The History of Psychedelics (Part 1 of 2)
The History of Psychedelics (Part 1 of 2)
Due to their counterculture connotations and rigid legal status, psychedelics were once considered a highly stigmatized topic.
Over the last decade however, a steady stream of groundbreaking research has proven that these powerful substances have the potential to safely treat a wide range of diseases.
Today, attitudes toward the industry have changed, and capital is flowing—resulting in a market that analysts predict could eventually be worth $100 billion.
The graphic above from Tryp Therapeutics is the first in a two-part series that explores how psychedelics have evolved over the last 6,000 years.
From Ancient Antidote to Breakthrough Medicine
Before we dive into the history of psychedelics, it’s important to understand what they are and how they work.
Psychedelics are drugs that alter cognitive processes and produce hallucinogenic effects. Broadly speaking, there are two categories that psychedelic substances fall into: entheogens, and synthetic drugs. Entheogenic psychedelics are derived from plants, while synthetic psychedelics are created in a laboratory.
Here are some of the most well known psychedelic substances explained:
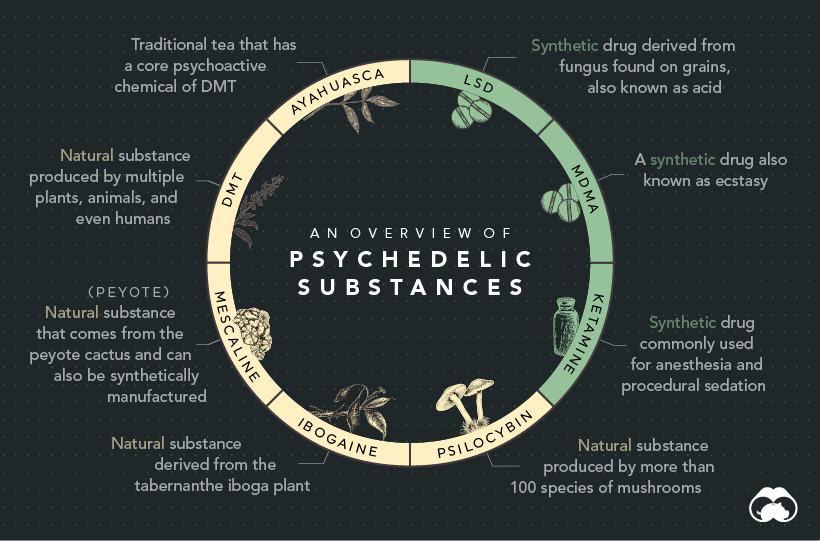
Certain psychedelics work by binding to serotonin receptors in the brain which produces psychoactive effects. Research suggests that when this happens, the structure of the brain changes—such as the number of connections between neutrons. This means that psychedelics could have the potential to rewire or repair circuits in the brain, hence their reputation for having healing powers.
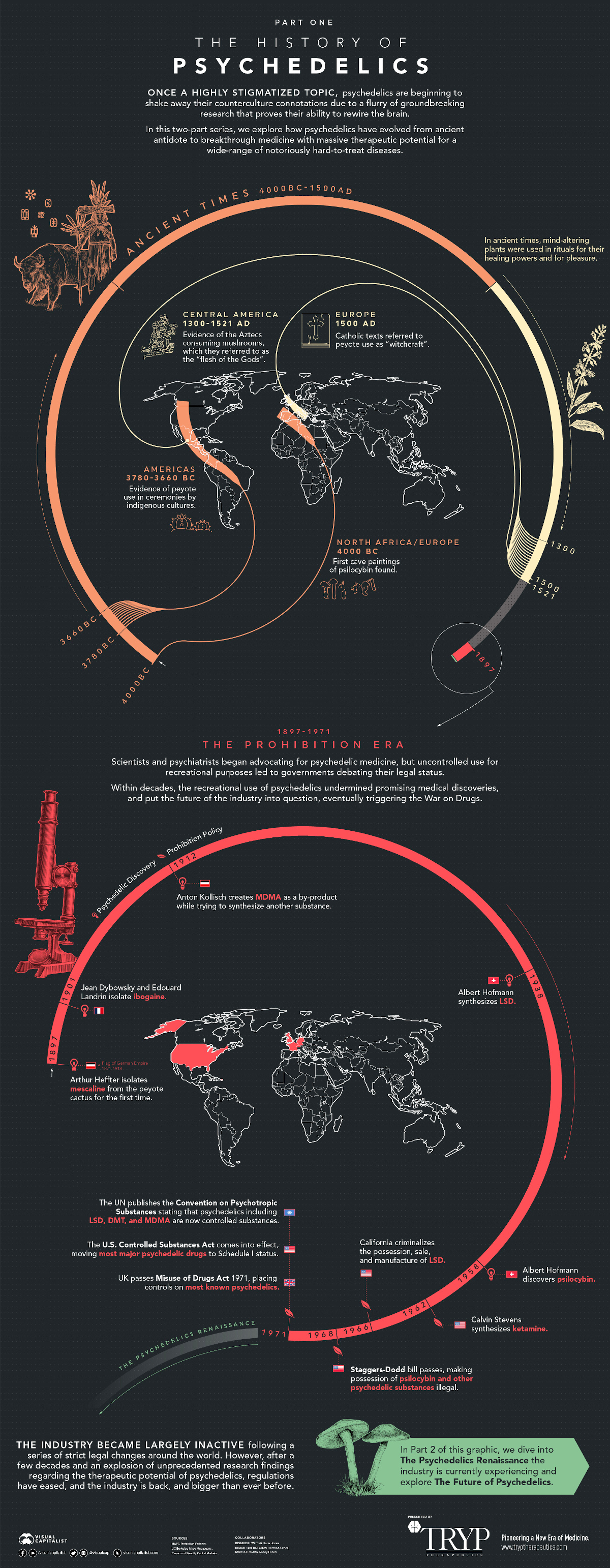
Ancient Times
While the science behind these mind-altering plants is only now beginning to become clear, they have in fact been used in rituals and ceremonies for thousands of years.
As a result, psychedelic substances have been hugely influential in shaping certain cultures and religions dating back to 4,000 BC. These cultures, particularly in the Americas, learned how to utilize psychoactive plants and mushrooms for medicinal purposes or to reach an altered state of consciousness.
| Year | Milestone | Region |
|---|---|---|
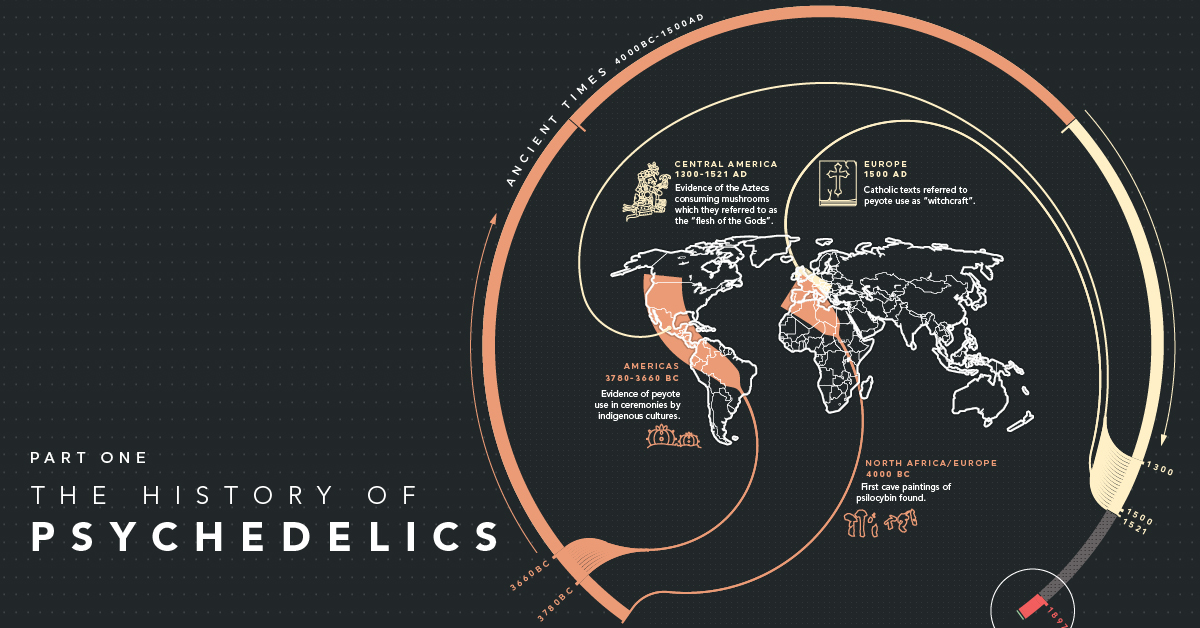
| 4000 BC | First cave paintings of psilocybin | Europe, North Africa |
| 3780-3660 BC | Evidence of ceremonial use of peyote by indigenous cultures | North and South America |
| 1300-1521 AD | Evidence of the Aztecs consuming mushrooms which they referred to as the “flesh of the Gods”. | Central America |
| 1500 AD | Catholic texts refer to peyote use as “witchcraft”. | Europe |
With that being said, evidence of how psychedelics were used in ancient times is often anecdotal, and therefore widely debated.
The Prohibition Era
In the 1800s, scientists and psychiatrists began discovering new kinds of drugs such as psilocybin and subsequently became advocates of psychedelic medicine. Unfortunately, uncontrolled drug use for recreational purposes led to governments across the world debating their legal status, and clamping down on restrictions.
| Year | Milestone | Region |
|---|---|---|
| 1897 | Arthur Heffter isolates mescaline from the peyote cactus for the first time. | Germany |
| 1901 | Jean Dybowsky and Edouard Landrin isolate ibogaine. | France |
| 1912 | Anton Kollisch created MDMA as a by-product while trying to synthesize another substance. | Germany |
| 1938 | Albert Hofmann synthesizes LSD. | Switzerland |
| 1958 | Albert Hofmann discovers psilocybin. | Switzerland |
| 1962 | Calvin Stevens synthesizes ketamine. | U.S. |
| 1966 | California criminalizes the possession, sale, and manufacture of LSD. | U.S. |
| 1968 | Staggers-Dodd bill passes, making possession of psilocybin and other psychedelic substances illegal. | U.S. |
| 1971 | The UN publishes the Convention on Psychotropic Substances stating that psychedelics including LSD, DMT, and MDMA are now controlled substances. | Global |
| 1971 | The U.S. Controlled Substances Act comes into effect, moving most major psychedelic drugs to Schedule I status. | U.S. |
| 1971 | UK passes Misuse of Drugs Act 1971, placing controls on most known psychedelics. | UK |
Within decades, the recreational use of psychedelics undermined promising medical discoveries, and put the future of the industry into question, eventually triggering the War on Drugs.
An Industry, Reborn
With these strict legal changes around the world, the psychedelics industry became largely inactive. But today, an explosion of unprecedented research findings surrounding the therapeutic potential of psychedelics has triggered many countries to reassess their decision to criminalize.
Now, the industry is back, and bigger than ever before. In Part 2 of The History of Psychedelics, we’ll dive into The Psychedelics Renaissance the industry is currently experiencing and discuss the exciting future of this promising sector.

-

 Sponsored3 years ago
Sponsored3 years agoMore Than Precious: Silver’s Role in the New Energy Era (Part 3 of 3)
Long known as a precious metal, silver in solar and EV technologies will redefine its role and importance to a greener economy.
-

 Sponsored7 years ago
Sponsored7 years agoThe History and Evolution of the Video Games Market
Everything from Pong to the rise of mobile gaming and AR/VR. Learn about the $100 billion video games market in this giant infographic.
-

 Sponsored8 years ago
Sponsored8 years agoThe Extraordinary Raw Materials in an iPhone 6s
Over 700 million iPhones have now been sold, but the iPhone would not exist if it were not for the raw materials that make the technology…
-

 Sponsored8 years ago
Sponsored8 years agoThe Industrial Internet, and How It’s Revolutionizing Mining
The convergence of the global industrial sector with big data and the internet of things, or the Industrial Internet, will revolutionize how mining works.