Technology
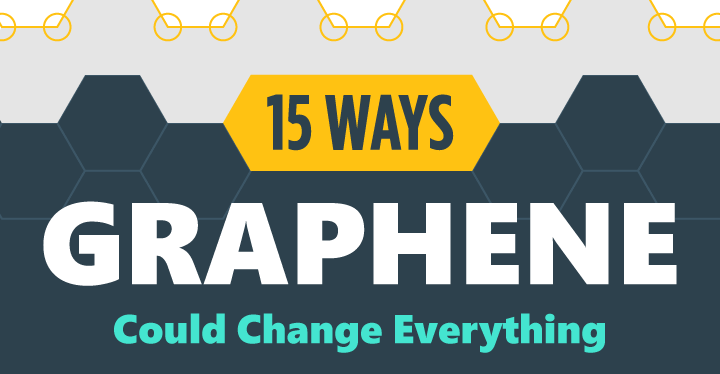
Graphene: The Game-Changing Material of the Future
Technology is only as good as the materials it is made from.
Much of the modern information era would not be possible without silicon and Moore’s Law, and electric cars would be much less viable without recent advances in the material science behind lithium-ion batteries.
That’s why graphene, a two-dimensional supermaterial made from carbon, is so exciting. It’s harder than diamonds, 300x stronger than steel, flexible, transparent, and a better conductor than copper (by about 1,000x).
If it lives up to its potential, graphene could revolutionize everything from computers to energy storage.
Graphene: Is It the Next Wonder Material?
The following infographic comes to us from 911Metallurgist, and it breaks down the incredible properties and potential applications of graphene.
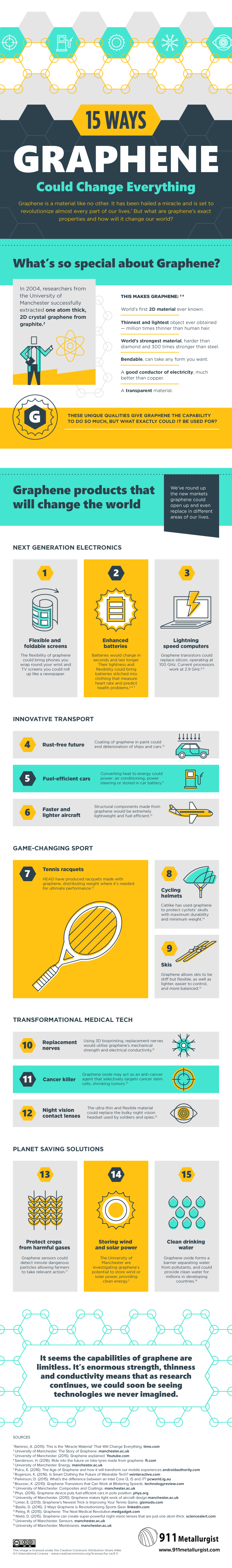
While the properties and applications of graphene are extremely enticing, there has one big traditional challenge with graphene: the cost of getting it.
The Ever-Changing Graphene Price
As you can imagine, synthesizing a material that is one atom thick is a process that has some major limitations. Since a sheet of graphene 1 mm thick (1/32 of an inch) requires three million layers of atoms, graphene has been quite cost-prohibitive to produce in large amounts.
Back in 2013, Nature reported that one micrometer-sized flake of graphene costed more than $1,000, which made graphene one of the most expensive materials on Earth. However, there has been quite some progress in this field since then, as scientists search for the “Holy Grail” in scaling graphene production processes.
By the end of 2015, Deloitte estimated that the market price per gram was close to $100. And today, graphene can now be ordered straight from a supplier like Graphenea, where multiple products are offered online ranging from graphene oxide (water dispersion) to monolayer graphene on silicon wafers.
One producer, NanoXplore, even estimates that graphene is now down to a cost of $0.10 per gram for good quality graphene, though this excludes graphene created through a CVD process (recognized as the highest level of quality available for bulk graphene).
The following graphic from Nature (2014) shows some methods for graphene production – though it should be noted that this is a quickly-changing discipline.
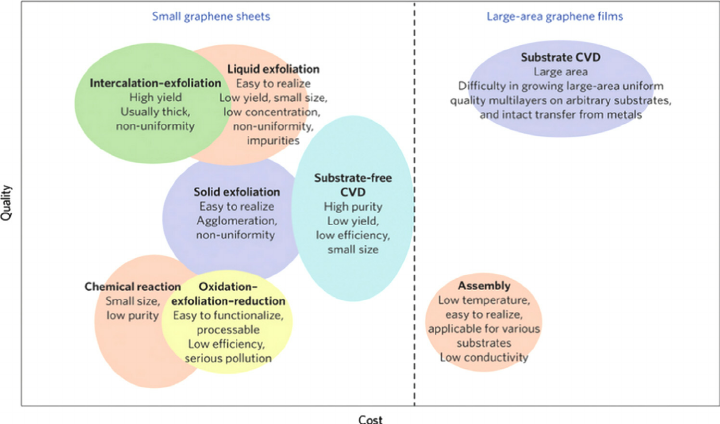
As the price of graphene trends down at an impressive rate, its applications will continue to grow. However, for graphene to be a true game-changer, it will have to be integrated into the supply chains of manufacturers, which will still take multiple years to accomplish.
Once graphene has “real world” applications, we’ll be able to see what can be made possible on a grander scale.
Technology
All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
Intel, TSMC, and more have received billions in subsidies from the U.S. CHIPS Act in 2024.

All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This visualization shows which companies are receiving grants from the U.S. CHIPS Act, as of April 25, 2024. The CHIPS Act is a federal statute signed into law by President Joe Biden that authorizes $280 billion in new funding to boost domestic research and manufacturing of semiconductors.
The grant amounts visualized in this graphic are intended to accelerate the production of semiconductor fabrication plants (fabs) across the United States.
Data and Company Highlights
The figures we used to create this graphic were collected from a variety of public news sources. The Semiconductor Industry Association (SIA) also maintains a tracker for CHIPS Act recipients, though at the time of writing it does not have the latest details for Micron.
| Company | Federal Grant Amount | Anticipated Investment From Company |
|---|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 Intel | $8,500,000,000 | $100,000,000,000 |
| 🇹🇼 TSMC | $6,600,000,000 | $65,000,000,000 |
| 🇰🇷 Samsung | $6,400,000,000 | $45,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Micron | $6,100,000,000 | $50,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 GlobalFoundries | $1,500,000,000 | $12,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Microchip | $162,000,000 | N/A |
| 🇬🇧 BAE Systems | $35,000,000 | N/A |
BAE Systems was not included in the graphic due to size limitations
Intel’s Massive Plans
Intel is receiving the largest share of the pie, with $8.5 billion in grants (plus an additional $11 billion in government loans). This grant accounts for 22% of the CHIPS Act’s total subsidies for chip production.
From Intel’s side, the company is expected to invest $100 billion to construct new fabs in Arizona and Ohio, while modernizing and/or expanding existing fabs in Oregon and New Mexico. Intel could also claim another $25 billion in credits through the U.S. Treasury Department’s Investment Tax Credit.
TSMC Expands its U.S. Presence
TSMC, the world’s largest semiconductor foundry company, is receiving a hefty $6.6 billion to construct a new chip plant with three fabs in Arizona. The Taiwanese chipmaker is expected to invest $65 billion into the project.
The plant’s first fab will be up and running in the first half of 2025, leveraging 4 nm (nanometer) technology. According to TrendForce, the other fabs will produce chips on more advanced 3 nm and 2 nm processes.
The Latest Grant Goes to Micron
Micron, the only U.S.-based manufacturer of memory chips, is set to receive $6.1 billion in grants to support its plans of investing $50 billion through 2030. This investment will be used to construct new fabs in Idaho and New York.
-

 Debt1 week ago
Debt1 week agoHow Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees