Energy
A Cost Comparison: Lithium Brine vs. Hard Rock Exploration
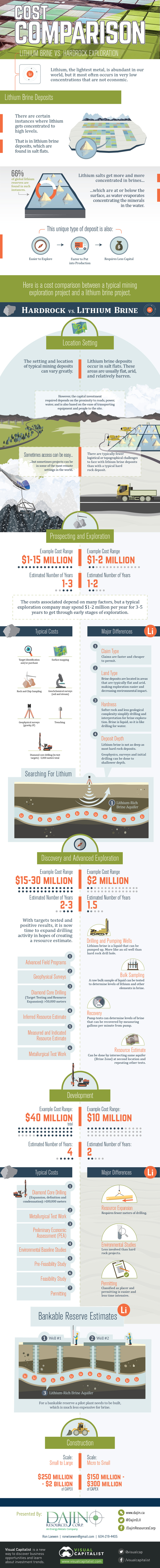
A Cost Comparison: Lithium Brine vs. Hard Rock Exploration
Lithium brine exploration infographic presented by: Dajin Resources
Capital is limited in the current mining exploration environment, so investors are increasingly looking for companies that have lower costs of doing business. Over the last four years, we’ve seen large-scale, low-grade projects go out of favour and investor preferences resting with low-CAPEX, high-return projects.
However, it is not only the construction costs and scale of a mine with which companies can save money. It can also be in initial prospecting, exploration, and the development of a project. The key here is for a company to be doing this work in a location setting that is easy to work in from logistical and cost perspectives. If a project is in a remote area in mountainous wilderness that requires setup of a camp and bush planes in and out, the payoff has to be that much higher.
This is where lithium brine deposits come in. Typically, they are located in salars (salt flats) which are flat, arid, and barren areas. This makes the logistics of setting up shop for exploration relatively straightforward, and also removes most topographical challenges of exploration.
Further, there are some other major benefits of lithium brine exploration from a cost perspective that makes it favourable to many hard rock projects. Lithium brine deposits are considered placer deposits and are easier to permit. Brine is also a liquid which means that drilling to find it is more akin to drilling for water, and once it is found the continuity is more straightforward. It’s also typically not located relatively close to surface, which limits the amount of meters drilled.
Once a deposit is discovered, advanced exploration and development can also be at a discount. Drilling wells and testing recovery are more like shallow oil wells or drilling for water. Finally, permitting for construction and production is faster because of the placer classification.
Lithium brine exploration has benefits from the angle of cost that make it less expensive than most comparable hard rock projects. However, their potential also depends on the price of lithium – we cover all of the elements of supply and demand for the light metal in this infographic.
Energy
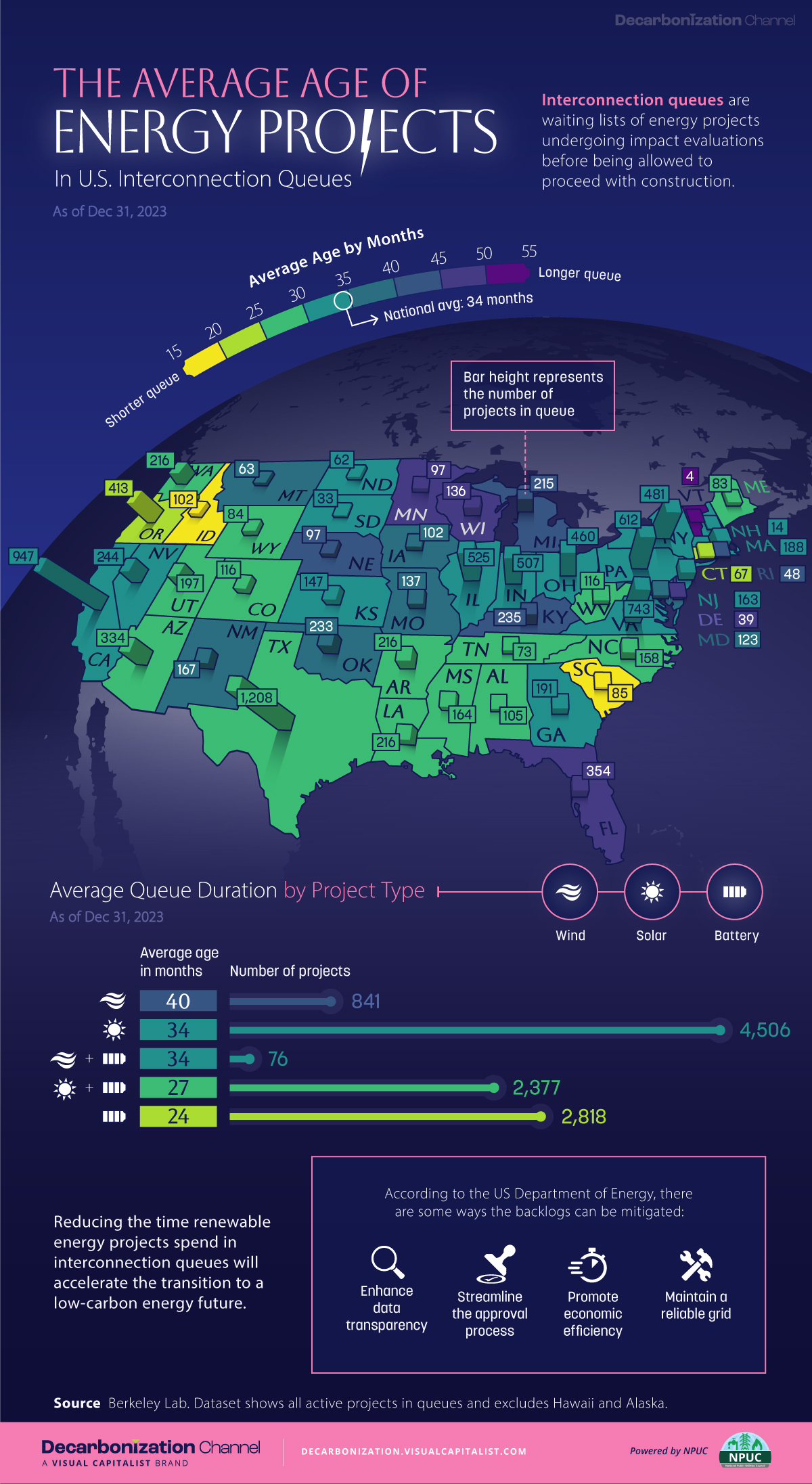
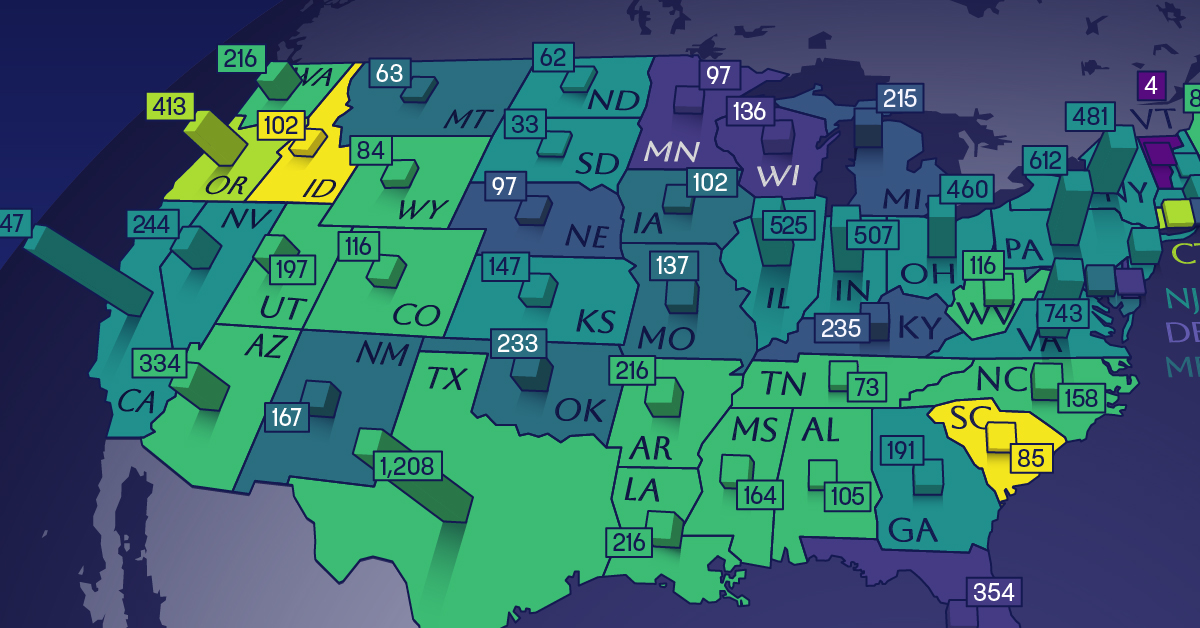
Mapped: The Age of Energy Projects in Interconnection Queues, by State
This map shows how many energy projects are in interconnection queues by state and how long these projects have been queued up, on average.
Age of Energy Projects in Interconnection Queues, by State
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
By the end of 2023, more than 11,000 energy projects were in interconnection queues in the United States, waiting for a green-light from regional grid operators to proceed with construction.
This map, created in partnership with the National Public Utilities Council, maps out the average age of active energy projects in interconnection queues by state, using data from Berkeley Lab.
Interconnection Queues, Explained
Interconnection queues are lists of energy projects that have made interconnection requests to their regional grid operators. Once submitted, these requests formally initiate the impact study process that each project goes through before grid connection, forming waiting lists for approval known as interconnection queues.
In recent years, both the number and generation capacity of queued projects have surged in the United States, along with the length of time spent in queue.
According to Berkeley Lab, the amount of generation capacity entering queues each year has risen by more than 550% from 2015 to 2023, with average queue duration rising from 3 years to 5 years the same period.
As a result of the growing backlog, a large proportion of projects ultimately withdraw from queues, leading to only 19% of applications reaching commercial operations.
The Backlog: Number of Projects and Average Wait Times
Of the 11,000 active projects in U.S. queues at the end of 2023, Texas, California, and Virginia had the most in queue; 1,208, 947, and 743, respectively.
When looking at the average ages of these projects, all three states hovered around the national average of 34 months (2.83 years), with Texas sporting 28 months, California 33, and Virginia 34.
Vermont, Minnesota, Wisconsin, and Florida, on the other hand, had the highest average queue durations; 54, 49, 47, and 46 months, respectively.
Average Queue Duration by Project Type
At the end of 2023, more than 95% of the generation capacity in active interconnection queues was for emission-free resources. The table below provides a breakdown.
| Project Type | Average Queue Duration (As of 12/31/2023) | Number of Projects in Queue |
|---|---|---|
| Wind | 40 months | 841 |
| Solar | 34 months | 4,506 |
| Wind+Battery | 34 months | 76 |
| Solar+Battery | 27 months | 2,377 |
| Battery | 24 months | 2,818 |
Wind projects had the highest wait times at the end of 2023 with an average age of 40 months (3.33 years). Solar projects, on the other hand, made up more than 40% of projects in queue.
Overall, reducing the time that these renewable energy projects spend in queues can accelerate the transition to a low-carbon energy future.
According to the U.S. Department of Energy, enhancing data transparency, streamlining approval processes, promoting economic efficiency, and maintaining a reliable grid are some of the ways this growing backlog can be mitigated.
-

 Culture6 days ago
Culture6 days agoThe World’s Top Media Franchises by All-Time Revenue
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoVisualizing the Average Lifespans of Mammals
-

 Brands2 weeks ago
Brands2 weeks agoHow Tech Logos Have Evolved Over Time
-

 Energy2 weeks ago
Energy2 weeks agoRanked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2023
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoCountries With the Largest Happiness Gains Since 2010
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoVC+: Get Our Key Takeaways From the IMF’s World Economic Outlook
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Countries That Have Become Sadder Since 2010
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoCharted: Who Has Savings in This Economy?