Technology
5G Revolution: Unlocking the Digital Age
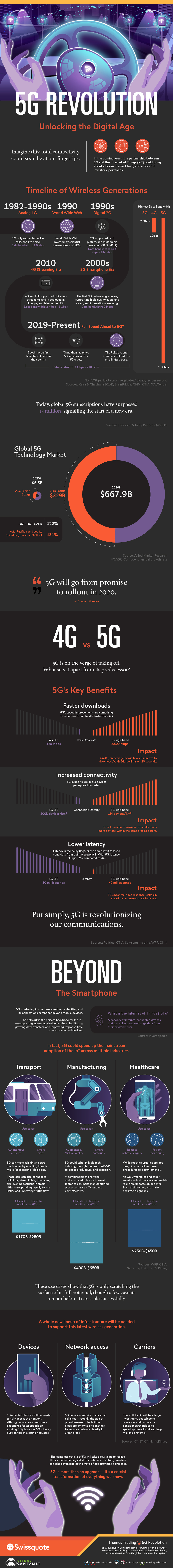
5G Revolution: Unlocking the Digital Age
Imagine if you were to jump straight from using a typewriter one day, to typing on a laptop the next. The speed and ease at which it would improve your tasks is undeniable.
With 5G, we’re on the cusp of a similar transition in the global communications system. Total connectivity could soon be at our fingertips.
Today’s infographic breaks down the potential that 5G promises, and the immense opportunities stemming from its implications for smart tech and the Internet of Things (IoT).
A Timeline of Wireless Generations
The world’s appetite for wireless speed has been insatiable. We’ve powered through five generations of wireless connectivity in just 40 years.
- 1982-1990s: Analog 1G
1G only supported voice calls, and little else.
Data bandwidth: 1.9 kbps - 1990s: Digital 2G
2G supported text, picture, and multimedia messaging (SMS, MMS).
Data bandwidth: 14.4 kbps – 384 kbps - 2000s: 3G Smartphone Era
The first 3G networks go online, supporting high-quality audio and video, and international roaming.
Data bandwidth: 2 Mbps - 2010: 4G Streaming Era
4G and LTE supported HD video streaming, and is deployed in Europe, and later in the U.S.
Data bandwidth: 2 Mbps – 1 Gbps - 2019-Present: Full Speed Ahead to 5G?
South Korea first launches 5G across the country, followed by 50 cities in China. The U.S., UK, and Germany also roll out 5G on a limited basis.
Data bandwidth: 1 Gbps – >10 Gbps
*k/M/Gbps: kilobytes/ megabytes/ gigabytes per second.
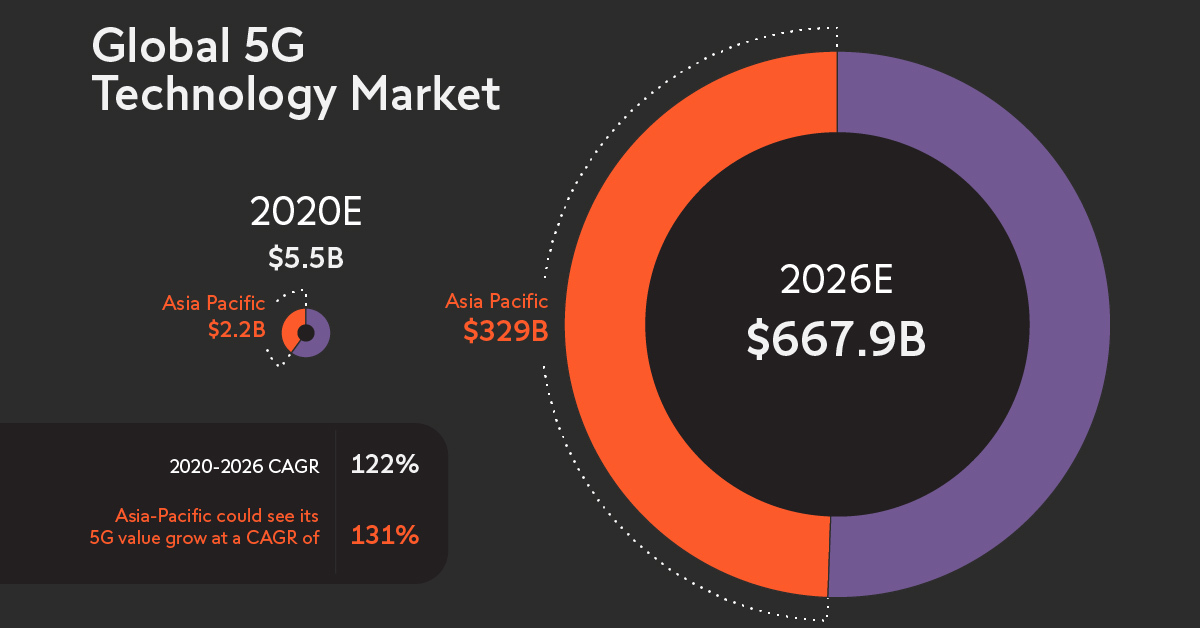
The global 5G market is projected to reach $668 billion at a 122% compound annual growth rate (2020-2026), with nearly half this growth coming from Asia-Pacific.
4G versus 5G: What’s the Difference?
5G is on the verge of taking off. What sets it apart from its predecessor?
For starters, 5G’s speed improvements are something to behold—it is up to 20x faster than 4G. On 4G, an average movie takes 6 minutes to download. With 5G, it will take less than 20 seconds.
| 4G | 5G | |
|---|---|---|
| Faster downloads Peak data date | 125 megabytes/second | 2,500 Mbs |
| Increased connectivity Devices supported per km² | 100,000 devices/km² | 1,000,000 devices/km² |
| Lower Latency Delay/ lag time | 50 milliseconds | <2 ms |
In other benefits, 5G supports 10x more devices per square kilometer. As a result, 5G will be able to seamlessly handle many more devices, within the same area as before. This is pivotal for its use in the imminent Internet of Things (IoT).
Finally, latency is the delay (lag), or the time that it takes to send data from point A to point B. With 5G, latency plunges 25x compared to 4G. This results in almost instantaneous data transfers.
5G will go from promise to roll-out in 2020.
Beyond the Smartphone
5G is one of the most anticipated technologies of our time, and with good reason. In the coming years, the partnership between 5G and the IoT could bring about a boom in smart tech, and this effect could trickle into growth for the economy and investor portfolios.
The 5G network is the perfect backbone for the IoT—supporting increasing device numbers, facilitating growing data transfers, and improving response time among connected devices.
According to McKinsey, 5G will likely speed up the mainstream adoption of the IoT across multiple industries:
1. Transport
5G enables self-driving cars to make “split second” decisions, making them safer. These cars can also connect to buildings, street lights, other cars, and even pedestrians in smart cities—responding rapidly to any issues and improving traffic flow.
These two use cases are estimated to bring a $170-$280 billion global GDP boost to the mobility sector by 2030.
2. Manufacturing
5G could usher in high-tech industry, using AR/VR to boost productivity and precision. Analytics and advanced robotics in smart factories can streamline manufacturing processes, leading to efficiency gains and cost savings. Altogether, the impact could be a $400-$650 billion GDP boost to the industry by 2030.
3. Healthcare
While robotic surgeries are not new, 5G could allow these procedures to occur remotely.
Wearables and other smart medical devices provide real-time updates on patients, and make accurate diagnoses. These two applications will contribute an additional $250-$450 billion in GDP to the healthcare space by 2030.
A New Wireless Era
5G is only scratching the surface of its full potential, though a few caveats remain before it can scale successfully. A whole new lineup of infrastructure will be needed to support this latest wireless generation, including enabled devices, network density and access, and getting telecoms operators and carriers on board.
The complete uptake of 5G will take a few years to realize. But as the technological shift continues to unfold, investors can take advantage of the wave of opportunities it presents.
5G is more than an upgrade—it’s a crucial transformation of major segments of the economy.
Technology
All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
Intel, TSMC, and more have received billions in subsidies from the U.S. CHIPS Act in 2024.

All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This visualization shows which companies are receiving grants from the U.S. CHIPS Act, as of April 25, 2024. The CHIPS Act is a federal statute signed into law by President Joe Biden that authorizes $280 billion in new funding to boost domestic research and manufacturing of semiconductors.
The grant amounts visualized in this graphic are intended to accelerate the production of semiconductor fabrication plants (fabs) across the United States.
Data and Company Highlights
The figures we used to create this graphic were collected from a variety of public news sources. The Semiconductor Industry Association (SIA) also maintains a tracker for CHIPS Act recipients, though at the time of writing it does not have the latest details for Micron.
| Company | Federal Grant Amount | Anticipated Investment From Company |
|---|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 Intel | $8,500,000,000 | $100,000,000,000 |
| 🇹🇼 TSMC | $6,600,000,000 | $65,000,000,000 |
| 🇰🇷 Samsung | $6,400,000,000 | $45,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Micron | $6,100,000,000 | $50,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 GlobalFoundries | $1,500,000,000 | $12,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Microchip | $162,000,000 | N/A |
| 🇬🇧 BAE Systems | $35,000,000 | N/A |
BAE Systems was not included in the graphic due to size limitations
Intel’s Massive Plans
Intel is receiving the largest share of the pie, with $8.5 billion in grants (plus an additional $11 billion in government loans). This grant accounts for 22% of the CHIPS Act’s total subsidies for chip production.
From Intel’s side, the company is expected to invest $100 billion to construct new fabs in Arizona and Ohio, while modernizing and/or expanding existing fabs in Oregon and New Mexico. Intel could also claim another $25 billion in credits through the U.S. Treasury Department’s Investment Tax Credit.
TSMC Expands its U.S. Presence
TSMC, the world’s largest semiconductor foundry company, is receiving a hefty $6.6 billion to construct a new chip plant with three fabs in Arizona. The Taiwanese chipmaker is expected to invest $65 billion into the project.
The plant’s first fab will be up and running in the first half of 2025, leveraging 4 nm (nanometer) technology. According to TrendForce, the other fabs will produce chips on more advanced 3 nm and 2 nm processes.
The Latest Grant Goes to Micron
Micron, the only U.S.-based manufacturer of memory chips, is set to receive $6.1 billion in grants to support its plans of investing $50 billion through 2030. This investment will be used to construct new fabs in Idaho and New York.
-

 Energy1 week ago
Energy1 week agoThe World’s Biggest Nuclear Energy Producers
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 United States2 weeks ago
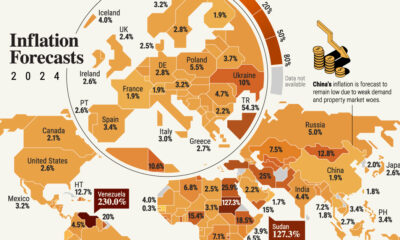
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024