Technology
Ranked: The World’s Top 25 Defense Companies by Revenue
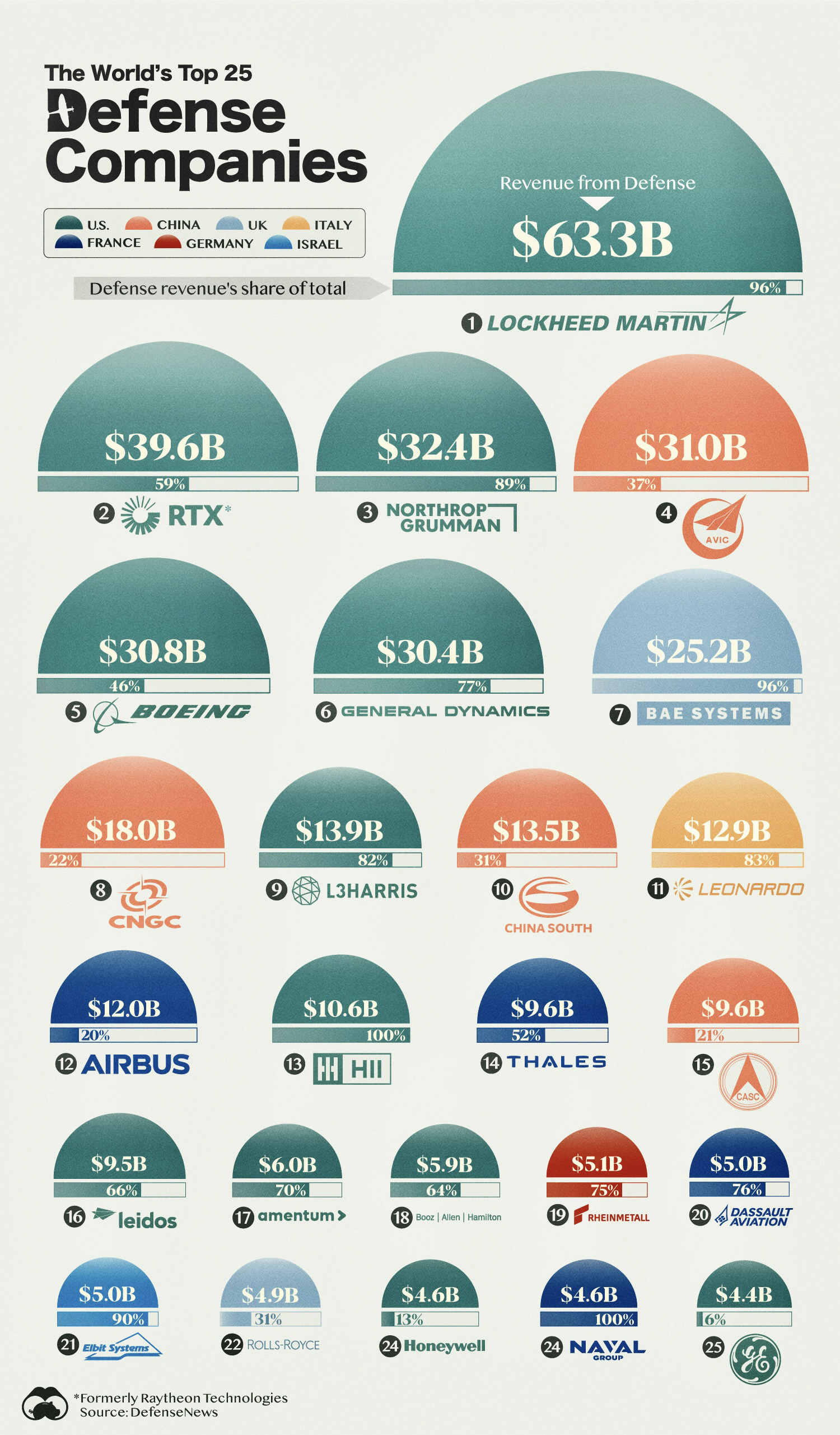
The Top 25 Defense Companies by Revenue
Every year, the world’s most powerful countries spend billions of dollars on defense—but where does this money actually flow?
To gain insight, we’ve ranked the world’s top 25 defense companies by 2022 revenues, using data from Defense News.
Note that our graphic shows each company’s revenues from defense, and not total revenues. This is because many companies such as Boeing also generate revenue from non-defense related industries and sectors.
Data and Country Highlights
The data we used to create this graphic is listed in the table below.
| Company | Revenues from Defense (USD billions) | Defense share of total revenue (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 Lockheed Martin | $63.3 | 96% |
| 🇺🇸 RTX Corp (formerly Raytheon Technologies) | $39.6 | 59% |
| 🇺🇸 Northrop Grumman | $32.4 | 89% |
| 🇨🇳 Aviation Industry Corporation of China | $31.0 | 37% |
| 🇺🇸 Boeing | $30.8 | 46% |
| 🇺🇸 General Dynamics | $30.4 | 77% |
| 🇬🇧 BAE Systems | $25.2 | 96% |
| 🇨🇳 China North Industries Group | $18.0 | 22% |
| 🇺🇸 L3Harris Technologies | $13.9 | 82% |
| 🇨🇳 China South Industries Group | $13.5 | 31% |
| 🇮🇹 Leonardo | $12.9 | 83% |
| 🇳🇱/🇫🇷 Airbus | $12.0 | 20% |
| 🇺🇸 HII | $10.6 | 100% |
| 🇫🇷 Thales | $9.6 | 52% |
| 🇨🇳 China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation | $9.6 | 21% |
| 🇺🇸 Leidos | $9.5 | 66% |
| 🇺🇸 Amentum | $6.0 | 70% |
| 🇺🇸 Booz Allen Hamilton | $5.9 | 64% |
| 🇩🇪 Rheinmetall AG | $5.1 | 75% |
| 🇫🇷 Dassault Aviation | $5.0 | 76% |
| 🇮🇱 Elbit Systems | $5.0 | 90% |
| 🇬🇧 Rolls-Royce | $4.9 | 31% |
| 🇺🇸 Honeywell | $4.6 | 13% |
| 🇫🇷 Naval Group | $4.6 | 100% |
| 🇺🇸 General Electric | $4.4 | 6% |
The U.S. and China are the most represented countries on this list, with 12 and four respective companies in the top 25.
Country Highlights: U.S.
The U.S. consistently has the world’s largest military budget, so it’s no surprise that American companies dominate this ranking. Here are some interesting facts about the top three:
Lockheed Martin
- Formed in 1995 by the merger of Lockheed Corporation and Martin Marietta
- While primarily known for producing advanced fighter jets like the F-35, the company is also working with NASA on the Orion spacecraft
RTX (formerly Raytheon Technologies)
- Raytheon produces a wide range of military equipment, including the Javelin portable anti-tank missile system.
- According to CSIS, the U.S. has supplied 7,000 Javelins to Ukraine, equal to roughly one-third of its stock.
Northrop Grumman
- Formed in 1994 by the merger of Northrop and Grumman Aerospace, this company is known for developing the B-2 stealth bomber.
- In August 2023, the company opened an office in Taiwan to “accelerate access to the company’s technologies”.
Country Highlights: China
China’s top three companies in this ranking are all state-owned enterprises.
Aviation Industry Corporation of China (AVIC)
- AVIC is China’s largest aerospace and defense company, also ranking 150th in the Fortune Global 500 (2023).
- Chengdu Aerospace Corporation, a subsidiary of AVIC, produces China’s first operational stealth fighter, the J-20.
China North Industries Group (CNIG)
- CNIG does business internationally under the name Norinco Group.
- In 2003, Norinco was sanctioned by the Bush administration for allegedly supplying Iran with missile technologies.
China South Industries Group (CSIG)
- CSIG produces military vehicles, ammunitions, and other equipment.
- The company also owns Changan Automobile, a major car brand in China and one of the world’s largest EV producers.
Other Highlights
Two European companies on this list that aren’t typically associated with the defense industry are Airbus and Rolls-Royce.
Airbus is one of the world’s largest producers of commercial airliners, and is widely used by major carriers alongside offerings from Boeing. When it comes to defense, Airbus produces a variety of military drones, fighters, and transports.
On the other hand, Rolls-Royce is a major supplier of aircraft and naval engines, and designs the nuclear propulsion systems for the UK’s submarine fleet.
It actually has no affiliation with Rolls-Royce Motor Cars, which is currently a subsidiary of BMW. The original company ran into financial difficulties in the 1970s, which led to the separation of the car and aero-engine businesses.
Correction: A previous version of this article contained incorrect revenue totals. The graphic has since been updated.
Technology
All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
Intel, TSMC, and more have received billions in subsidies from the U.S. CHIPS Act in 2024.

All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This visualization shows which companies are receiving grants from the U.S. CHIPS Act, as of April 25, 2024. The CHIPS Act is a federal statute signed into law by President Joe Biden that authorizes $280 billion in new funding to boost domestic research and manufacturing of semiconductors.
The grant amounts visualized in this graphic are intended to accelerate the production of semiconductor fabrication plants (fabs) across the United States.
Data and Company Highlights
The figures we used to create this graphic were collected from a variety of public news sources. The Semiconductor Industry Association (SIA) also maintains a tracker for CHIPS Act recipients, though at the time of writing it does not have the latest details for Micron.
| Company | Federal Grant Amount | Anticipated Investment From Company |
|---|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 Intel | $8,500,000,000 | $100,000,000,000 |
| 🇹🇼 TSMC | $6,600,000,000 | $65,000,000,000 |
| 🇰🇷 Samsung | $6,400,000,000 | $45,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Micron | $6,100,000,000 | $50,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 GlobalFoundries | $1,500,000,000 | $12,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Microchip | $162,000,000 | N/A |
| 🇬🇧 BAE Systems | $35,000,000 | N/A |
BAE Systems was not included in the graphic due to size limitations
Intel’s Massive Plans
Intel is receiving the largest share of the pie, with $8.5 billion in grants (plus an additional $11 billion in government loans). This grant accounts for 22% of the CHIPS Act’s total subsidies for chip production.
From Intel’s side, the company is expected to invest $100 billion to construct new fabs in Arizona and Ohio, while modernizing and/or expanding existing fabs in Oregon and New Mexico. Intel could also claim another $25 billion in credits through the U.S. Treasury Department’s Investment Tax Credit.
TSMC Expands its U.S. Presence
TSMC, the world’s largest semiconductor foundry company, is receiving a hefty $6.6 billion to construct a new chip plant with three fabs in Arizona. The Taiwanese chipmaker is expected to invest $65 billion into the project.
The plant’s first fab will be up and running in the first half of 2025, leveraging 4 nm (nanometer) technology. According to TrendForce, the other fabs will produce chips on more advanced 3 nm and 2 nm processes.
The Latest Grant Goes to Micron
Micron, the only U.S.-based manufacturer of memory chips, is set to receive $6.1 billion in grants to support its plans of investing $50 billion through 2030. This investment will be used to construct new fabs in Idaho and New York.
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoHow Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Environment2 weeks ago
Environment2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001













