Markets
The Average Investor Lost 3.1% in 2015
Contrarian investors pride themselves in running a different direction than the majority of the pack. They find opportunities in asset classes that are universally hated by the masses, and try to carve out their own convictions by downplaying popular sentiment.
However, at the end of the day, contrarians will concede that it is nice to know how the investing masses are doing.
That’s why the data provided by Openfolio is so beautiful – it combines investing with the openness and connecting nature of social networks. Through this process, the collective portfolios of 50,000 investors can be analyzed and broken down by specific variables to bring out unique insight.
Here’s a few insights from 2015 that come from their data:
1. The average investor in the U.S. was down 3.09%.
Here’s the breakdown of performance by region:
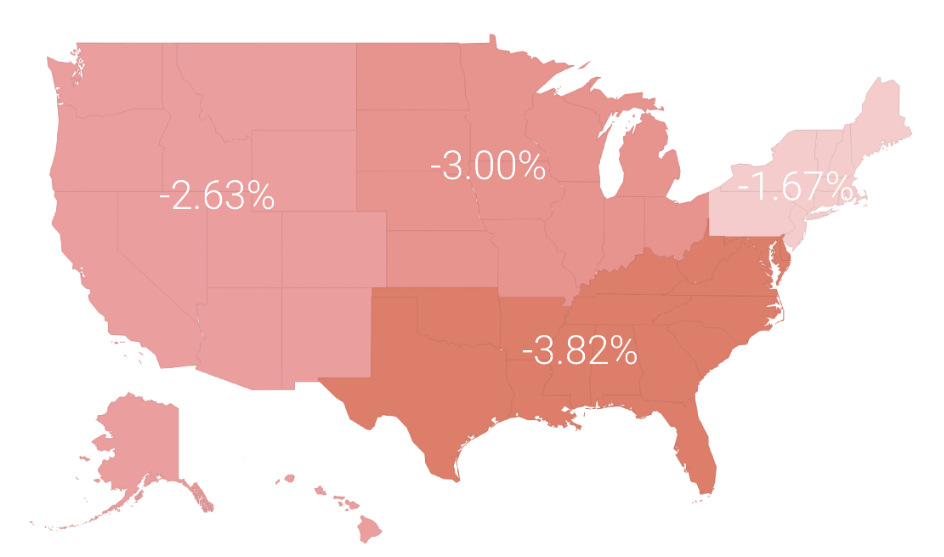
About one-third of total investors made money on the year, while two-thirds lost money on the year. Regionally, the Southeast did the poorest over 2015, mainly because of an overexposure to energy in their portfolios.
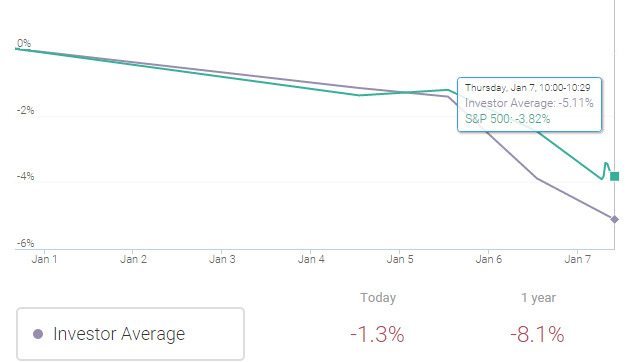
So far, the average investor is already down 5.1% in 2016 YTD:
2. Older investors did better in 2015.
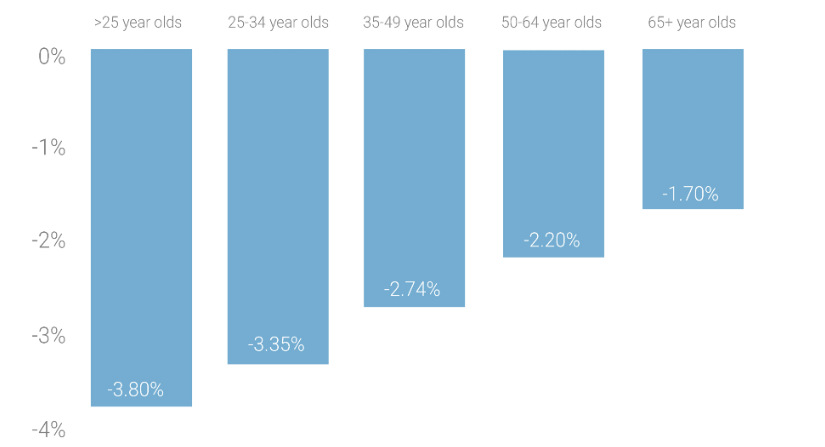
In a risky and volatile year, it is no surprise to see that more conservative and experienced investors did better. Openfolio’s insight here is that younger investors tend to concentrate more on individual stocks, and lack portfolio diversification.
3. Teachers had the best-performing portfolios.
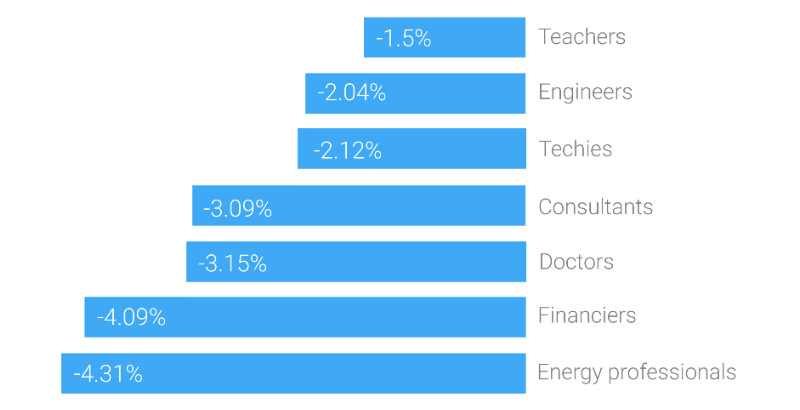
Energy professionals particularly suffered, likely because of overexposure to the oil patch in their investment portfolios.
Markets
Mapped: The Most Valuable Company in Each Southeast Asian Country
Six businesses in the broader financial space are present on this list of the largest companies, by market cap, in each Southeast Asian country.

The Most Valuable Company in Each Southeast Asian Country
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Southeast Asia has been emerging as an economic powerhouse in the past decade. However, there are very noticeable disparities in the sizes of the largest publicly-traded corporations in countries within the region.
In this visualization, we map the most valuable company in each Southeast Asian country, by their market capitalization in current U.S. dollars as of April 18th, 2024.
Data for this visualization and article is sourced from Companiesmarketcap.com, and the Laos and Yangon stock exchanges.
Southeast Asia’s Biggest Companies are Banks
The most valuable companies in Indonesia and Singapore, Bank Central Asia and DBS Group, are each worth more than $60 billion, and both are banks.
In the quartet of Malaysia, Thailand, Vietnam, and the Philippines, the largest companies by market cap are all worth around $20 billion. Out of the four, two are banks.
| Country | Company | Market Cap |
|---|---|---|
| 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 🏦 Bank Central Asia | $73B |
| 🇸🇬 Singapore | 🏦 DBS Group | $69B |
| 🇲🇾 Malaysia | 🏦 Maybank | $28B |
| 🇹🇭 Thailand | ⛽ PTT PCL | $27B |
| 🇻🇳 Vietnam | 🏦 Vietcombank | $20B |
| 🇵🇭 Philippines | 📈 SM Investments Corporation | $20B |
| 🇰🇭 Cambodia | 🚢 Sihanoukville Autonomous Port | $1B |
| 🇱🇦 Laos | 🏭 LALCO | $312M |
| 🇲🇲 Myanmar | 📈 First Myanmar Investment | $139M |
Note: Figures are rounded, and current as of April 18th, 2024.
Cambodia stands by itself, with its most valuable publicly listed company, Sihanoukville Autonomous Port, worth $1 billion.
Meanwhile, LALCO in Laos is a credit leasing company worth $312 million and Myanmar’s biggest company, First Myanmar Investment, is worth $139 million.
Finally, Brunei and Timor-Leste do not have public stock exchanges, but for different reasons.
Most of Brunei’s economy relies on the state-owned oil sector, which also helps make its sultan the world’s second-richest monarch. However, in Timor-Leste, a small population combined with limited access to credit and liquidity has led to limited opportunities for the creation of publicly-listed companies or an exchange.
-

 Economy7 days ago
Economy7 days agoRanked: The Top 20 Countries in Debt to China
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Countries That Have Become Sadder Since 2010
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoCharted: Who Has Savings in This Economy?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoVisualizing AI Patents by Country
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoEconomic Growth Forecasts for G7 and BRICS Countries in 2024
-

 Wealth2 weeks ago
Wealth2 weeks agoCharted: Which City Has the Most Billionaires in 2024?
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoAll of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
-

 Green1 week ago
Green1 week agoThe Carbon Footprint of Major Travel Methods