Politics
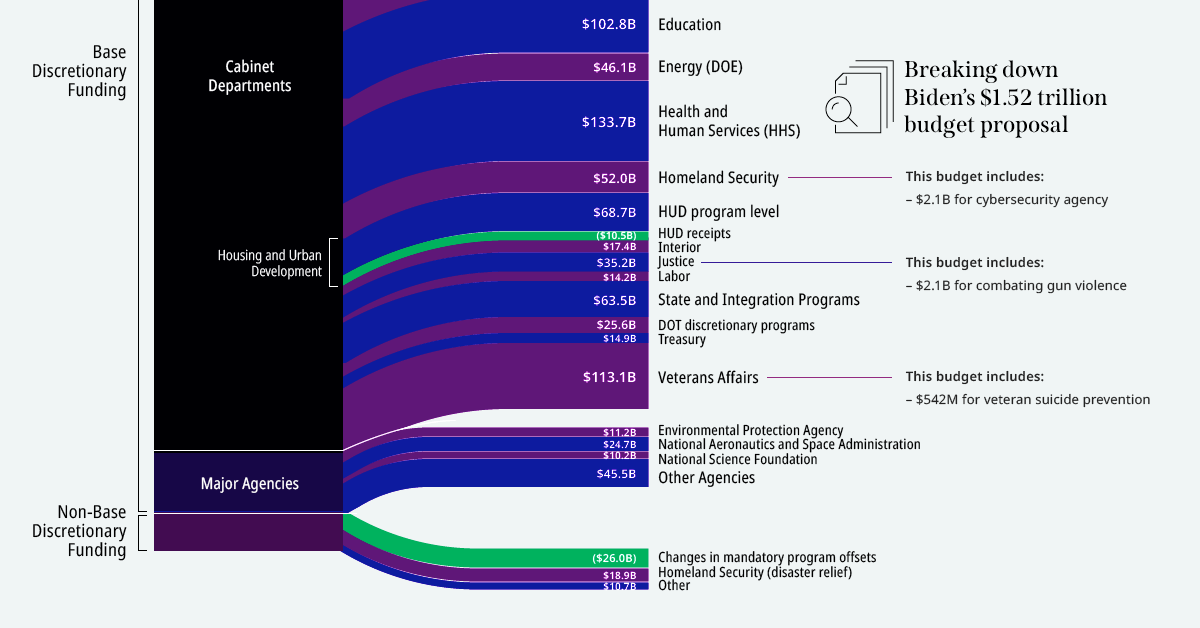
Visualizing Biden’s $1.52 Trillion Budget Proposal for 2022
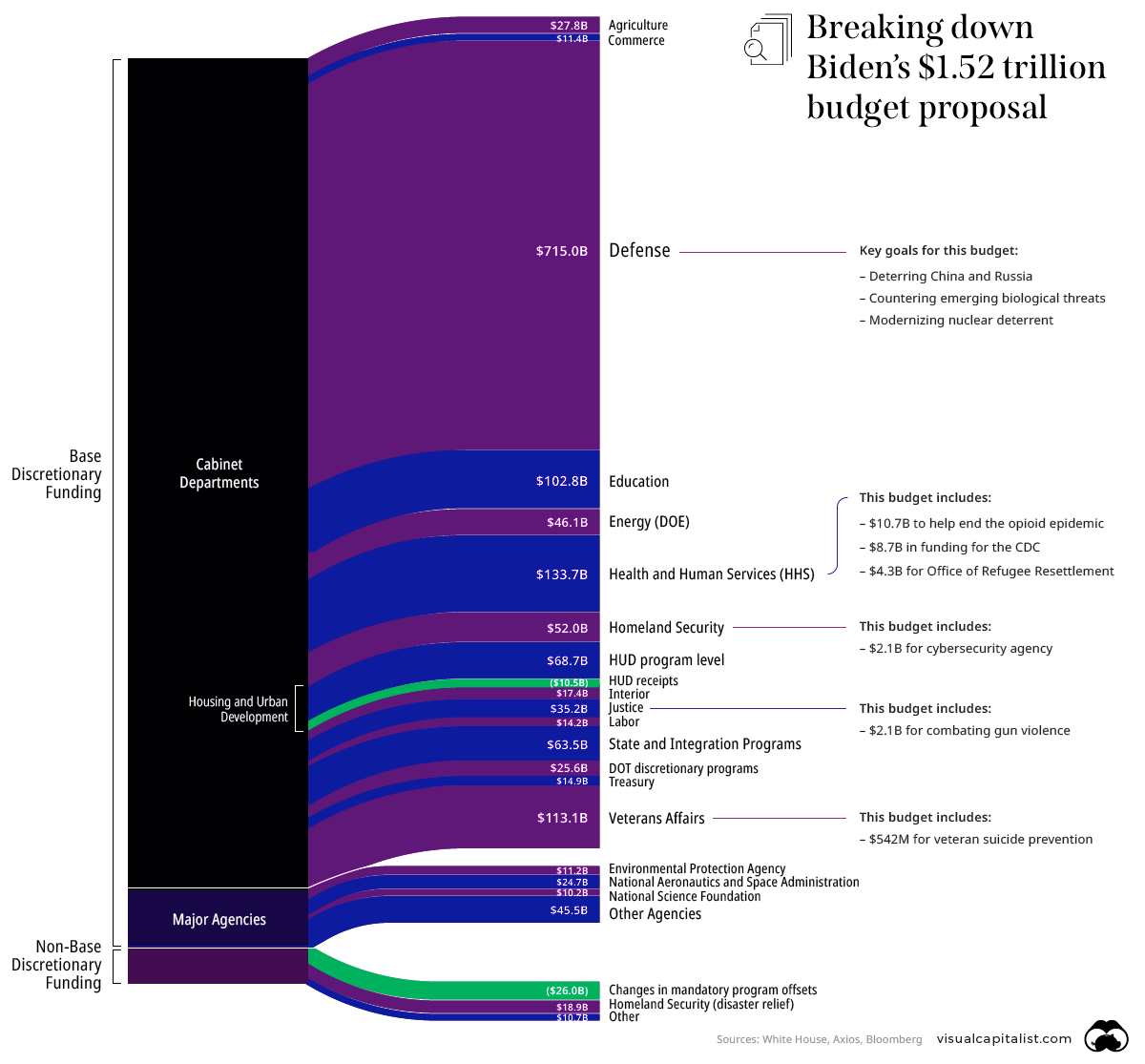
Visualizing Biden’s Budget Proposal for 2022
On April 9th, President Joe Biden released his first budget proposal plan for the 2022 fiscal year.
The $1.52 trillion discretionary budget proposes boosts in funding that would help combat climate change, support disease control, and subsidize social programs.
This graphic outlines some key takeaways from Biden’s budget proposal plan and highlights how funds could be allocated in the next fiscal year.
U.S. Federal Budget 101
Before diving into the proposal’s key takeaways, it’s worth taking a step back to cover the basics around the U.S. federal budget process, for those who aren’t familiar.
Each year, the president of the U.S. is required to present a federal budget proposal to Congress. It’s usually submitted each February, but this year’s proposal has been delayed due to alleged issues with the previous administration during the handover of office.
Biden’s publicized budget only includes discretionary spending for now—a full budget that includes mandatory spending is expected to be released in the next few months.
Key Takeaways From Biden’s Budget Proposal
Overall, Biden’s proposed budget would increase funds for a majority of cabinet departments. This is a drastic pivot from last year’s proposal, which was focused on budget cuts.
Here’s a look at some of the biggest departmental changes, and their proposed spending for 2022:
| Department | 2022 Proposed Spending (Billions) | % Change from 2021 |
|---|---|---|
| Education | $29.8 | 41% |
| Commerce | $11.4 | 28% |
| Health and Human Services | $131.7 | 24% |
| Environmental Protection Agency | $11.2 | 21% |
| Interior | $17.4 | 16% |
| Agriculture | $27.8 | 16% |
| Housing and Urban Development | $68.7 | 15% |
| Transportation | $25.6 | 14% |
| Labor | $14.2 | 14% |
| State and International Aid | $63.5 | 12% |
| Treasury | $14.9 | 11% |
| Energy | $46.1 | 10% |
| Small Business Administration | $0.9 | 9% |
| Veteran Affairs | $113.1 | 8% |
| Justice | $17.4 | 5% |
| Defense | $715.0 | 2% |
One of the biggest boosts in spending is for education. The proposed $29.8 billion would be a 41% increase from 2021. The extra funds would support students in high-poverty schools, as well as children with disabilities.
Health and human services is also a top priority in Biden’s budget, perhaps unsurprisingly given the global pandemic. But the boost in funds extends beyond disease control. Biden’s budget allocates $1.6 billion towards mental health grants and $10.7 billion to help stop the opioid crisis.
There are increases across all major budget categories, but defense will see the smallest increase from 2021 spending, at 2%. It’s worth noting that defense is also the biggest budget category by far, and with a total of $715 billion allocated, the budget lists deterring threats from China and Russia as a major goal.
Which Bills Will Make it Through?
It’s important to reiterate that this plan is just a proposal. Each bill needs to get passed through Congress before it becomes official.
Considering the slim majority held by Democrats, it’s unlikely that Biden’s budget will make it through Congress without any changes. Over the next few months, it’ll be interesting to see what makes it through the wringer.
United States
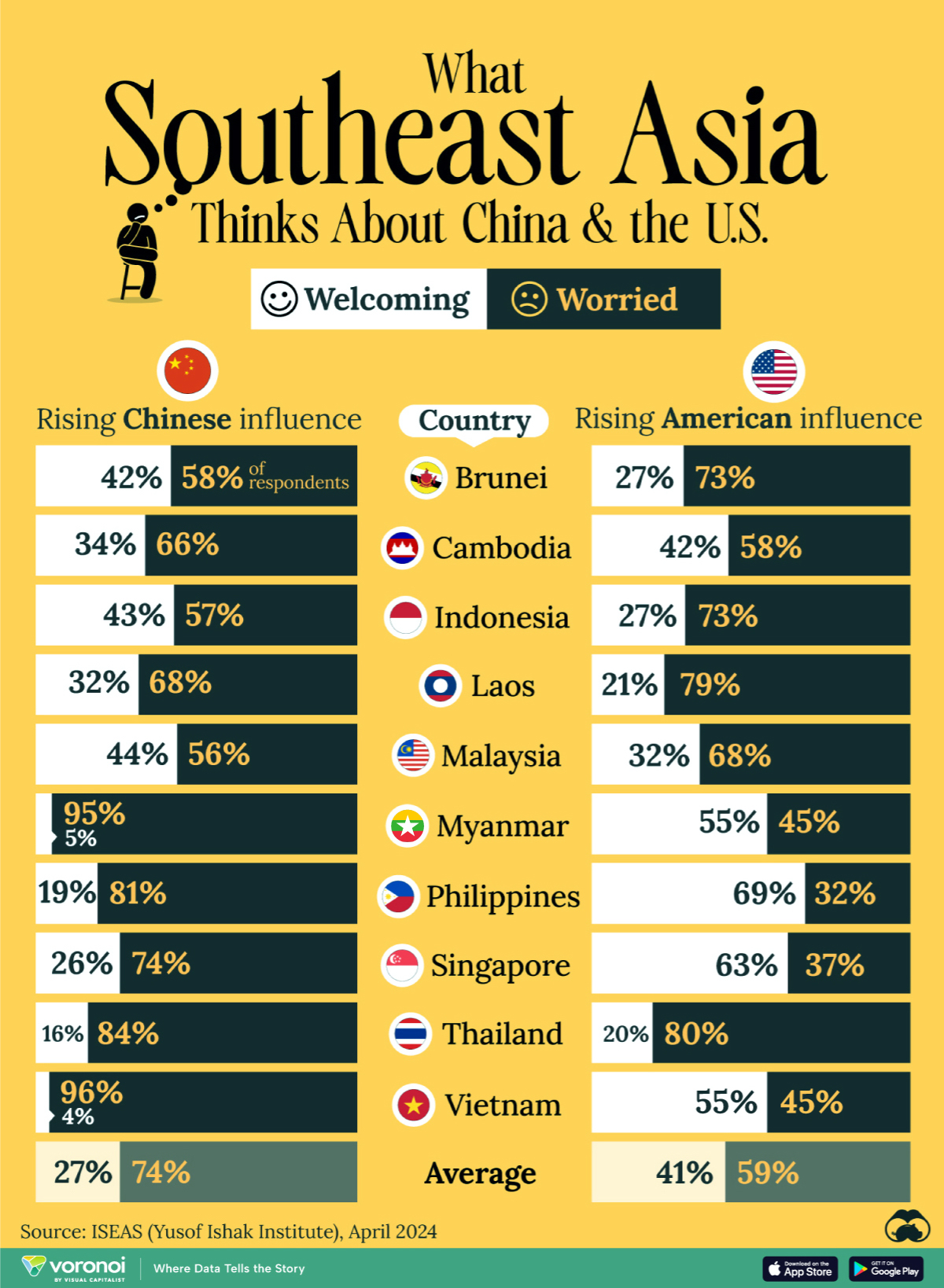
Charted: What Southeast Asia Thinks About China & the U.S.
A significant share of respondents from an ASEAN-focused survey are not happy about rising American and Chinese influence in the region.
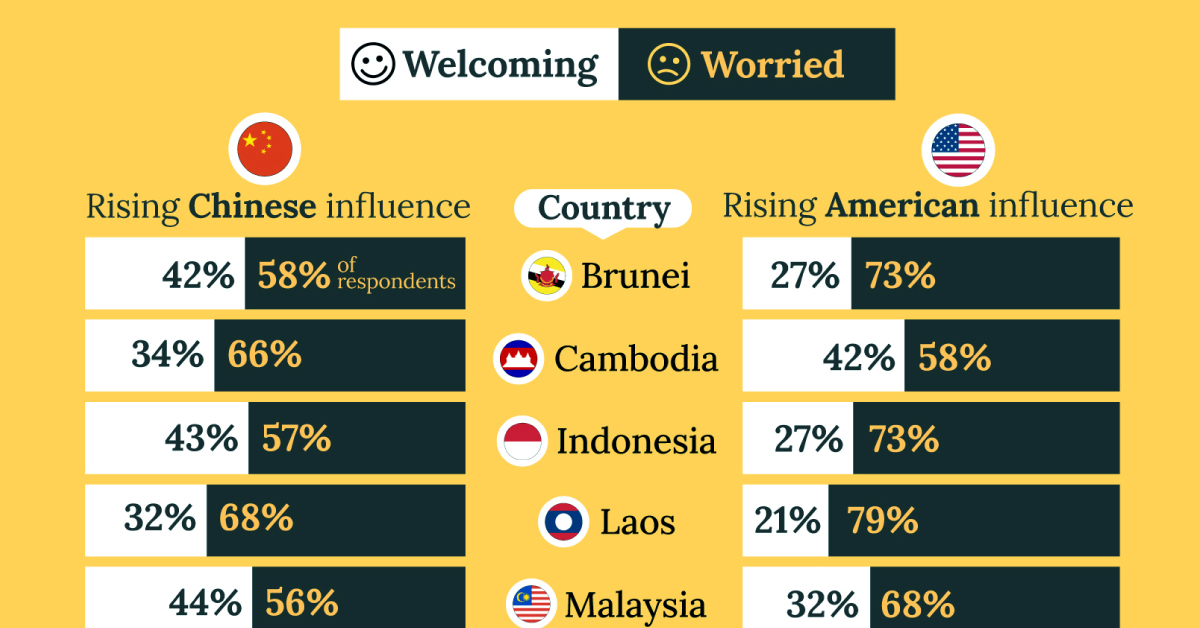
What Southeast Asia Thinks About China & the U.S.
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
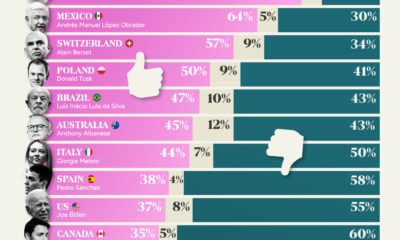
This chart visualizes the results of a 2024 survey conducted by the ASEAN Studies Centre at the ISEAS-Yusof Ishak Institute. Nearly 2,000 respondents were asked if they were worried or welcoming of rising Chinese and American geopolitical influence in their country.
The countries surveyed all belong to the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), a political and economic union of 10 states in Southeast Asia.
Feelings Towards China
On average, a significant share of respondents from all 10 countries are worried about rising influence from both the U.S. and China.
However, overall skepticism is higher for China, at 74% (versus 59% for U.S.).
| Country | Worried About Growing 🇨🇳 Influence | Welcome Growing 🇨🇳 Influence |
|---|---|---|
| 🇧🇳 Brunei | 58% | 42% |
| 🇰🇭 Cambodia | 66% | 34% |
| 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 57% | 43% |
| 🇱🇦 Laos | 68% | 32% |
| 🇲🇾 Malaysia | 56% | 44% |
| 🇲🇲 Myanmar | 95% | 5% |
| 🇵🇭 Philippines | 81% | 19% |
| 🇸🇬 Singapore | 74% | 26% |
| 🇹🇭 Thailand | 84% | 16% |
| 🇻🇳 Vietnam | 96% | 4% |
| Average | 74% | 27% |
The recently-cooled but still active territorial concerns over the South China Sea may play a significant role in these responses, especially in countries which are also claimants over the sea.
For example, in Vietnam over 95% of respondents said they were worried about China’s growing influence.
Feelings Towards America
Conversely, rising American influence is welcomed in two countries with competing claims in the South China Sea, the Philippines (69%) and Vietnam (55%).
| Country | Worried About Growing 🇺🇸 Influence | Welcome Growing 🇺🇸 Influence |
|---|---|---|
| 🇧🇳 Brunei | 73% | 27% |
| 🇰🇭 Cambodia | 58% | 42% |
| 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 73% | 27% |
| 🇱🇦 Laos | 79% | 21% |
| 🇲🇾 Malaysia | 68% | 32% |
| 🇲🇲 Myanmar | 45% | 55% |
| 🇵🇭 Philippines | 32% | 69% |
| 🇸🇬 Singapore | 37% | 63% |
| 🇹🇭 Thailand | 80% | 20% |
| 🇻🇳 Vietnam | 45% | 55% |
| Average | 59% | 41% |
Despite this, on a regional average, more respondents worry about growing American influence (59%) than they welcome it (41%).
Interestingly, it seems almost every ASEAN nation has a clear preference for one superpower over the other.
The only exception is Thailand, where those surveyed were not a fan of either option, with 84% worried about China, and 80% worried about the U.S.
-

 Healthcare4 days ago
Healthcare4 days agoWhat Causes Preventable Child Deaths?
-

 voronoi2 weeks ago
voronoi2 weeks agoBest Visualizations of April on the Voronoi App
-

 Wealth2 weeks ago
Wealth2 weeks agoCharted: Which Country Has the Most Billionaires in 2024?
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoThe Top Private Equity Firms by Country
-

 Jobs1 week ago
Jobs1 week agoThe Best U.S. Companies to Work for According to LinkedIn
-

 Economy1 week ago
Economy1 week agoRanked: The Top 20 Countries in Debt to China
-
 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoCharted: Trust in Government Institutions by G7 Countries
-

 Energy1 week ago
Energy1 week agoMapped: The Age of Energy Projects in Interconnection Queues, by State