Healthcare
Where COVID-19 is Rising and Falling Around the World
Where COVID-19 is Rising and Falling Around the World
It’s been just over two months since New York declared a state of emergency, and global stock markets were hammered as the fears of a full-blown crisis began to take hold.
Since then, we’ve seen detailed, daily coronavirus coverage in most of the major news outlets. With such a wealth of information available, it can be hard to keep track of the big picture of what’s happening around the world.
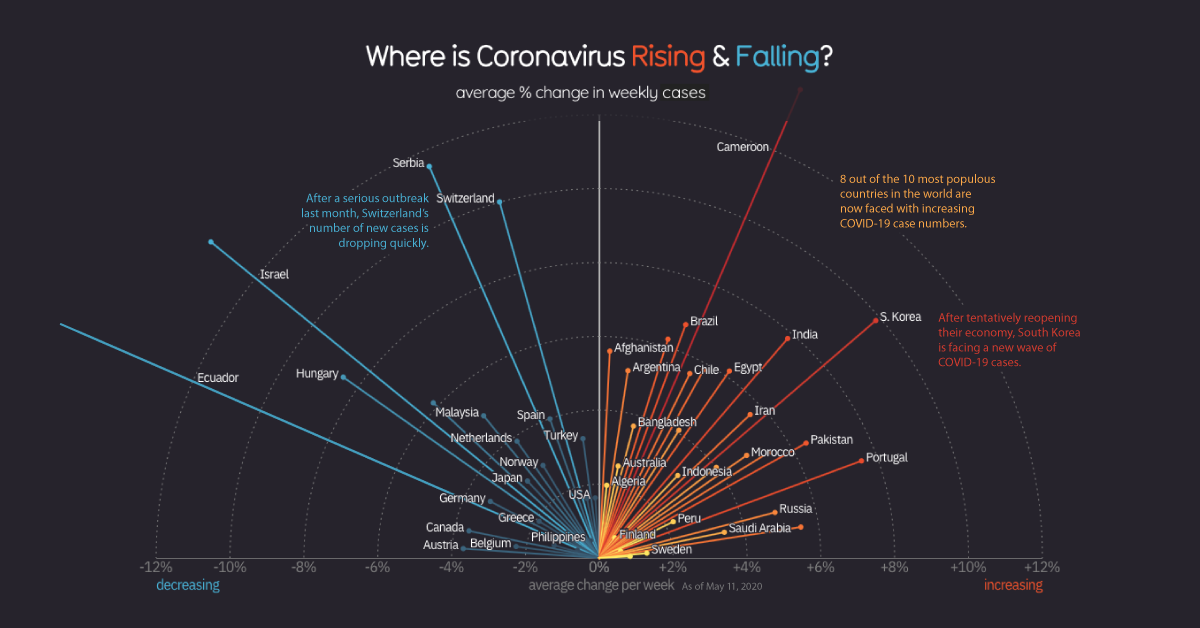
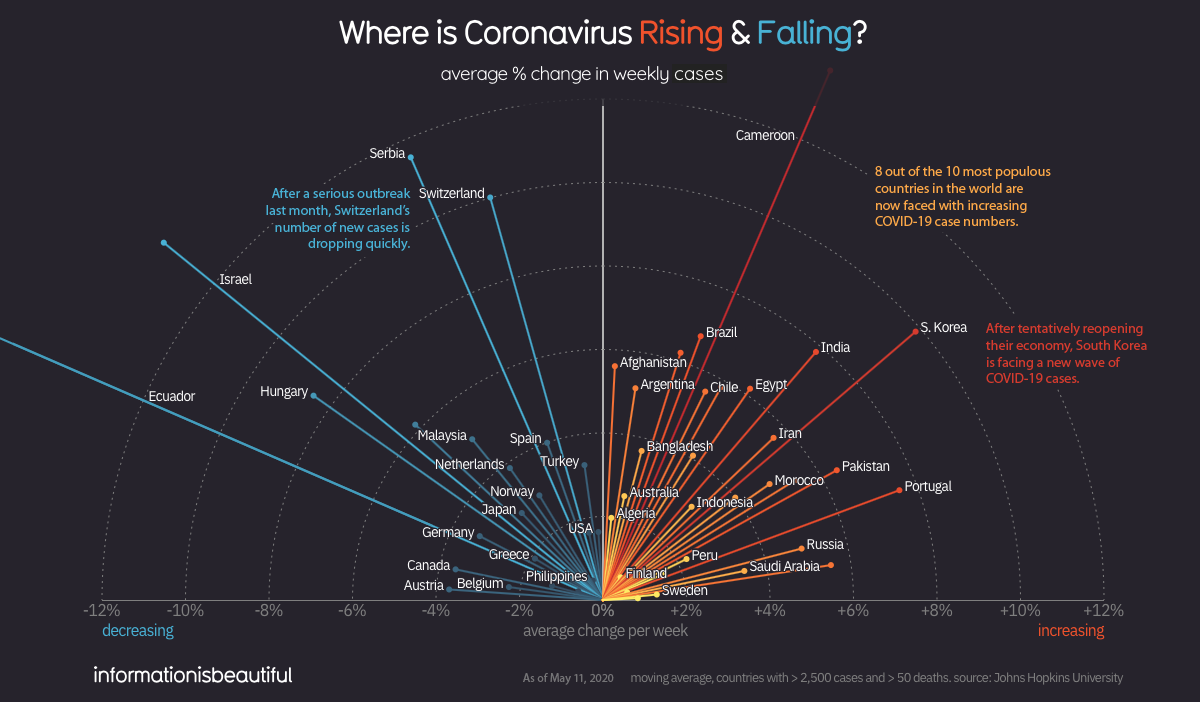
Today’s graphic, adapted from Information is Beautiful, is an efficient look at where the virus is fading away, and where new infection hotspots are emerging.
The Ebb and Flow of Coronavirus Cases
First, the good news: the number of new confirmed COVID-19 cases has started to level off on a global basis. This metric was rising rapidly until the beginning of April — but since then, it has plateaued and is holding steady (for now).
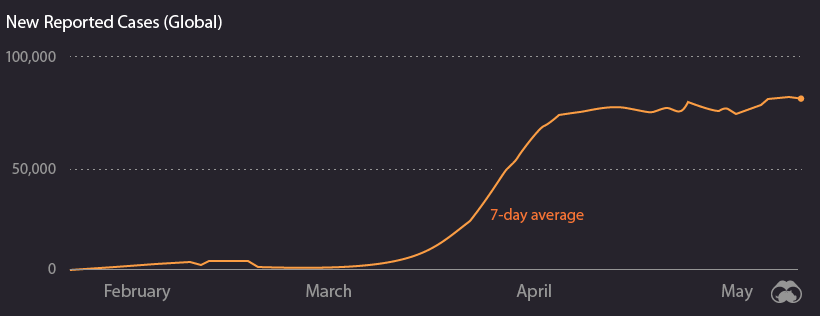
Of course, the global total doesn’t tell the whole story. Different countries, and even regions within countries, are in very different phases of dealing with the pandemic.
Let’s look at the current situation around the world.
New Cases: Falling
Many of the countries that experienced early outbreaks of COVID-19 are now seeing a drop-off in the number of new cases.
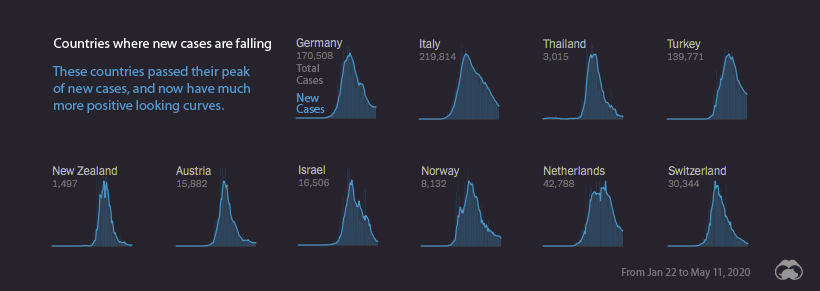
Italy, which experienced one of the most severe outbreaks, is finally emerging from the world’s longest nationwide lockdown. Switzerland and the Netherlands both had some of the highest confirmed case rates per capita, but are now in better situations as fresh cases drop off.
The narrow, pointy curves exhibited by New Zealand and Austria give us an indication of where containment measures were successful at curbing the spread of the virus. This type of pronounced curve is less common, and is generally seen in nations with smaller populations.
New Cases: Leveling Off
For many of the world’s major economies, containing the spread of the virus has proven exceptionally difficult. Despite increased testing and lockdown measures, the United States still has one of the steepest infection trajectory curves. The UK also has a very similar new case curve.
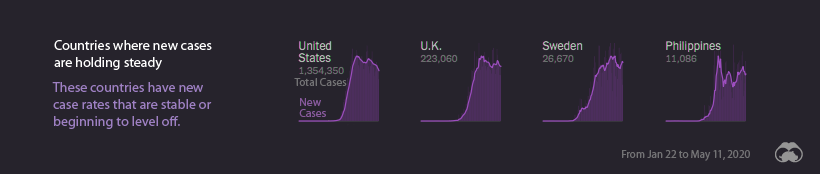
Even as countries’ curves begin to flatten and level off, there is still a danger of new flare-ups of the virus – as is now the case in South Korea and China. Even in Singapore, which saw early success in containing the virus, is experiencing a rise in new COVID-19 cases.
New Cases: Rising
Some countries – particularly developing economies – are only in the beginning stages of facing COVID-19’s rapid spread. This is a cause for concern, as many of the countries with steeply rising curves have larger populations and fewer resources to deal with a pandemic.
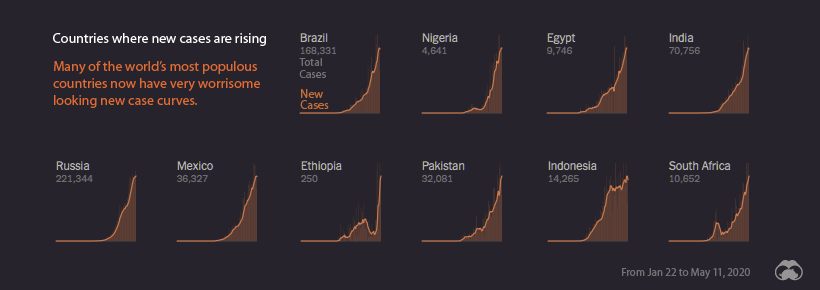
In late March, as the virus was spreading rapidly through Europe, Russia appeared to have avoided an outbreak within its borders. Today, however, that situation is much different. Russia has the world’s steepest infection trajectory curve, with the number of cases on a course to double roughly every five days.
The countries in the image above have a combined population of 2.8 billion people, so as COVID-19 continues to spread through those countries, the eyes of the world will be watching.
Healthcare
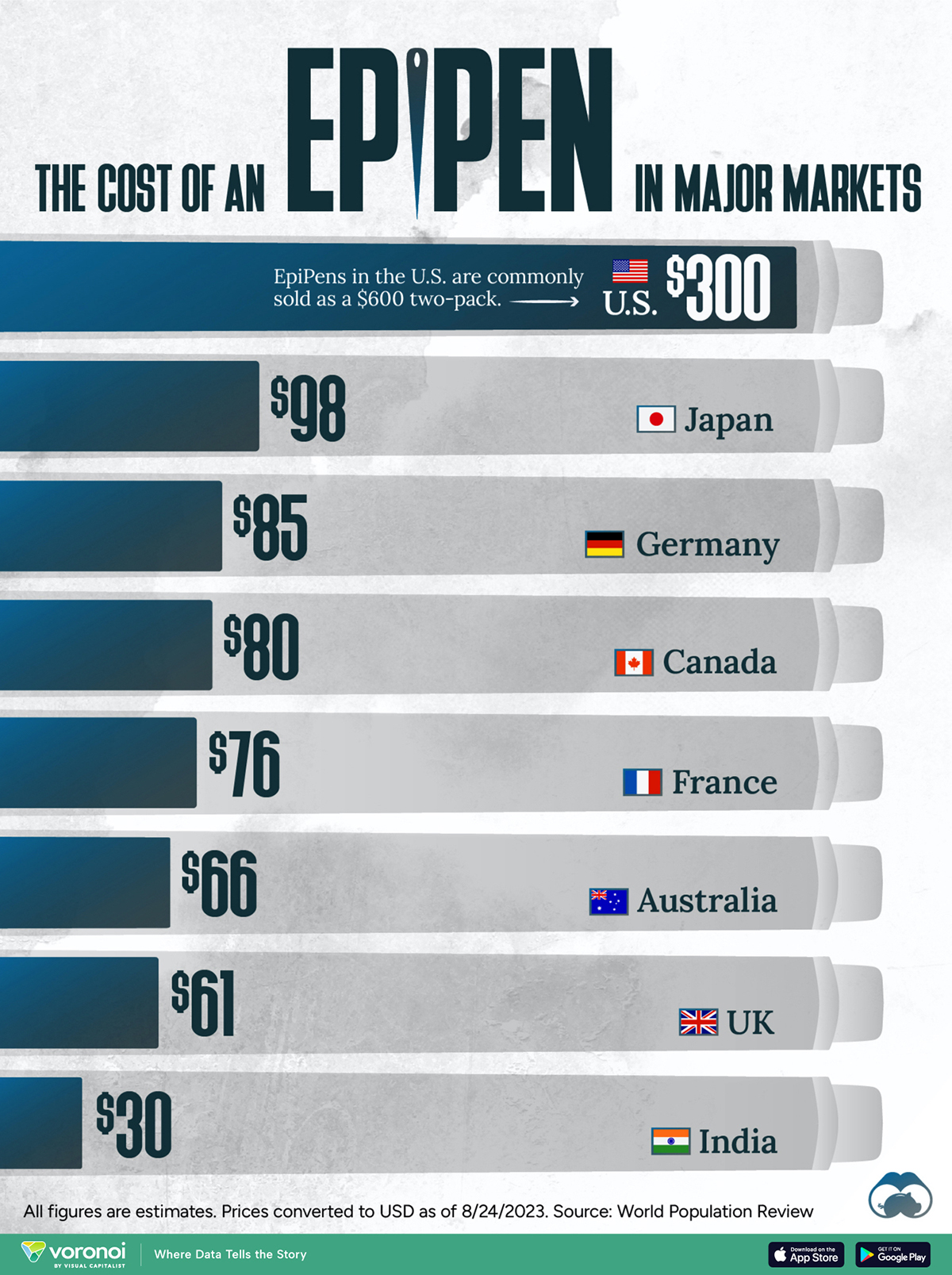
The Cost of an EpiPen in Major Markets
This visualization compares EpiPen prices around the world, with the U.S. having the highest prices by far.

The Cost of an EpiPen in Major Markets
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
EpiPens are auto-injectors containing epinephrine, a drug that can treat or reverse severe allergic reactions, potentially preventing death.
The global epinephrine market was valued at $1.75 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $4.08 billion by 2030. North America represents over 60% of the market.
EpiPens, however, can be prohibitively expensive in some regions.
In this graphic, we present estimated EpiPen prices in major global markets, compiled by World Population Review and converted to U.S. dollars as of August 2023.
Why are U.S. Prices so High?
The U.S. stands out as the most expensive market for EpiPens, despite over 1 million Americans having epinephrine prescriptions. After Mylan (now part of Pfizer) acquired the rights to produce EpiPens in the U.S. in 2007, the cost of a two-pack skyrocketed to $600, up from about $60.
| Country | Price (USD) |
|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 U.S. | 300* |
| 🇯🇵 Japan | 98 |
| 🇩🇪 Germany | 85 |
| 🇨🇦 Canada | 80 |
| 🇫🇷 France | 76 |
| 🇦🇺 Australia | 66 |
| 🇬🇧 UK | 61 |
| 🇮🇳 India | 30 |
*Per unit cost. Commonly sold as a two-pack, meaning total cost is equal to $600
Former Mylan CEO Heather Bresch defended the price hikes to Congress, citing minimal profit margins. Mylan eventually settled with the U.S. government for a nine-figure sum.
Notably, EpiPens are available at a fraction of the cost in other developed countries like Japan, Germany, and Canada.
Making EpiPens More Affordable
Efforts to improve EpiPen affordability are underway in several U.S. states. For instance, the Colorado House approved a $60 price cap on epinephrine, now under review by the state Senate.
Similar measures in Rhode Island, Delaware, Missouri, and Vermont aim to ensure insurance coverage for epinephrine, which is not currently mandatory, although most health plans cover it.
-

 Debt1 week ago
Debt1 week agoHow Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees