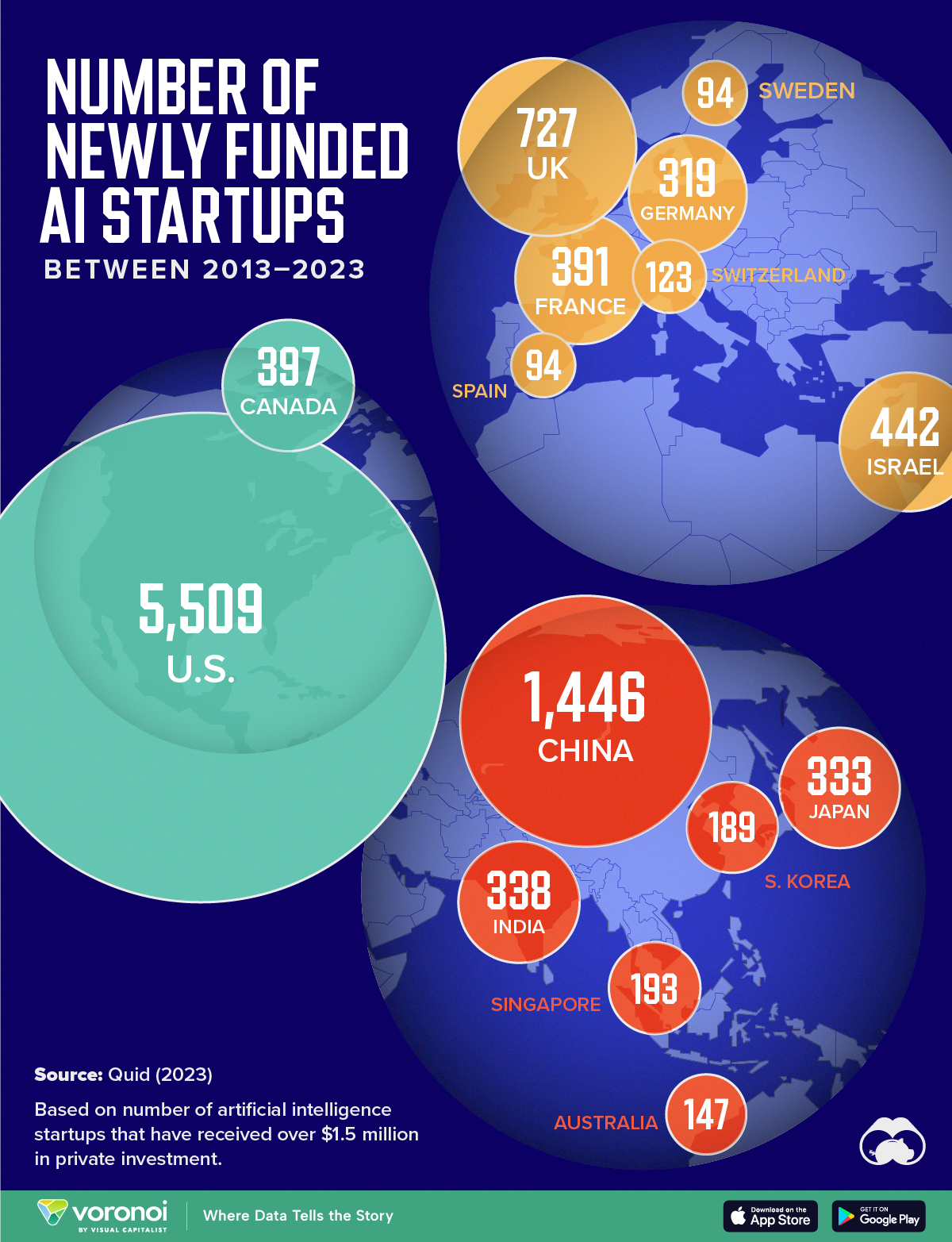
Mapped: The Number of AI Startups By Country
![]() See this visualization first on the Voronoi app.
See this visualization first on the Voronoi app.
Mapped: The Number of AI Startups By Country
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
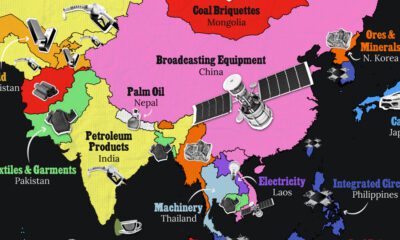
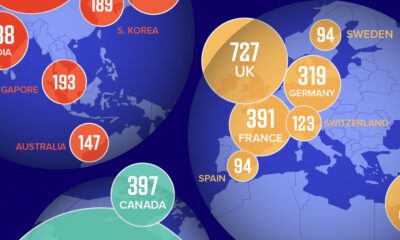
Amidst the recent expansion of artificial intelligence (AI), we’ve visualized data from Quid (accessed via Stanford’s 2024 AI Index Report) to highlight the top 15 countries which have seen the most AI startup activity over the past decade.
The figures in this graphic represent the number of newly funded AI startups within that country, in the time period of 2013 to 2023. Only companies that received over $1.5 million in private investment were considered.
Data and Highlights
The following table lists all of the numbers featured in the above graphic.
| Rank | Geographic area | Number of newly funded AI startups (2013-2023) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇺🇸 United States | 5,509 |
| 2 | 🇨🇳 China | 1,446 |
| 3 | 🇬🇧 United Kingdom | 727 |
| 4 | 🇮🇱 Israel | 442 |
| 5 | 🇨🇦 Canada | 397 |
| 6 | 🇫🇷 France | 391 |
| 7 | 🇮🇳 India | 338 |
| 8 | 🇯🇵 Japan | 333 |
| 9 | 🇩🇪 Germany | 319 |
| 10 | 🇸🇬 Singapore | 193 |
| 11 | 🇰🇷 South Korea | 189 |
| 12 | 🇦🇺 Australia | 147 |
| 13 | 🇨🇭 Switzerland | 123 |
| 14 | 🇸🇪 Sweden | 94 |
| 15 | 🇪🇸 Spain | 94 |
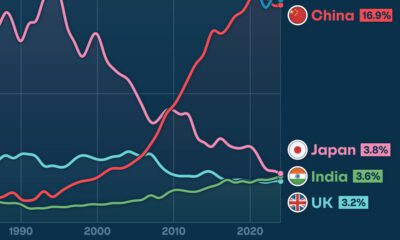
From this data, we can see that the U.S., China, and UK have established themselves as major hotbeds for AI innovation.
In terms of funding, the U.S. is massively ahead, with private AI investment totaling $335 billion between 2013 to 2023. AI startups in China raised $104 billion over the same timeframe, while those in the UK raised $22 billion.
Further analysis reveals that the U.S. is widening this gap even more. In 2023, for example, private investment in the U.S. grew by 22% from 2022 levels. Meanwhile, investment fell in China (-44%) and the UK (-14.1%) over the same time span.
Where is All This Money Flowing To?
Quid also breaks down total private AI investment by focus area, providing insight into which sectors are receiving the most funding.
| Focus Area | Global Investment in 2023 (USD billions) |
|---|---|
| 🤖 AI infrastructure, research, and governance | $18.3 |
| 🗣️ Natural language processing | $8.1 |
| 📊 Data management | $5.5 |
| ⚕️ Healthcare | $4.2 |
| 🚗 Autonomous vehicles | $2.7 |
| 💰 Fintech | $2.1 |
| ⚛️ Quantum computing | $2.0 |
| 🔌 Semiconductor | $1.7 |
| ⚡ Energy, oil, and gas | $1.5 |
| 🎨 Creative content | $1.3 |
| 📚 Education | $1.2 |
| 📈 Marketing | $1.1 |
| 🛸 Drones | $1.0 |
| 🔒 Cybersecurity | $0.9 |
| 🏭 Manufacturing | $0.9 |
| 🛒 Retail | $0.7 |
| 🕶️ AR/VR | $0.7 |
| 🛡️ Insurtech | $0.6 |
| 🎬 Entertainment | $0.5 |
| 💼 VC | $0.5 |
| 🌾 Agritech | $0.5 |
| ⚖️ Legal tech | $0.4 |
| 👤 Facial recognition | $0.3 |
| 🌐 Geospatial | $0.2 |
| 💪 Fitness and wellness | $0.2 |
Attracting the most money is AI infrastructure, research, and governance, which refers to startups that are building AI applications (like OpenAI’s ChatGPT).
The second biggest focus area is natural language processing (NLP), which is a type of AI that enables computers to understand and interpret human language. This technology has numerous use cases for businesses, particularly in financial services, where NLP can power customer support chatbots and automated wealth advisors.
With $8 billion invested into NLP-focused startups during 2023, investors appear keenly aware of this technology’s transformative potential.
Learn More About AI From Visual Capitalist
If you enjoyed this graphic, be sure to check out Visualizing AI Patents by Country.
Technology
Charting the Next Generation of Internet
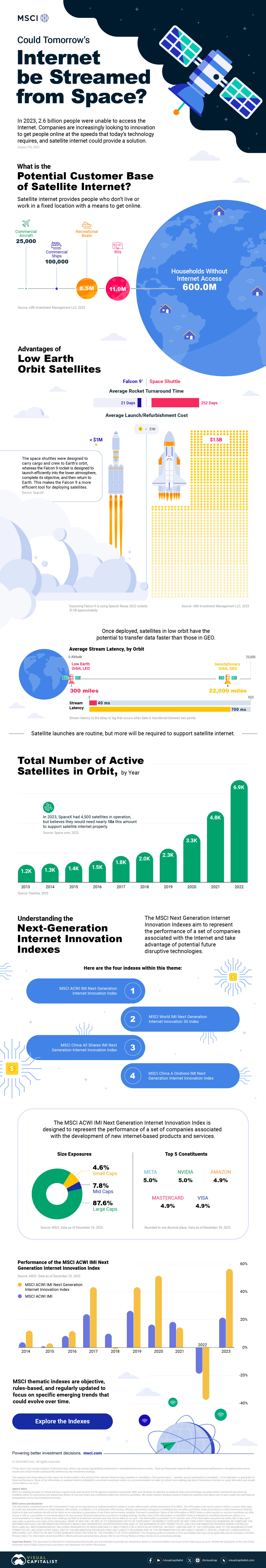
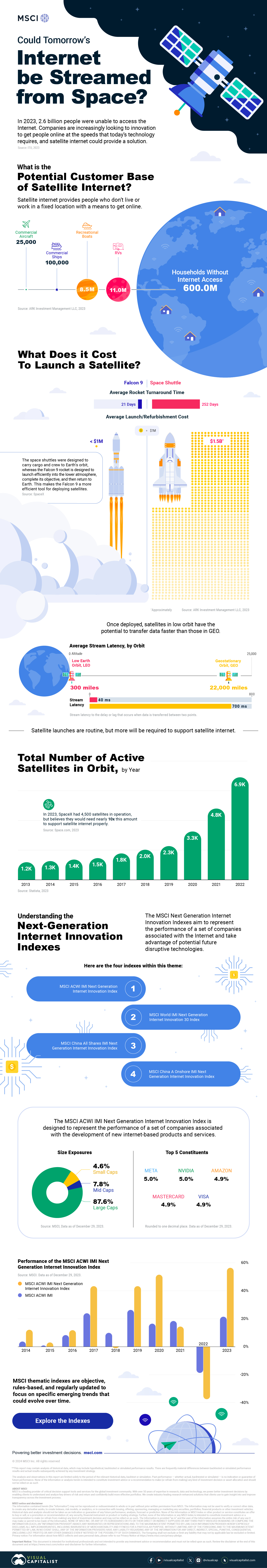
In this graphic, Visual Capitalist has partnered with MSCI to explore the potential of satellite internet as the next generation of internet innovation.
Could Tomorrow’s Internet be Streamed from Space?
In 2023, 2.6 billion people could not access the internet. Today, companies worldwide are looking to innovative technology to ensure more people are online at the speed of today’s technology.
Could satellite internet provide the solution?
In collaboration with MSCI, we embarked on a journey to explore whether tomorrow’s internet could be streamed from space.
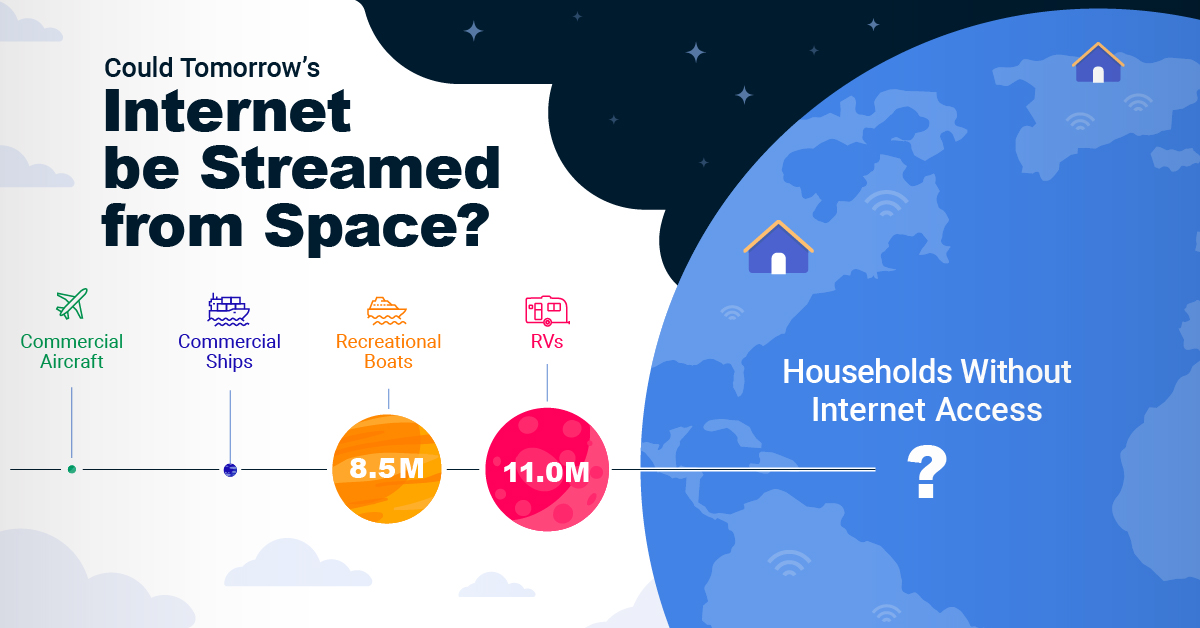
Satellite Internet’s Potential Customer Base
Millions of people live in rural communities or mobile homes, and many spend much of their lives at sea or have no fixed abode. So, they cannot access the internet simply because the technology is unavailable.
Satellite internet gives these communities access to the internet without requiring a fixed location. Consequently, the volume of people who could get online using satellite internet is significant:
| Area | Potential Subscribers |
|---|---|
| Households Without Internet Access | 600,000,000 |
| RVs | 11,000,000 |
| Recreational Boats | 8,500,000 |
| Ships | 100,000 |
| Commercial Aircraft | 25,000 |
Advances in Satellite Technology
Satellite internet is not a new concept. However, it has only recently been that roadblocks around cost and long turnaround times have been overcome.
NASA’s space shuttle, until it was retired in 2011, was the only reusable means of transporting crew and cargo into orbit. It cost over $1.5 billion and took an average of 252 days to launch and refurbish.
In stark contrast, SpaceX’s Falcon 9 can now launch objects into orbit and maintain them at a fraction of the time and cost, less than 1% of the space shuttle’s cost.
| Average Rocket Turnaround Time | Average Launch/Refurbishment Cost | |
|---|---|---|
| Falcon 9* | 21 days | < $1,000,000 |
| Space Shuttle | 252 days | $1,500,000,000 (approximately) |
Satellites are now deployed 300 miles in low Earth orbit (LEO) rather than 22,000 miles above Earth in Geostationary Orbit (GEO), previously the typical satellite deployment altitude.
What this means for the consumer is that satellite internet streamed from LEO has a latency of 40 ms, which is an optimal internet connection. Especially when compared to the 700 ms stream latency experienced with satellite internet streamed from GEO.
What Would it Take to Build a Satellite Internet?
SpaceX, the private company that operates Starlink, currently has 4,500 satellites. However, the company believes it will require 10 times this number to provide comprehensive satellite internet coverage.
Charting the number of active satellites reveals that, despite the increasing number of active satellites, many more must be launched to create a comprehensive satellite internet.
| Year | Number of Active Satellites |
|---|---|
| 2022 | 6,905 |
| 2021 | 4,800 |
| 2020 | 3,256 |
| 2019 | 2,272 |
| 2018 | 2,027 |
| 2017 | 1,778 |
| 2016 | 1,462 |
| 2015 | 1,364 |
| 2014 | 1,262 |
| 2013 | 1,187 |
Next-Generation Internet Innovation
Innovation is at the heart of the internet’s next generation, and the MSCI Next Generation Innovation Index exposes investors to companies that can take advantage of potentially disruptive technologies like satellite internet.
You can gain exposure to companies advancing access to the internet with four indexes:
- MSCI ACWI IMI Next Generation Internet Innovation Index
- MSCI World IMI Next Generation Internet Innovation 30 Index
- MSCI China All Shares IMI Next Generation Internet Innovation Index
- MSCI China A Onshore IMI Next Generation Internet Innovation Index
MSCI thematic indexes are objective, rules-based, and regularly updated to focus on specific emerging trends that could evolve.

Click here to explore the MSCI thematic indexes

-
 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoCountries With the Highest Rates of Crypto Ownership
While the U.S. is a major market for cryptocurrencies, two countries surpass it in terms of their rates of crypto ownership.
-
 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoMapped: The Number of AI Startups By Country
Over the past decade, thousands of AI startups have been funded worldwide. See which countries are leading the charge in this map graphic.
-

 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks agoAll of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
Intel, TSMC, and more have received billions in subsidies from the U.S. CHIPS Act in 2024.
-

 AI3 weeks ago
AI3 weeks agoVisualizing AI Patents by Country
See which countries have been granted the most AI patents each year, from 2012 to 2022.
-

 Brands4 weeks ago
Brands4 weeks agoHow Tech Logos Have Evolved Over Time
From complete overhauls to more subtle tweaks, these tech logos have had quite a journey. Featuring: Google, Apple, and more.
-

 AI1 month ago
AI1 month agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
Nvidia is coming for Intel’s crown. Samsung is losing ground. AI is transforming the space. We break down revenue for semiconductor companies.
-

 United States5 days ago
United States5 days agoMapped: Countries Where Recreational Cannabis is Legal
-
 Healthcare2 weeks ago
Healthcare2 weeks agoLife Expectancy by Region (1950-2050F)
-
 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Growth of a $1,000 Equity Investment, by Stock Market
-
 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoMapped: Europe’s GDP Per Capita, by Country
-
 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoCharted: What Frustrates Americans About the Tax System
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoCountries With the Highest Rates of Crypto Ownership
-

 Mining1 week ago
Mining1 week agoWhere the World’s Aluminum is Smelted, by Country
-

 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week agoVisualizing the Tax Burden of Every U.S. State