Technology
The 3 Types of Quantum Computers and Their Applications

The 3 Types of Quantum Computers and Their Applications
It’s an exciting time in computing.
Just days ago, Google’s AlphaGo AI took an insurmountable lead in the 3,000 year-old game of Go against the reigning world champion, Lee Sedol. In a five-game series, the score is now 3-1 for the machine with one game left on March 15, 2016 in Seoul, South Korea.
While IBM’s Deep Blue beat reigning chess champion Garry Kasparov in 1997 by using brute force, Go is a game with more possible moves than atoms in the known universe (literally). Therefore, the technology doesn’t yet exist to make such calculations in short amounts of time.
Google had to take a different approach: to beat the grand master, it needed to enable AlphaGo to self-improve through deep learning.
AlphaGo’s historical decision is a milestone for artificial intelligence, and now the technology community is anxiously waiting to see what’s next for AI. Some say that it is beating a human world champion at a real-time strategy game such as Starcraft, while others look to quantum computing – technology that could raise the potential power of AI exponentially.
What is Quantum Computing?
While everyday analog computing is limited to having a single value of either 0 or 1 for each bit, quantum computing uses quantum bits (qubits) that are simultaneously in both states (0 and 1) at the same time.
The consequence of this superposition, as it’s called, is that quantum computers are able to test every solution of a problem at once. Further, because of this exponential relationship, such computers should be able to double their quantum computing power with each additional qubit.
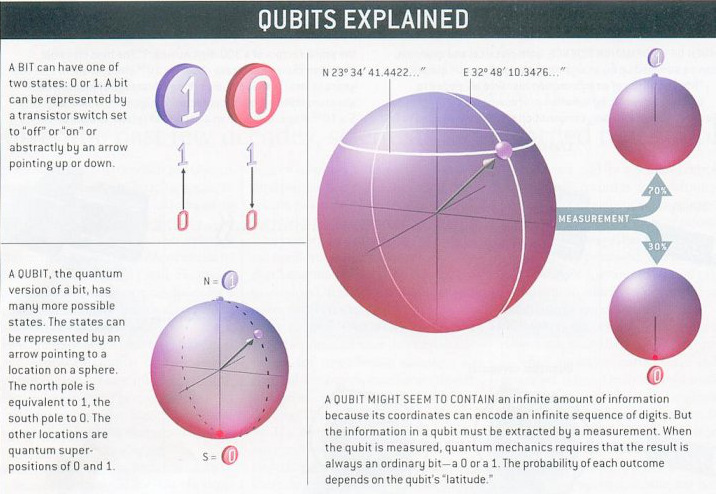
Image credit: Universe Review
Types of Quantum Computers
There are three types of quantum computers that are considered to be possible by IBM. Shown in the above infographic, they range from a quantum annealer to a universal quantum.
The quantum annealer has been successfully developed by Canadian company D-Wave, but it is difficult to tell whether it actually has any real “quantumness” thus far. Google added credibility to this notion in December 2015, when it revealed tests showing that its D-Wave quantum computer was 3,600 times faster than a supercomputer at solving specific, complex problems.
Expert opinion, however, is still skeptical on these claims. Such criticisms also shed light on the major limitation of quantum annealers, which is that they may only be engineered to solve very specific optimization problems, and have limited general practicality.
The holy grail of quantum computing is the universal quantum, which could allow for exponentially faster calculations with more generality.
However, building such a device ends up posing a number of important technical challenges. Quantum particles turn out to be quite fickle, and the smallest interference from light or sound can create errors in the computing process.
Doing calculations at exponential speeds is not very useful when those calculations are incorrect.
The Market and Applications
IBM highlights just some of the possibilities around universal quantum computers in a recent press release:
A universal quantum computer uses quantum mechanics to process massive amounts of data and perform computations in powerful new ways not possible with today’s conventional computers. This type of leap forward in computing could one day shorten the time to discovery for life-saving cancer drugs to a fraction of what it is today; unlock new facets of artificial intelligence by vastly accelerating machine learning; or safeguard cloud computing systems to be impregnable from cyber-attack.
This means that quantum computing could be a trillion dollar market, touching massive future markets such as artificial intelligence, robotics, defense, cryptography, and pharmaceuticals.
However, until a universal quantum can be built, the market remains fairly limited in size and focused on R&D. Quantum computing is expected to surpass a market of $5 billion market by 2020.
As a final note: its worth seeing where quantum computing sits on Gartner’s emerging technology hype cycle:
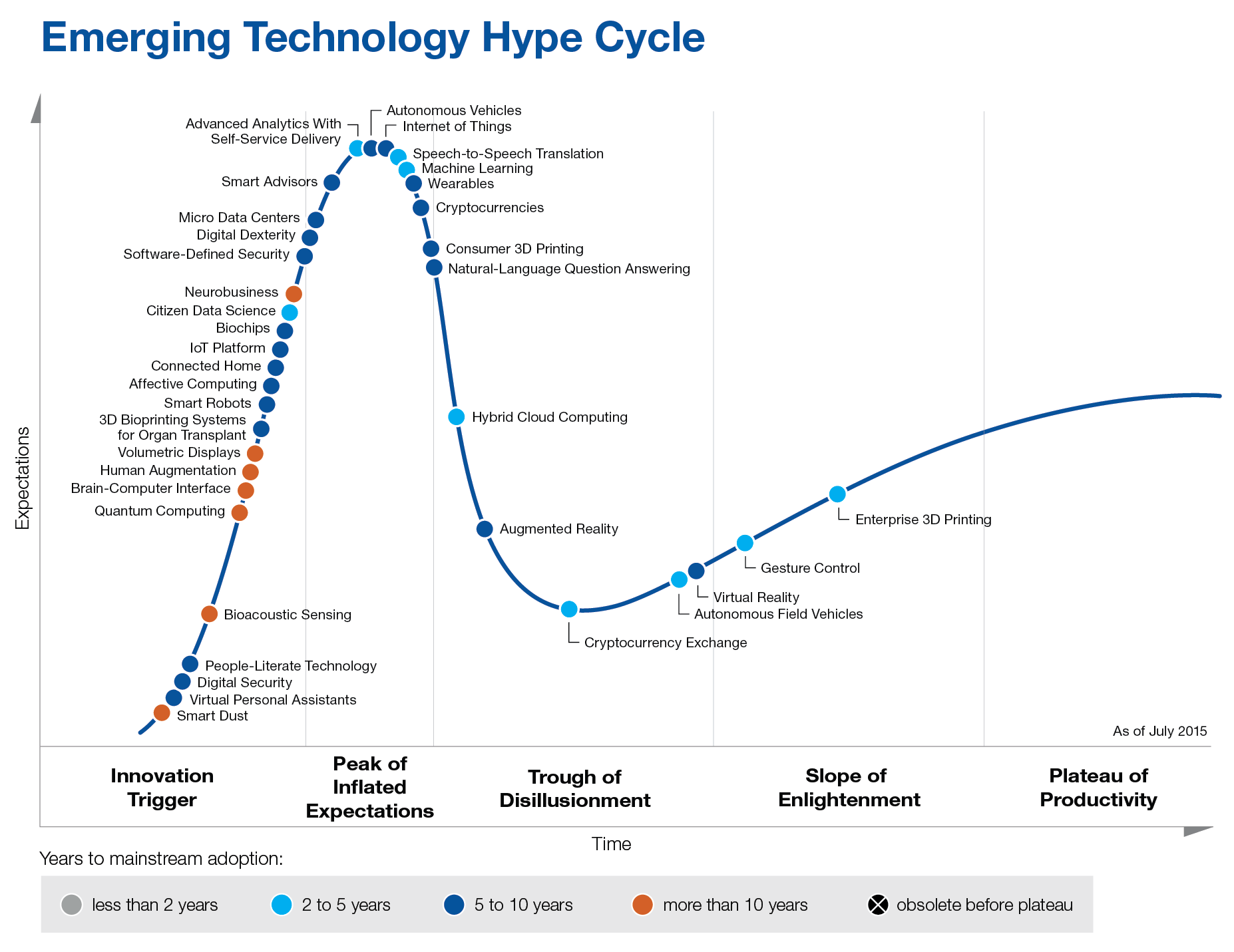
Gartner still describes it as being “10 years or more” away from reaching the plateau.
Technology
All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
Intel, TSMC, and more have received billions in subsidies from the U.S. CHIPS Act in 2024.

All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This visualization shows which companies are receiving grants from the U.S. CHIPS Act, as of April 25, 2024. The CHIPS Act is a federal statute signed into law by President Joe Biden that authorizes $280 billion in new funding to boost domestic research and manufacturing of semiconductors.
The grant amounts visualized in this graphic are intended to accelerate the production of semiconductor fabrication plants (fabs) across the United States.
Data and Company Highlights
The figures we used to create this graphic were collected from a variety of public news sources. The Semiconductor Industry Association (SIA) also maintains a tracker for CHIPS Act recipients, though at the time of writing it does not have the latest details for Micron.
| Company | Federal Grant Amount | Anticipated Investment From Company |
|---|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 Intel | $8,500,000,000 | $100,000,000,000 |
| 🇹🇼 TSMC | $6,600,000,000 | $65,000,000,000 |
| 🇰🇷 Samsung | $6,400,000,000 | $45,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Micron | $6,100,000,000 | $50,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 GlobalFoundries | $1,500,000,000 | $12,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Microchip | $162,000,000 | N/A |
| 🇬🇧 BAE Systems | $35,000,000 | N/A |
BAE Systems was not included in the graphic due to size limitations
Intel’s Massive Plans
Intel is receiving the largest share of the pie, with $8.5 billion in grants (plus an additional $11 billion in government loans). This grant accounts for 22% of the CHIPS Act’s total subsidies for chip production.
From Intel’s side, the company is expected to invest $100 billion to construct new fabs in Arizona and Ohio, while modernizing and/or expanding existing fabs in Oregon and New Mexico. Intel could also claim another $25 billion in credits through the U.S. Treasury Department’s Investment Tax Credit.
TSMC Expands its U.S. Presence
TSMC, the world’s largest semiconductor foundry company, is receiving a hefty $6.6 billion to construct a new chip plant with three fabs in Arizona. The Taiwanese chipmaker is expected to invest $65 billion into the project.
The plant’s first fab will be up and running in the first half of 2025, leveraging 4 nm (nanometer) technology. According to TrendForce, the other fabs will produce chips on more advanced 3 nm and 2 nm processes.
The Latest Grant Goes to Micron
Micron, the only U.S.-based manufacturer of memory chips, is set to receive $6.1 billion in grants to support its plans of investing $50 billion through 2030. This investment will be used to construct new fabs in Idaho and New York.
-

 Science7 days ago
Science7 days agoVisualizing the Average Lifespans of Mammals
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoThe Largest Earthquakes in the New York Area (1970-2024)
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: The Countries With the Most Air Pollution in 2023















