Technology
Amazon’s Massive Distribution Network in One Giant Visualization
View a high resolution version of this graphic.
Amazon’s Massive Distribution Network in One Visualization
View the high resolution version of today’s graphic by clicking here.
Last year, Amazon shipped over 5 billion (with a “B”) Prime packages, and the retail giant’s ecommerce market share in the U.S. is on the verge of surpassing 50%.
Moving that kind of volume takes an impressive amount of technical sophistication, manpower, and distribution infrastructure. While Amazon does lean on third parties for deliveries and warehousing, the company is also building an increasingly expansive distribution network in an attempt to manage the entire process.
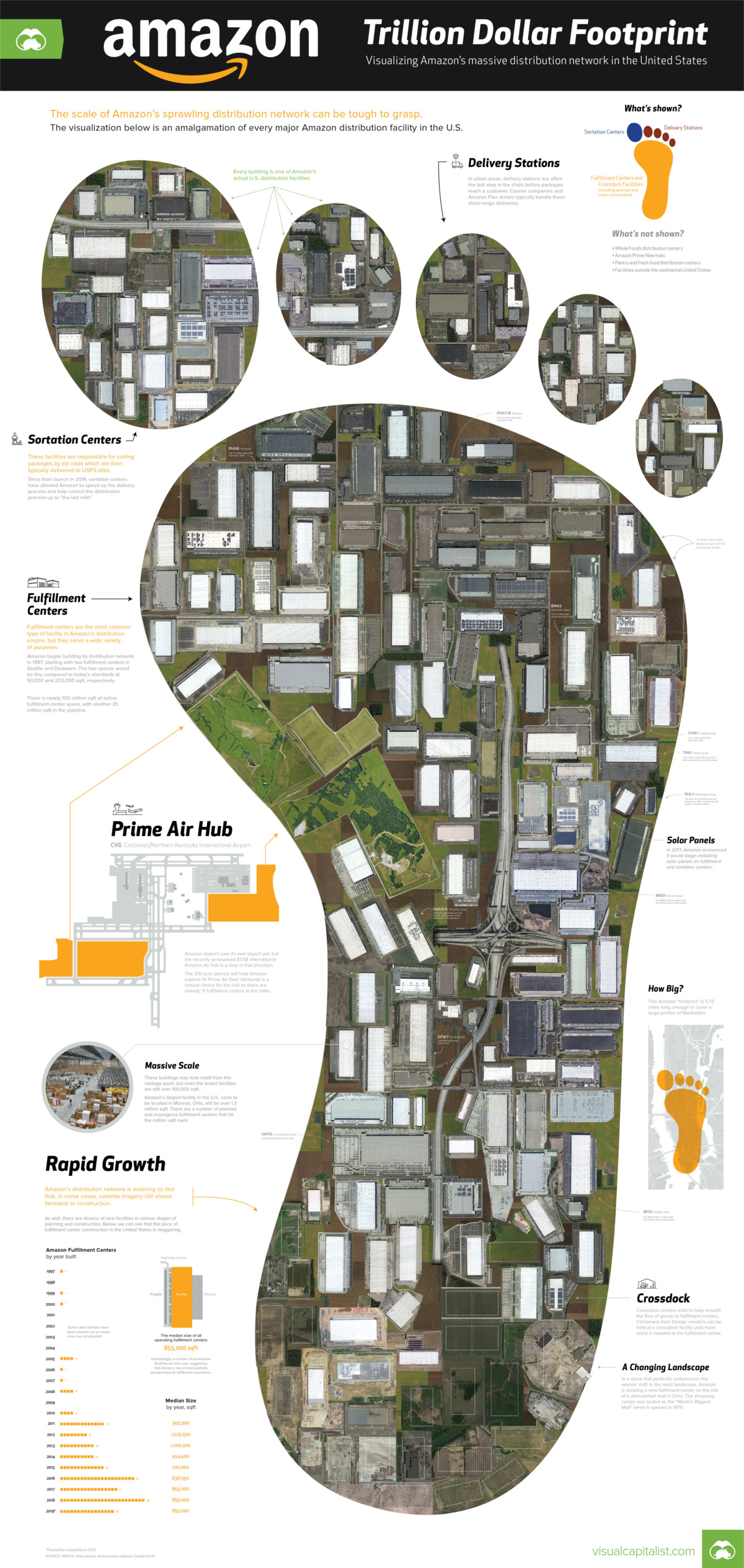
Today’s visualization, which uses comprehensive data from MWPVL International, examines the estimated 124 million square feet of active space in the U.S., as well as the 40 million in Amazon’s construction pipeline.
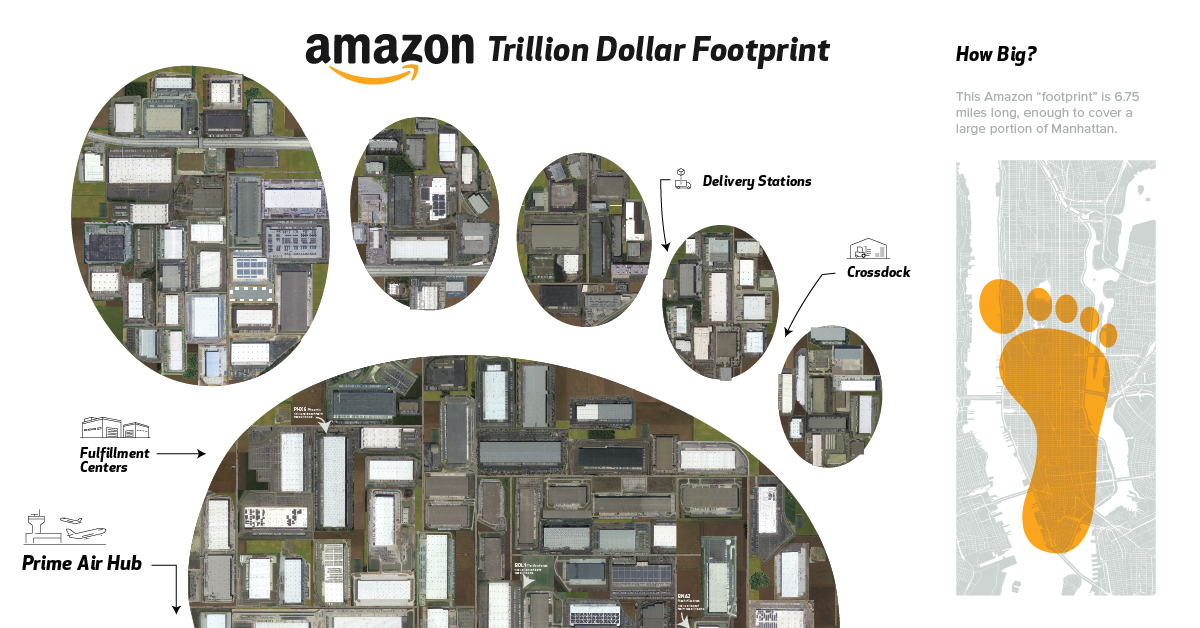
To create our graphical footprint of Amazon’s warehouses in the infographic, we’ve used satellite imagery of every Amazon facility in the U.S. and stitched it all together.
Pieces of the Puzzle
There are a few types of facilities that make up the vast network of Amazon’s warehouses:
Crossdock Centers
Containers from foreign vendors can be held at a crossdock facility until more stock is needed at the fulfillment center. This is the back-end of the distribution chain.
Fulfillment Centers
Fulfillment centers are the most common type of facility in Amazon’s distribution empire, but they serve a wide variety of purposes.
Amazon began building its distribution network in 1997, starting with two fulfillment centers in Seattle and Delaware. The two spaces would be tiny compared to today’s standards at 93,000 and 202,000 square feet, respectively. Now, there is nearly 100 million square feet of active fulfillment center space, with another 35 million on the way.
Sortation Centers
These facilities are responsible for sorting packages by zip code which are then typically delivered to USPS sites. Since being introduced in 2014, sortation centers have allowed Amazon to speed up the delivery process and to help control the distribution process up to “the last mile”.
Delivery Stations
In urban areas, delivery stations are often the last step in the chain before packages reach a customer. Courier companies – and increasingly Amazon Flex drivers – typically handle these short-range deliveries. These stations are often located near airports.
Prime Now Hubs
These smaller locations are specifically designed for speed. Prime Now hubs carry a more limited selection of items – including Whole Foods inventory – that are delivered within two hours of clicking “buy”. There are currently around 50 of these facilities in urban areas around the United States, but that number is expected to increase dramatically in the near future.
Prime Air Hub
Amazon doesn’t own its own airport yet, but the recently announced $1.5B international Prime Air Hub is a step in that direction.
The 210-acre parcels will help Amazon expand its Prime Air fleet while reducing its reliance on companies like UPS and FedEx. Kentucky is a natural choice for the hub as there are already 11 fulfillment centers in the state.
Fighting for the Last Mile
Over the years, Amazon has optimized every aspect of the distribution system, but one final hurdle remains.
Conquering the last mile – the final leg before a package reaches its destination – has proven tricky, in part because USPS already has a well-honed strategy for delivering to all the nation’s residents.
The company’s earnest recruitment drive for Amazon Flex is the latest in a long line of attempts to decrease reliance on third parties for package delivery. Also, by tapping into on-demand labor, Amazon hopes to reduce costs and have more flexibility during volume surges like Black Friday.
This desire to own the entire process is being reflected in the company’s roster of distribution facilities. The massive fulfillment centers aren’t going anywhere, but we may see a lot more smaller delivery hubs in cities and towns across America.
Technology
All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
Intel, TSMC, and more have received billions in subsidies from the U.S. CHIPS Act in 2024.

All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This visualization shows which companies are receiving grants from the U.S. CHIPS Act, as of April 25, 2024. The CHIPS Act is a federal statute signed into law by President Joe Biden that authorizes $280 billion in new funding to boost domestic research and manufacturing of semiconductors.
The grant amounts visualized in this graphic are intended to accelerate the production of semiconductor fabrication plants (fabs) across the United States.
Data and Company Highlights
The figures we used to create this graphic were collected from a variety of public news sources. The Semiconductor Industry Association (SIA) also maintains a tracker for CHIPS Act recipients, though at the time of writing it does not have the latest details for Micron.
| Company | Federal Grant Amount | Anticipated Investment From Company |
|---|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 Intel | $8,500,000,000 | $100,000,000,000 |
| 🇹🇼 TSMC | $6,600,000,000 | $65,000,000,000 |
| 🇰🇷 Samsung | $6,400,000,000 | $45,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Micron | $6,100,000,000 | $50,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 GlobalFoundries | $1,500,000,000 | $12,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Microchip | $162,000,000 | N/A |
| 🇬🇧 BAE Systems | $35,000,000 | N/A |
BAE Systems was not included in the graphic due to size limitations
Intel’s Massive Plans
Intel is receiving the largest share of the pie, with $8.5 billion in grants (plus an additional $11 billion in government loans). This grant accounts for 22% of the CHIPS Act’s total subsidies for chip production.
From Intel’s side, the company is expected to invest $100 billion to construct new fabs in Arizona and Ohio, while modernizing and/or expanding existing fabs in Oregon and New Mexico. Intel could also claim another $25 billion in credits through the U.S. Treasury Department’s Investment Tax Credit.
TSMC Expands its U.S. Presence
TSMC, the world’s largest semiconductor foundry company, is receiving a hefty $6.6 billion to construct a new chip plant with three fabs in Arizona. The Taiwanese chipmaker is expected to invest $65 billion into the project.
The plant’s first fab will be up and running in the first half of 2025, leveraging 4 nm (nanometer) technology. According to TrendForce, the other fabs will produce chips on more advanced 3 nm and 2 nm processes.
The Latest Grant Goes to Micron
Micron, the only U.S.-based manufacturer of memory chips, is set to receive $6.1 billion in grants to support its plans of investing $50 billion through 2030. This investment will be used to construct new fabs in Idaho and New York.
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoHow Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Environment2 weeks ago
Environment2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001