Misc
50 Cognitive Biases in the Modern World

50 Cognitive Biases in the Modern World
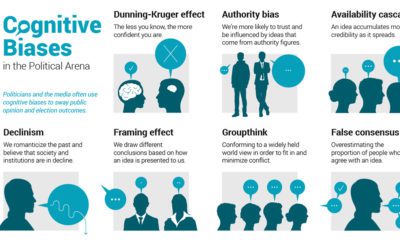
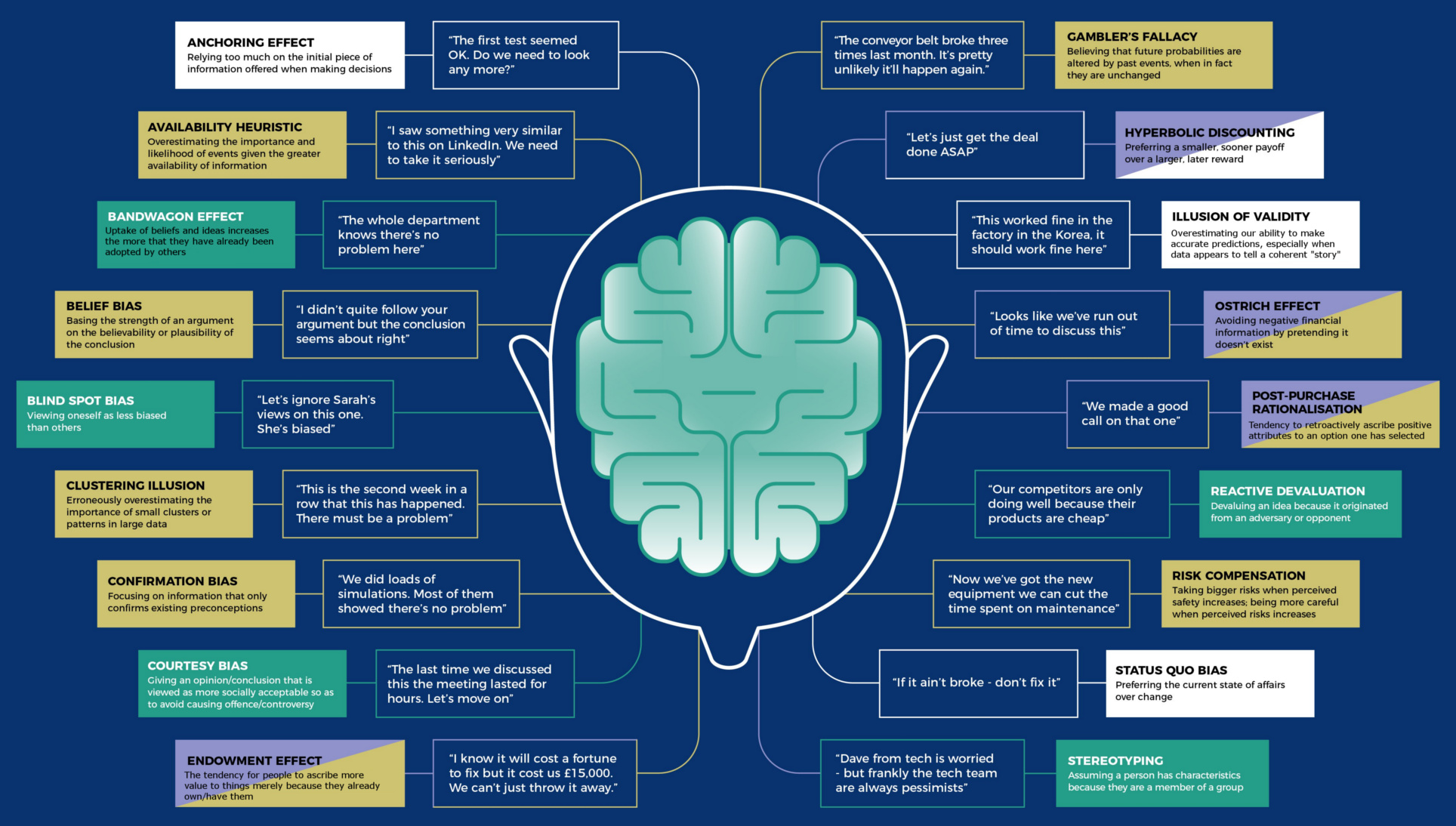
Cognitive biases are widely accepted as something that makes us human.
Every day, systematic errors in our thought process impact the way we live and work. But in a world where everything we do is changing rapidly—from the way we store information to the way we watch TV—what really classifies as rational thinking?
It’s a question with no right or wrong answer, but to help us decide for ourselves, today’s infographic from TitleMax lists 50 cognitive biases that we may want to become privy to.
In the name of self-awareness, here’s a closer look at three recently discovered biases that we are most prone to exhibiting in the modern world.
Automation Bias
AI-infused applications are becoming incredibly good at “personalizing” our content, but will there come a time when we let algorithms make all of our decisions?
Automation bias refers to the tendency to favor the suggestions of automated systems.
Take Netflix, for example. Everything we see on the platform is the result of algorithms—even the preview images that are generated. Then, to harness the power of data and machine learning, Netflix categorizes its content into tens of thousands of micro-genres. Pairing these genre tags with a viewer’s history allows them to assign several of over 2,000 “taste profiles” to each user.
And while there’s nothing wrong with allowing Netflix to guide what we watch, there’s an enormous sea of content standing by. Estimates from 2015 claimed it would take nearly four years to watch all of Netflix’s content. Thousands more hours of content have since been added.
If we want to counter this cognitive bias, finding a new favorite series on platforms like Netflix may require some good old-fashioned human curiosity.
The Google Effect
Also known as “digital amnesia”, the aptly named Google Effect describes our tendency to forget information that can be easily accessed online.
First described in 2011 by Betsy Sparrow (Columbia University) and her colleagues, their paper described the results of several memory experiments involving technology.
In one experiment, participants typed trivia statements into a computer and were later asked to recall them. Half believed the statements were saved, and half believed the statements were erased. The results were significant: participants who assumed they could look up their statements did not make much effort to remember them.
Because search engines are continually available to us, we may often be in a state of not feeling we need to encode the information internally. When we need it, we will look it up.
– Sparrow B, et al. Science 333, 777 (2011)
Our modern brains appear to be re-prioritizing the information we hold onto. Notably, the study doesn’t suggest we’re becoming less intelligent—our ability to learn offline remains the same.
The IKEA Effect
Identified in 2011 by Michael Norton (Harvard Business School) and his colleagues, this cognitive bias refers to our tendency to attach a higher value to things we help create.
Combining the Ikea Effect with other related traits, such as our willingness to pay a premium for customization, is a strategy employed by companies seeking to increase the intrinsic value that we attach to their products.
For instance, American retailer Build-A-Bear Workshop is anchored around creating a highly interactive customer experience. With the help of staff, children (or adults) can assemble their stuffed animals from scratch, then add clothing and accessories at extra cost.
Nike also incorporates this bias into its offering. The footwear company offers a Nike By You line of customizable products, where customers pay a premium to design bespoke shoes with an extensive online configurator.
While there’s nothing necessarily wrong with our susceptibility to the Ikea Effect, understanding its significance may help us make more appropriate decisions as consumers.
What Can We Do?
As we navigate an increasingly complex world, it’s natural for us to unconsciously adopt new patterns of behavior.
Becoming aware of our cognitive biases, and their implications, can help us stay on the right course.
Demographics
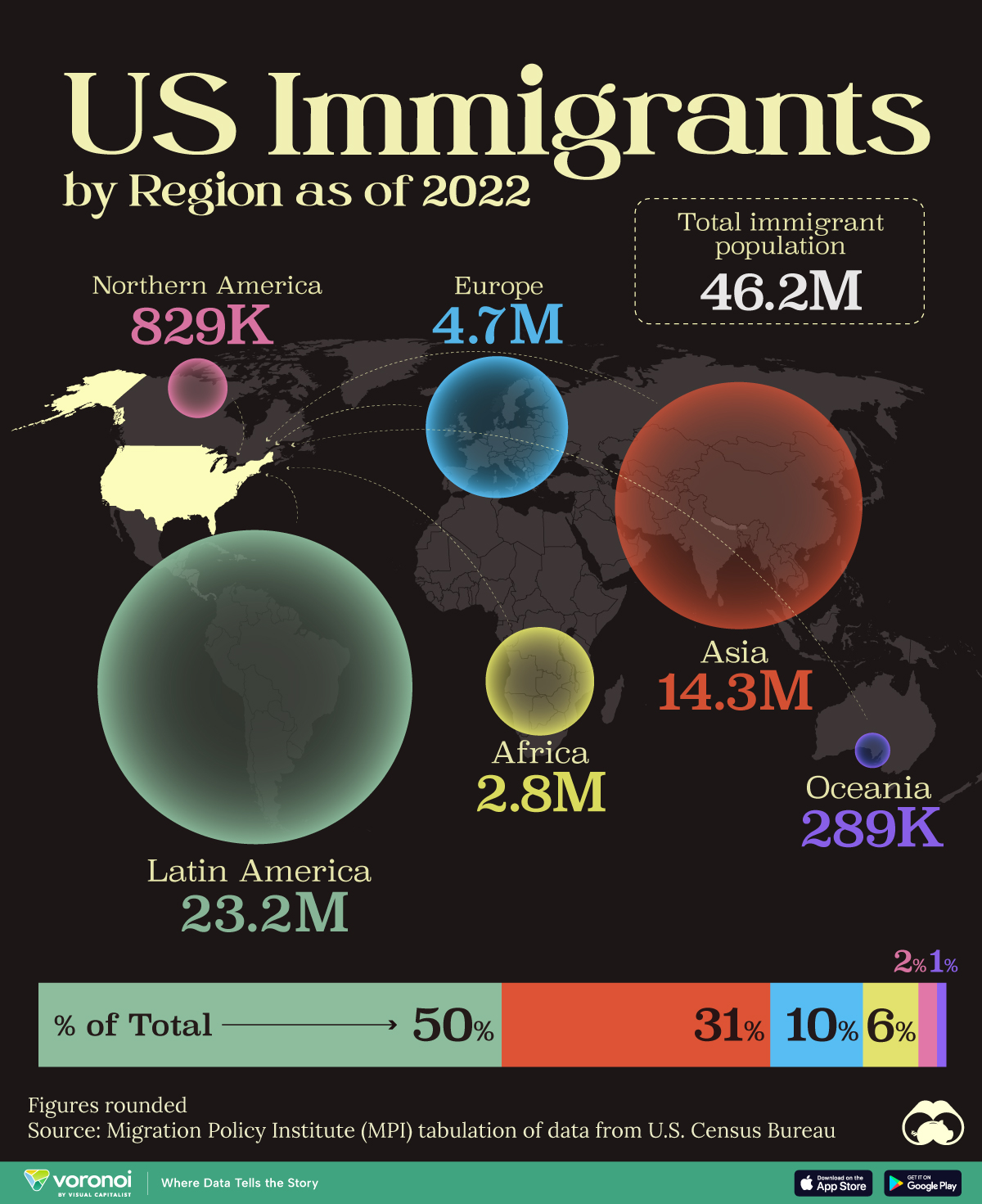
Mapped: U.S. Immigrants by Region
This map shows which regions U.S. immigrants came from, highlighting Asia and Latin America as the biggest sources.
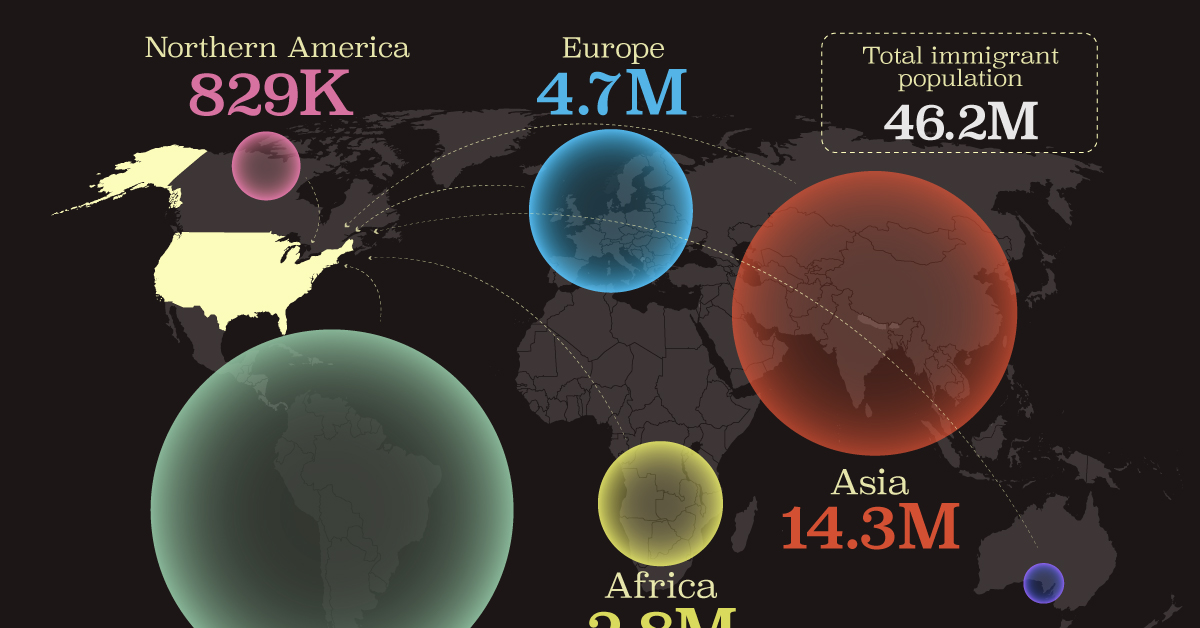
Breaking Down America’s Immigrant Population
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
The United States is home to more immigrants than any other nation, surpassing the combined totals of the next four countries: Germany, Saudi Arabia, Russia, and the United Kingdom.
To add context to this impressive fact, we’ve illustrated the regions from which U.S. immigrants originated. “Immigrants” in this context refers to individuals who are residing in the United States but were not U.S. citizens at birth.
These statistics were sourced from the Migration Policy Institute, which analyzed data from the U.S. Census Bureau’s 2022 American Community Survey (ACS).
U.S. Immigrants by Region
From this graphic, we can see that Asia and Latin America emerge as the primary sources of immigration, collectively accounting for 81% of America’s 46.2 million immigrants.
| Region | # of Immigrants | % of Total |
|---|---|---|
| Europe | 4,728,948 | 10 |
| Asia | 14,349,080 | 31 |
| Africa | 2,752,965 | 6 |
| Oceania | 288,560 | 1 |
| Northern America | 828,702 | 2 |
| Latin America | 23,233,834 | 50 |
| Total | 46,182,089 | 100 |
Latin America alone contributes half of the immigrant population. Mexico stands out as the largest contributor to U.S. immigration, with 10.7 million immigrants, attributable to its geographical proximity and historical ties.
Economic factors, including wage disparity and employment opportunities, drive many Mexicans to seek better prospects north of the border.
From Asia, the two largest country sources are China (2.2 million) and India (2.8 million).
Learn More About U.S. Immigration From Visual Capitalist
If you enjoyed this post, be sure to check out Why Do People Immigrate to the U.S.? This visualization shows the different reasons why immigrants chose to come to America in 2021.
-

 Healthcare4 days ago
Healthcare4 days agoWhat Causes Preventable Child Deaths?
-

 voronoi2 weeks ago
voronoi2 weeks agoBest Visualizations of April on the Voronoi App
-

 Wealth2 weeks ago
Wealth2 weeks agoCharted: Which Country Has the Most Billionaires in 2024?
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoThe Top Private Equity Firms by Country
-

 Jobs1 week ago
Jobs1 week agoThe Best U.S. Companies to Work for According to LinkedIn
-

 Economy1 week ago
Economy1 week agoRanked: The Top 20 Countries in Debt to China
-
 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoCharted: Trust in Government Institutions by G7 Countries
-

 Energy1 week ago
Energy1 week agoMapped: The Age of Energy Projects in Interconnection Queues, by State