Technology
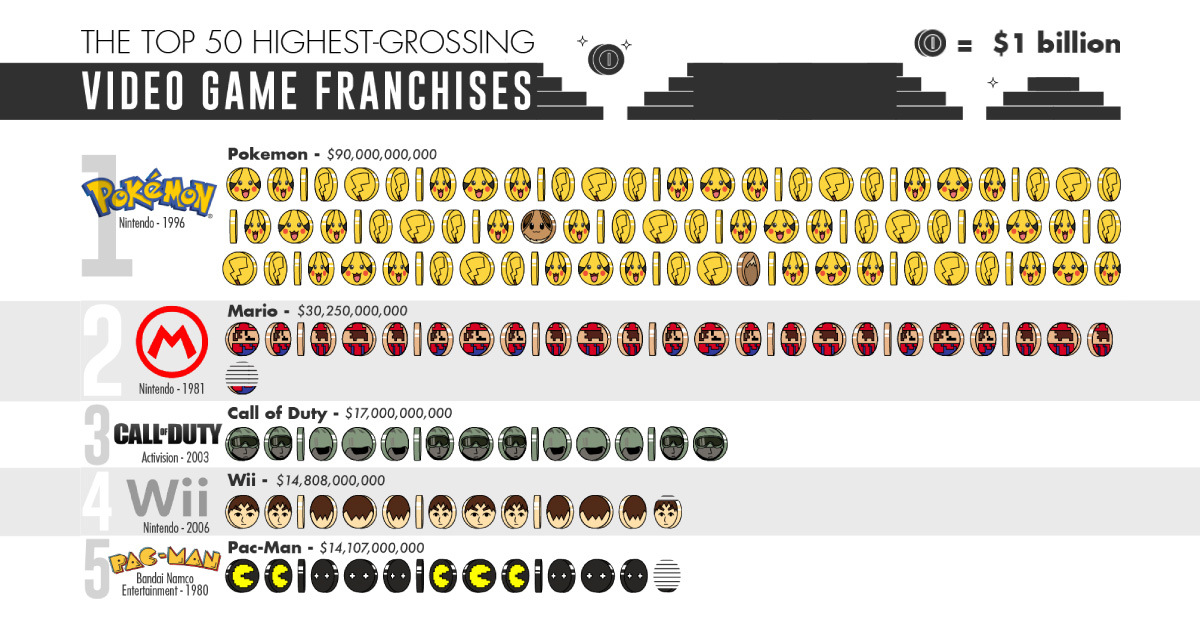
The 50 Biggest Video Game Franchises by Total Revenue

The 50 Biggest Video Game Franchises by Total Revenue
When the world’s first video game, Tennis for Two, was revealed at a science fair in 1958, people were fascinated—there was clearly something special.
Since these humble beginnings, video games have rode waves of technological advancements to burgeon into a $100+ billion industry. To visualize this success, today’s infographic from TitleMax lists the top 50 highest-grossing video games franchises.
While this feat is impressive on its own, the way many of these franchises generate their revenue may come as a shock.
How Do Video Games Generate Billions?
Video games first saw large-scale commercial success in the 1980s, in what some describe as the “golden age of arcade games”. As arcades popped up across America, renowned classics like Pac-man and Space Invaders raked in large sums of money, one coin at a time.
Today, there are two revenue models generally followed by video game publishers—the traditional pay-to-play (P2P) model, and the newer free-to-play (F2P) model.
For much of the industry’s modern history, P2P models have been the default option. A developer incurs costs to produce its games, so it sells them to consumers to recover costs and make a profit.
Under a F2P model, however, the developer essentially distributes its games for free. Players don’t have to pay anything if they don’t want to, and the developer runs the risk that it may never recoup its costs.
So why would a developer ever choose a F2P model? Let’s look at industry data from 2019:
| Platform | Free-to-play (F2P) Revenue | Pay-to-play (P2P) Revenue |
|---|---|---|
| Mobile | $64.4B | -- |
| PC | $21.1B | $5.2B |
| Console | $1.6B | $13.8B |
| Total | $87.1B | $19.0B |
Source: SuperData
Those aren’t typos. F2P games accounted for a whopping 82% of industry revenue in 2019. What’s more, is that this gap continues to grow: since the previous year, F2P revenue grew 6%, while P2P revenue fell by 5%.
The Power of Discretionary Spending
There’s a number of F2P franchises listed in today’s graphic which have grossed well over a billion dollars in total revenue.
| Rank | Franchise | Developer | Platform | Gross Revenue |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #15 | League of Legends | Riot Games¹ | PC | $8.4B |
| #21 | Arena of Valor | Tencent | Mobile | $6.4B |
| #23 | Clash of Clans | Supercell² | Mobile | $6.0B |
| #27 | Candy Crush Saga | King³ | Mobile | $4.9B |
| #40 | Maple Story | Nexon | PC | $3.0B |
| #46 | Fortnite | Epic Games⁴ | Console, Mobile, PC | $2.5B |
| #47 | Clash Royale | Supercell² | Mobile | $2.0B |
¹wholly-owned subsidiary of Tencent, ²majority-owned subsidiary of Tencent, ³wholly-owned subsidiary of Activision Blizzard, ⁴Tencent owns a 40% stake.
Because these types of games are often published for PC or mobile phone (most people have at least one of these), their accessibility becomes a key advantage. This is especially true in China, where video game consoles like Xbox have been banned in the past.
Yet, simply amassing a large player base isn’t enough. With no money being paid upfront, developers must create compelling incentives for players to willingly part with their cash.
League of Legends
League of Legends, one of the world’s most popular video games, is widely considered a successful pioneer in this regard.
When developer Riot Games chose a F2P model for its game, it took a gamble. The model was largely unproven for titles of its genre, and it’s main source of revenue was set to be the sale of purely cosmetic items called “character skins”.
Nobody would have tried Legends if we put a price point in front of it because the game is tough to sell
—Marc Merrill, Co-founder of Riot Games
Part of the game’s incentive to spend comes from its longevity—League of Legends has just entered its 11th year. Rather than release a new title, the developer makes continuous improvements to the existing game, with each iteration dubbed as a new “season”.
If a traditional P2P game represents a movie, League of Legends could then be considered a long-running TV show. For example, while there’s been one League of Legends since 2009, there’s been 11 Call of Duty titles over that same time frame.
Joining the Party
Some of the world’s most successful video game franchises, which have historically published games under the P2P model, are also expanding into free games with great success.
For Pokémon (#1 in gross revenue), product diversification is nothing new. While the franchise manages a universe of offerings from physical merchandise to movies, its free mobile augmented reality (AR) game, Pokémon Go, may be one of its most successful endeavors.
The game, which leads players out into the real world to catch virtual monsters, was a massive sensation when it launched in 2016. In fact, it was so popular (and distracting) it’s been estimated to have contributed to more than 100,000 car accidents.
Four years since its release, Pokémon Go is a shining example of what the F2P model can achieve—the game has racked up over 1 billion downloads and generated an incredible $3 billion in revenues.
| Year | Gross Revenue | % Change |
|---|---|---|
| 2016 | $832M | - |
| 2017 | $589M | -29% |
| 2018 | $816M | +38% |
| 2019 | $894M | +10% |
| Total | $3,131M | - |
Source: Sensor Tower Store Intelligence
Part of Pokémon Go’s incentive to spend comes from its incredibly unique social experience—it
turns real world landmarks into hubs where players can gather. By simply leveraging the capabilities of existing smartphones, it’s also extremely accessible.
Is Free the New Norm?
As more and more franchises successfully expand into free games, it’s clear that the F2P model will be the primary driver of future growth. The relatively higher accessibility of F2P games is also crucial to tap into the quickly growing esports industry.
However, traditional P2P games, which are now being called “premium games”, still have some merit to them. These games are often associated with a higher level of quality which people are happy to pay for.
Yet, as the legitimacy and success of the F2P model continues to develop, this quality gap could also shrink in the future.
Editor’s note: The revenue figures in today’s infographic include merchandise and other related products.
Technology
All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
Intel, TSMC, and more have received billions in subsidies from the U.S. CHIPS Act in 2024.

All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This visualization shows which companies are receiving grants from the U.S. CHIPS Act, as of April 25, 2024. The CHIPS Act is a federal statute signed into law by President Joe Biden that authorizes $280 billion in new funding to boost domestic research and manufacturing of semiconductors.
The grant amounts visualized in this graphic are intended to accelerate the production of semiconductor fabrication plants (fabs) across the United States.
Data and Company Highlights
The figures we used to create this graphic were collected from a variety of public news sources. The Semiconductor Industry Association (SIA) also maintains a tracker for CHIPS Act recipients, though at the time of writing it does not have the latest details for Micron.
| Company | Federal Grant Amount | Anticipated Investment From Company |
|---|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 Intel | $8,500,000,000 | $100,000,000,000 |
| 🇹🇼 TSMC | $6,600,000,000 | $65,000,000,000 |
| 🇰🇷 Samsung | $6,400,000,000 | $45,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Micron | $6,100,000,000 | $50,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 GlobalFoundries | $1,500,000,000 | $12,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Microchip | $162,000,000 | N/A |
| 🇬🇧 BAE Systems | $35,000,000 | N/A |
BAE Systems was not included in the graphic due to size limitations
Intel’s Massive Plans
Intel is receiving the largest share of the pie, with $8.5 billion in grants (plus an additional $11 billion in government loans). This grant accounts for 22% of the CHIPS Act’s total subsidies for chip production.
From Intel’s side, the company is expected to invest $100 billion to construct new fabs in Arizona and Ohio, while modernizing and/or expanding existing fabs in Oregon and New Mexico. Intel could also claim another $25 billion in credits through the U.S. Treasury Department’s Investment Tax Credit.
TSMC Expands its U.S. Presence
TSMC, the world’s largest semiconductor foundry company, is receiving a hefty $6.6 billion to construct a new chip plant with three fabs in Arizona. The Taiwanese chipmaker is expected to invest $65 billion into the project.
The plant’s first fab will be up and running in the first half of 2025, leveraging 4 nm (nanometer) technology. According to TrendForce, the other fabs will produce chips on more advanced 3 nm and 2 nm processes.
The Latest Grant Goes to Micron
Micron, the only U.S.-based manufacturer of memory chips, is set to receive $6.1 billion in grants to support its plans of investing $50 billion through 2030. This investment will be used to construct new fabs in Idaho and New York.
-

 Energy1 week ago
Energy1 week agoThe World’s Biggest Nuclear Energy Producers
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024