Mining
The Looming Copper Supply Crunch

The Looming Copper Supply Crunch
This infographic is presented by Western Copper & Gold
Copper is among the three most used metals in the world, and high quantities of the red metal must be mined every year to meet global demand.
The market for copper is equal to approximately $120 billion each year, which rivals that of even iron ore, the most widely traded metal. This is because infrastructure, technology, and automobiles consume massive amounts of copper.
Behind silver, copper is the second best metal for conducting electricity. That’s why 75% of copper is used in electrical wires or for wiring in machinery. From power grids to motherboards, copper wire is indispensable to modern society.
Copper is also essential for green energy and a sustainable future. For example, each generation of car needs more copper wiring: a gasoline-powered car needs 55 lbs, while hybrids and electric vehicles need 110 lbs and 165 lbs respectively. Further, it is estimated that an average of 3.6 tonnes of copper is used for each MW of wind power.
The Copper Supply Problem
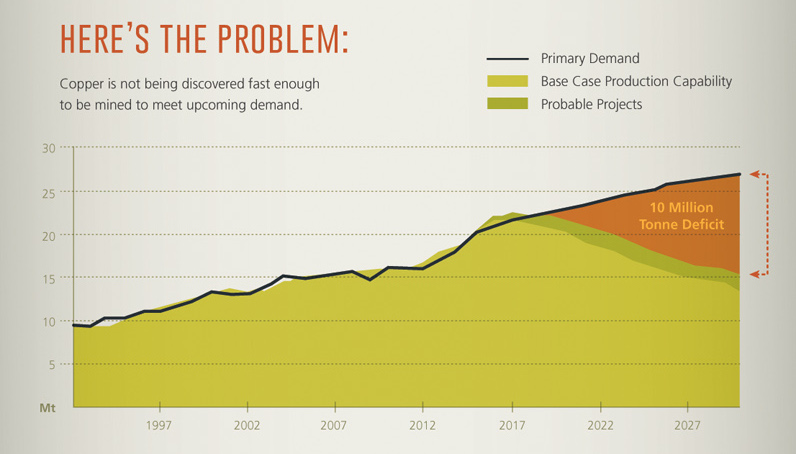
The problem is: copper is not being discovered fast enough to meet upcoming demand. A study by Wood Mackenzie found that there will be a 10 million tonne supply deficit by 2028. That’s equal to the annual production of the world’s biggest copper mine (Escondida) multiplied by a factor of ten.
There are several reasons for this.
First, it now takes longer to go from discovery to production than ever before in the mining industry. Geological, environmental, and political challenges have brought the average lead time to around 20 years for new mines.
Beyond all of the challenges above, the economics also have to line up. Thomson Reuters GFMS estimates that for new copper supply to be incentivized to come online, the copper price must be $3.50 per pound.
Copper mining is all about grade or scale. The majority of global output comes from mega mines that have massive economies of scale to reduce costs. However, it has been a long-running trend that the grades for these established mines are dropping.
A good example of this is Escondida, the world’s largest copper mine which is located in Chile. It produced 6% of global copper output in 2014, but the mine is facing a similar problem to that of other large copper projects: grades are dropping. In 2007, the copper grade was 1.72%, but it is predicted to drop to half of that in upcoming years. In fact, BHP Billiton is expecting a year-over-year decline of 24% between 2015 and 2016.
Codelco is the world’s largest copper miner overall, and has recently announced a $25 billion investment plan to expand aging mines. It will spend $5 billion each year, but it expects no significant gain in production for its efforts.
The Coming Supply Gap
Add these factors together, and stocks of copper are at their lowest levels since 2008. Further, 4% of the world’s copper mining capacity falls off the table each year, which means that this must be replaced somehow.
With 10 Escondidas needed to fill a 10 million tonne supply deficit by 2028, metals investors need to stay vigilant as changes in the market will be coming.
Lithium
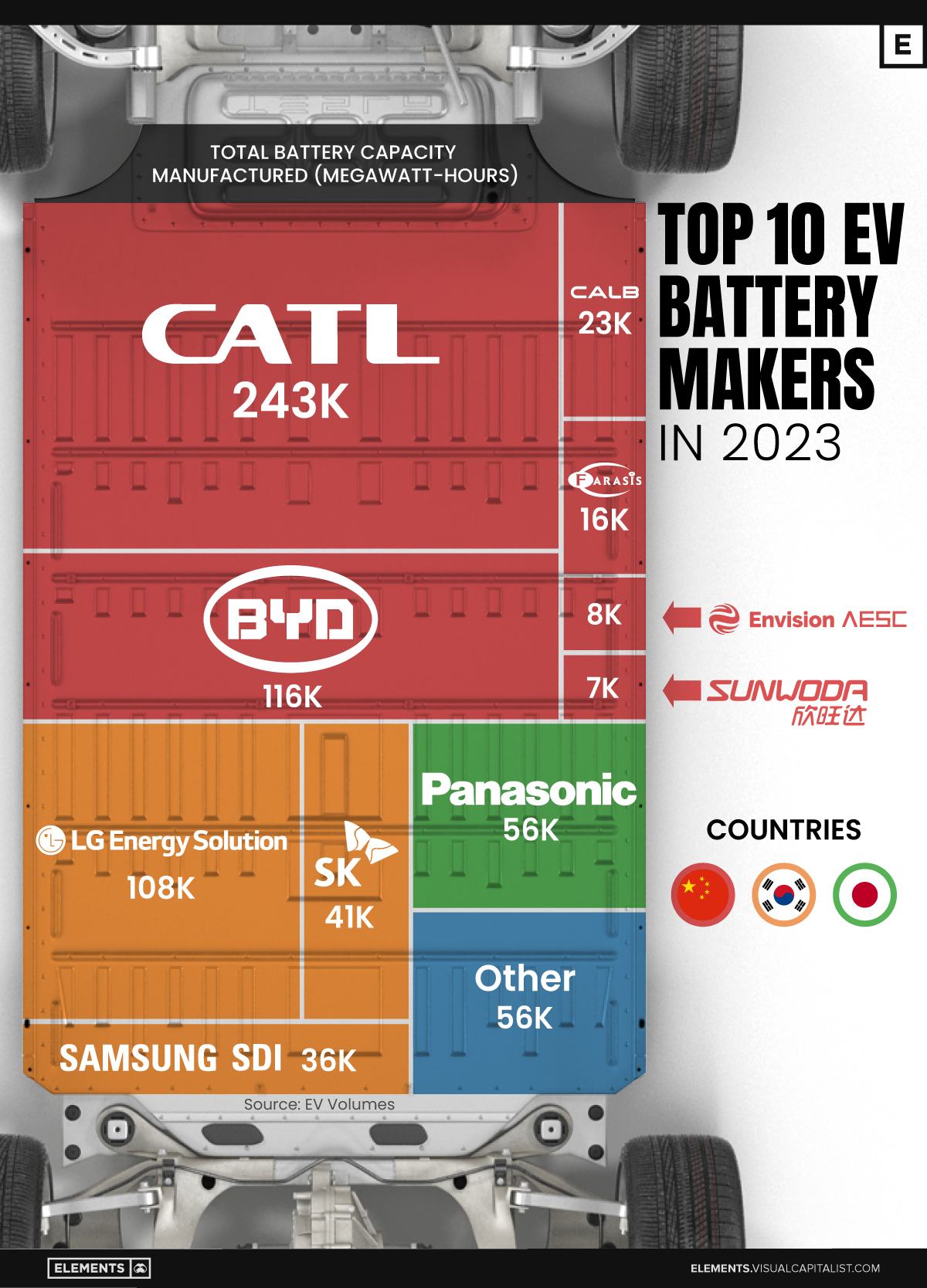
Ranked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2023
Asia dominates this ranking of the world’s largest EV battery manufacturers in 2023.
The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2023
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Despite efforts from the U.S. and EU to secure local domestic supply, all major EV battery manufacturers remain based in Asia.
In this graphic we rank the top 10 EV battery manufacturers by total battery deployment (measured in megawatt-hours) in 2023. The data is from EV Volumes.
Chinese Dominance
Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited (CATL) has swiftly risen in less than a decade to claim the title of the largest global battery group.
The Chinese company now has a 34% share of the market and supplies batteries to a range of made-in-China vehicles, including the Tesla Model Y, SAIC’s MG4/Mulan, and various Li Auto models.
| Company | Country | 2023 Production (megawatt-hour) | Share of Total Production |
|---|---|---|---|
| CATL | 🇨🇳 China | 242,700 | 34% |
| BYD | 🇨🇳 China | 115,917 | 16% |
| LG Energy Solution | 🇰🇷 Korea | 108,487 | 15% |
| Panasonic | 🇯🇵 Japan | 56,560 | 8% |
| SK On | 🇰🇷 Korea | 40,711 | 6% |
| Samsung SDI | 🇰🇷 Korea | 35,703 | 5% |
| CALB | 🇨🇳 China | 23,493 | 3% |
| Farasis Energy | 🇨🇳 China | 16,527 | 2% |
| Envision AESC | 🇨🇳 China | 8,342 | 1% |
| Sunwoda | 🇨🇳 China | 6,979 | 1% |
| Other | - | 56,040 | 8% |
In 2023, BYD surpassed LG Energy Solution to claim second place. This was driven by demand from its own models and growth in third-party deals, including providing batteries for the made-in-Germany Tesla Model Y, Toyota bZ3, Changan UNI-V, Venucia V-Online, as well as several Haval and FAW models.
The top three battery makers (CATL, BYD, LG) collectively account for two-thirds (66%) of total battery deployment.
Once a leader in the EV battery business, Panasonic now holds the fourth position with an 8% market share, down from 9% last year. With its main client, Tesla, now sourcing batteries from multiple suppliers, the Japanese battery maker seems to be losing its competitive edge in the industry.
Overall, the global EV battery market size is projected to grow from $49 billion in 2022 to $98 billion by 2029, according to Fortune Business Insights.
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoHow Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001