Visualizing Carbon Storage in Earth’s Ecosystems
The following content is sponsored by the Carbon Streaming Corporation
Visualizing Carbon Storage in Earth’s Ecosystems
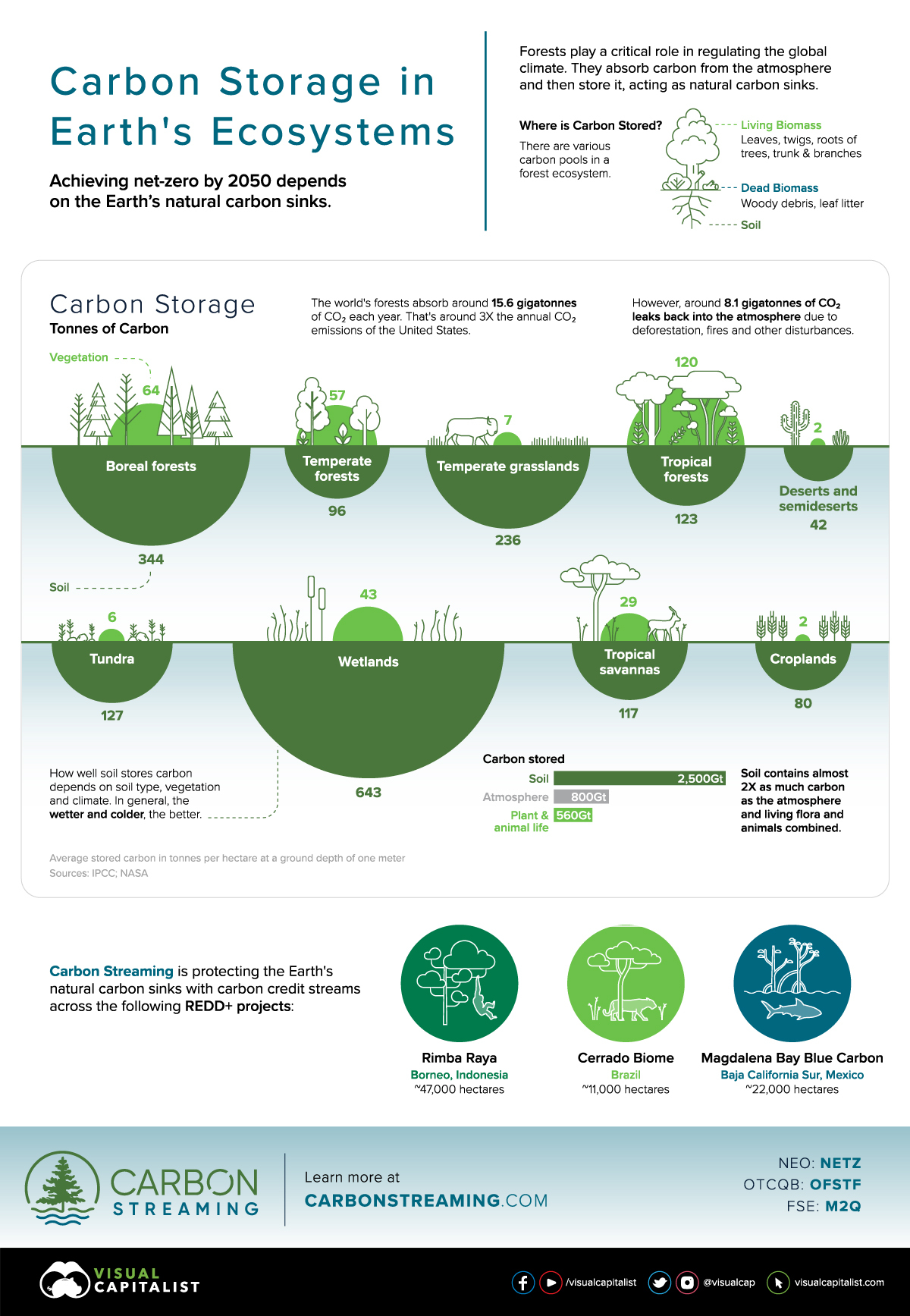
Each year, the world’s forests absorb roughly 15.6 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide (CO2).
To put it in perspective, that’s around three times the annual CO2 emissions of the U.S. or about 40% of global CO2 emissions. For this reason, forests serve as a vital tool in regulating the global temperature and achieving net-zero emissions by 2050.
In this graphic sponsored by Carbon Streaming Corporation, we look at the Earth’s natural carbon sinks, and break down their carbon storage.
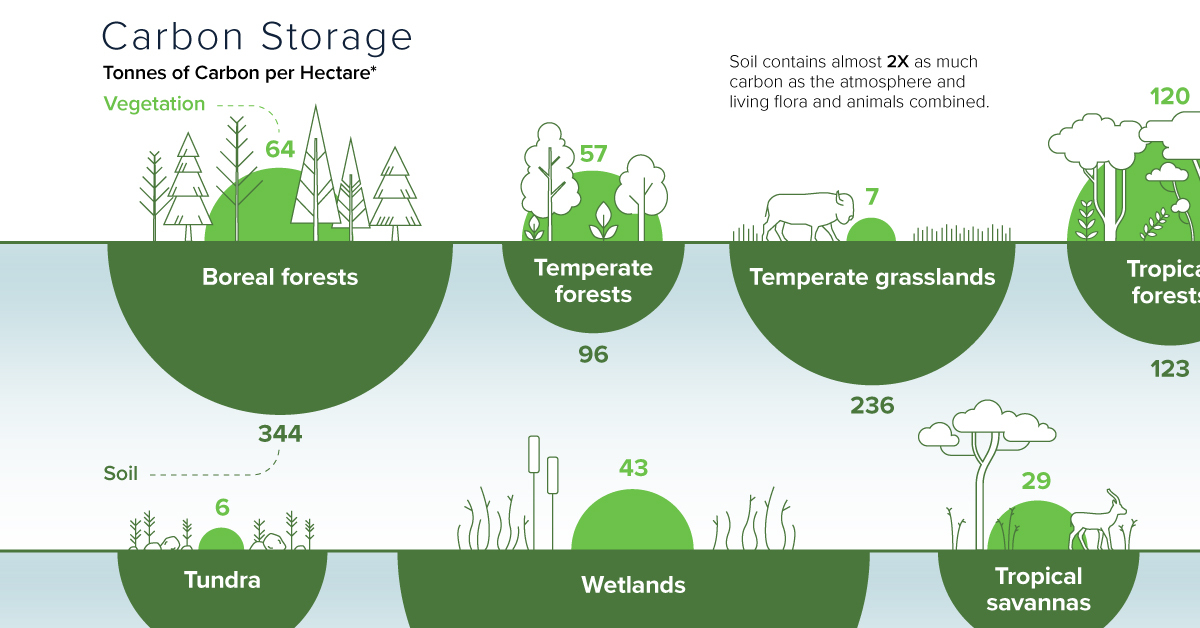
Carbon Storage by Ecosystem
Forests contain several carbon sinks, from living biomass such as roots and leaves to soil. In fact, soil contains nearly twice as much carbon than the atmosphere, plant, and animal life combined.
- Soil: 2,500 gigatonnes (Gt)
- Atmosphere: 800 Gt
- Plant & animal life: 560 Gt
The soil type, vegetation, and climate all affect how carbon is stored. For example, colder and wetter climates promote the most effective carbon storage in soil.
| Global Carbon Storage* (Tonnes of carbon per hectare) | Vegetation | Soil |
|---|---|---|
| Wetlands | 43 | 643 |
| Boreal forests | 64 | 344 |
| Temperate grasslands | 7 | 236 |
| Tundra | 6 | 127 |
| Tropical forests | 120 | 123 |
| Tropical savannas | 29 | 117 |
| Temperate forests | 57 | 96 |
| Croplands | 2 | 80 |
Deserts and semideserts | 2 | 42 |
*Average stored carbon in tonnes per hectare at a ground depth of one meter
Source: IPCC
Wetlands are substantial reservoirs of carbon. Despite occupying only 5-8% of the Earth’s land surface, they hold between 20 to 30% of all estimated organic soil carbon.
Risks to Natural Carbon Sinks
Around 8.1 billion tonnes of CO2 leaks back into the atmosphere each year.
Over the last 20 years, the world has lost about 10% of its tree cover, or 411 million hectares (Mha). The main causes behind this are forestry (119 Mha), commodity-driven deforestation (103 Mha), and wildfires (89 Mha). What’s more, research suggests that Amazon rainforests emit more carbon than they absorb due to record levels of fires, many of which are deliberately set to clear for commodity production.
With the increasing frequency of wildfires and deforestation, the world’s forests are at risk of releasing carbon. Protecting and preserving these biomes is critical to the Earth’s carbon balance and mitigating climate change.
Carbon Credits Provide a Solution
Given the risk of losing critical carbon sinks, carbon credits play an important role in preserving these ecosystems.
Carbon credits can help finance projects that reduce or remove GHG emissions from the atmosphere. From improved forest management to reforestation, there are a number of different types of carbon projects across wetlands, grasslands, and various forests:
- Reforestation and Afforestation
- Avoided Deforestation
- Natural forest management
- Wetland restoration
For instance, a carbon credit project may preserve endangered tropical lowland peat swamp forests spanning thousands of hectares, such as the Rimba Raya Biodiversity Reserve Project in Indonesia, one of the projects that Carbon Streaming has a carbon credit stream.
Through this project, forests are prevented from being converted into palm oil plantations to reduce and avoid 130 million tonnes of GHG emissions during the 30 years of the project.
Another example would be the Cerrado Biome Project in Brazil, another carbon offset project where Carbon Streaming has a stream agreement. This project is protecting and preserving native forests and grasslands from being converted to commercial agriculture.
Importantly, these projects would not be economically viable without the sale of carbon credits.
Protecting Stored Carbon
To prevent further loss of stored carbon, government policies, NGO-led initiatives, and the financing of carbon offset projects are gaining momentum. Taken together, they offer the critical intervention needed to preserve the earth’s carbon vaults.

-

 Sponsored3 years ago
Sponsored3 years agoMore Than Precious: Silver’s Role in the New Energy Era (Part 3 of 3)
Long known as a precious metal, silver in solar and EV technologies will redefine its role and importance to a greener economy.
-

 Sponsored7 years ago
Sponsored7 years agoThe History and Evolution of the Video Games Market
Everything from Pong to the rise of mobile gaming and AR/VR. Learn about the $100 billion video games market in this giant infographic.
-

 Sponsored8 years ago
Sponsored8 years agoThe Extraordinary Raw Materials in an iPhone 6s
Over 700 million iPhones have now been sold, but the iPhone would not exist if it were not for the raw materials that make the technology…
-

 Sponsored8 years ago
Sponsored8 years agoThe Industrial Internet, and How It’s Revolutionizing Mining
The convergence of the global industrial sector with big data and the internet of things, or the Industrial Internet, will revolutionize how mining works.