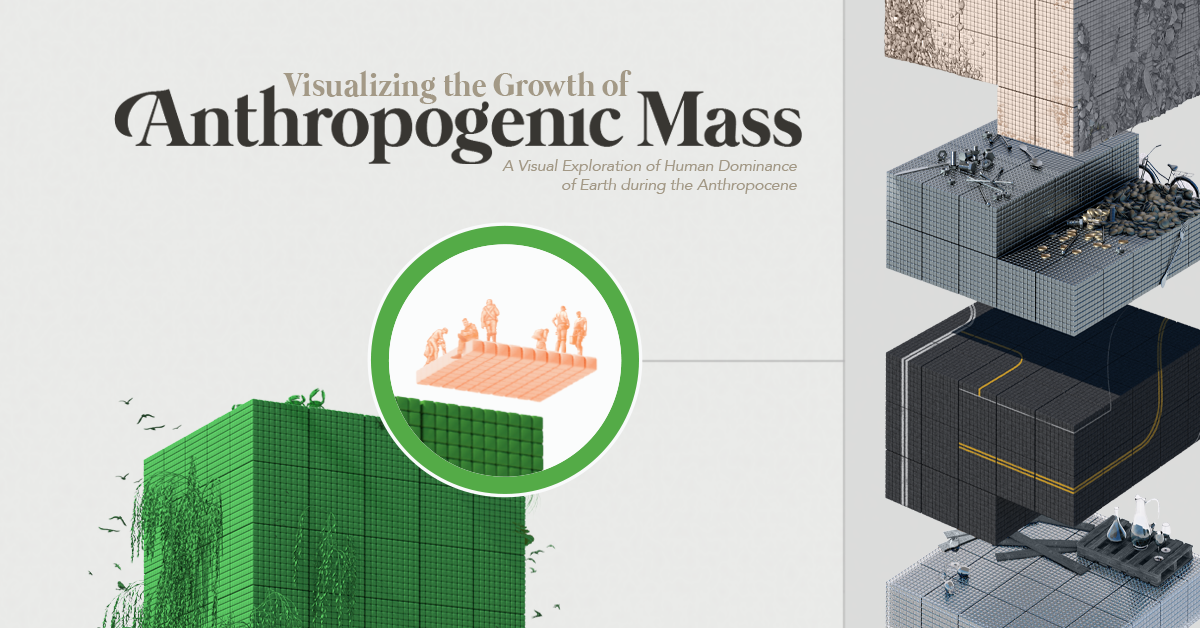
Green
Visualizing the Accumulation of Human-Made Mass on Earth
![]() Subscribe to the Elements free mailing list for more like this
Subscribe to the Elements free mailing list for more like this
Visualizing the Accumulation of Human-Made Mass on Earth
This was originally posted on Elements. Sign up to the free mailing list to get beautiful visualizations on natural resource megatrends in your email every week.
The world is not getting any bigger but the human population continues to grow, consuming more and more resources and altering the very environment we rely on.
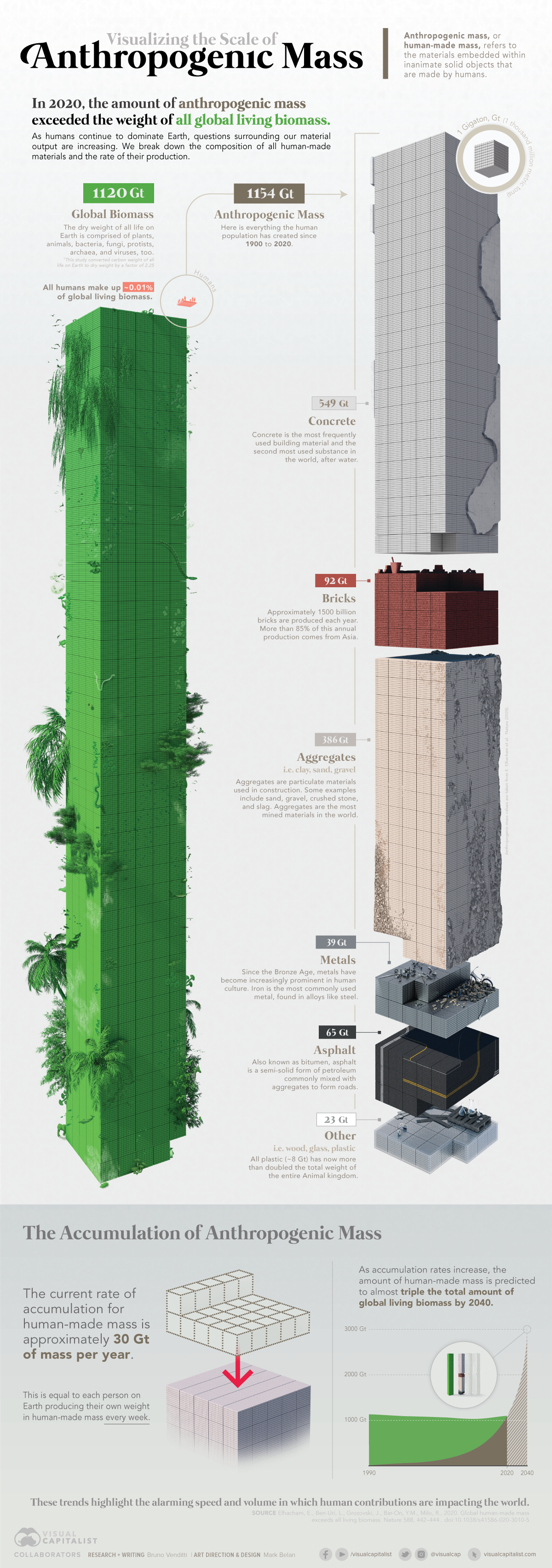
In 2020, the amount of human-made mass, or anthropogenic mass, exceeded for the first time the dry weight (except for water and fluids) of all life on Earth, including humans, animals, plants, fungi, and even microorganisms.
In this infographic based on a study published in Nature, we break down the composition of all human-made materials and the rate of their production.
A Man-made Planet
Anthropogenic mass is defined as the mass embedded in inanimate solid objects made by humans that have not been demolished or taken out of service—which is separately defined as anthropogenic mass waste.
Over the past century or so, human-made mass has increased rapidly, doubling approximately every 20 years. The collective mass of these materials has gone from 3% of the world’s biomass in 1900 to being on par with it today.
While we often overlook the presence of raw materials, they are what make the modern economy possible. To build roads, houses, buildings, printer paper, coffee mugs, computers, and all other human-made things, it requires billions of tons of fossil fuels, metals and minerals, wood, and agricultural products.
Human-Made Mass
Every year, we extract almost 90 billion tons of raw materials from the Earth. A single smartphone, for example, can carry roughly 80% of the stable elements on the periodic table.
The rate of accumulation for anthropogenic mass has now reached 30 gigatons (Gt)—equivalent to 30 billion metric tons—per year, based on the average for the past five years. This corresponds to each person on the globe producing more than his or her body weight in anthropogenic mass every week.
At the top of the list is concrete. Used for building and infrastructure, concrete is the second most used substance in the world, after water.
| Human-Made Mass | Description | 1900 (mass/Gt) | 1940 (mass/Gt) | 1980 (mass/Gt) | 2020 (mass/Gt) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concrete | Used for building and infrastructure, including cement, gravel and sand | 2 | 10 | 86 | 549 |
| Aggregates | Gravel and sand, mainly used as bedding for roads and buildings | 17 | 30 | 135 | 386 |
| Bricks | Mostly composed of clay and used for constructions | 11 | 16 | 28 | 92 |
| Asphalt | Bitumen, gravel and sand, used mainly for road construction/pavement | 0 | 1 | 22 | 65 |
| Metals | Mostly iron/steel, aluminum and copper | 1 | 3 | 13 | 39 |
| Other | Solid wood products, paper/paperboard, container and flat glass and plastic | 4 | 6 | 11 | 23 |
Bricks and aggregates like gravel and sand also represent a big part of human-made mass.
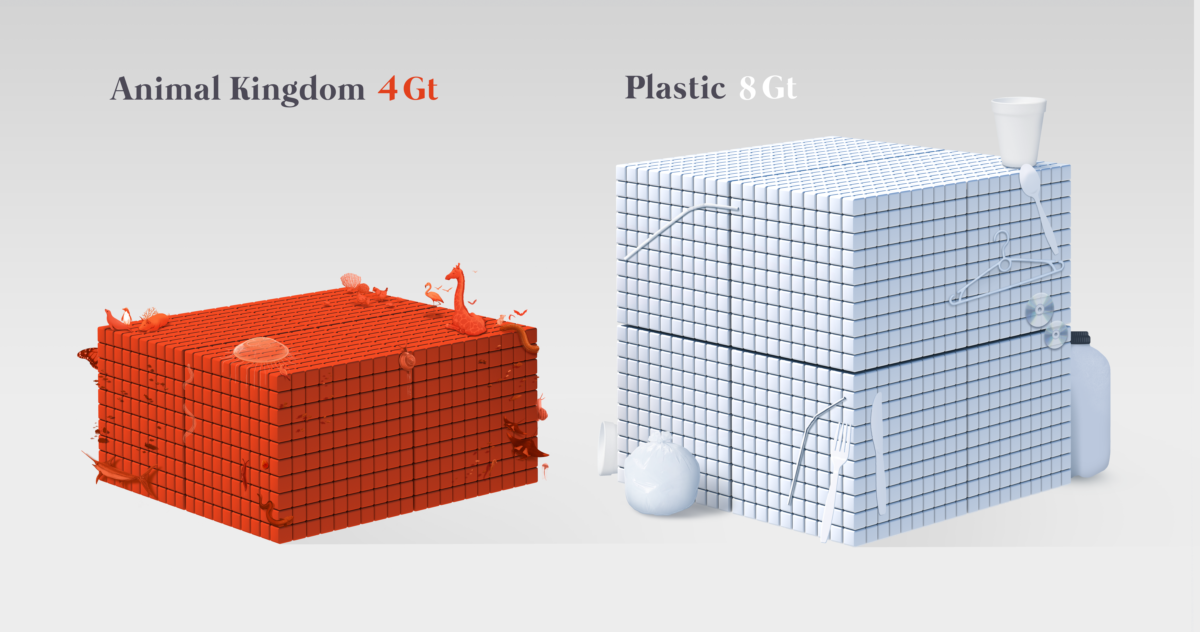
Although small compared to other materials in our list, the mass of plastic we’ve made is greater than the overall mass of all terrestrial and marine animals combined.
As the rate of growth of human-made mass continues to accelerate, it could become triple the total amount of global living biomass by 2040.
Can We Work It Out?
While the mass of humans is only about 0.01% of all biomass, our impact is like no other form of life on Earth. We are one of the few species that can alter the environment to the point of affecting all life.
At the current pace, the reserves of some materials like fossil fuels and minerals could run out in less than 100 years. As a result, prospectors are widening their search as they seek fresh sources of raw materials, exploring places like the Arctic, the deep sea, and even asteroids.
As the world population continues to increase, so does the pressure on the natural environment. It is an unavoidable fact that consumption will increase, but in an era of net-zero policies and carbon credits, accounting for the human impact on the environment will be more important than ever.
Environment
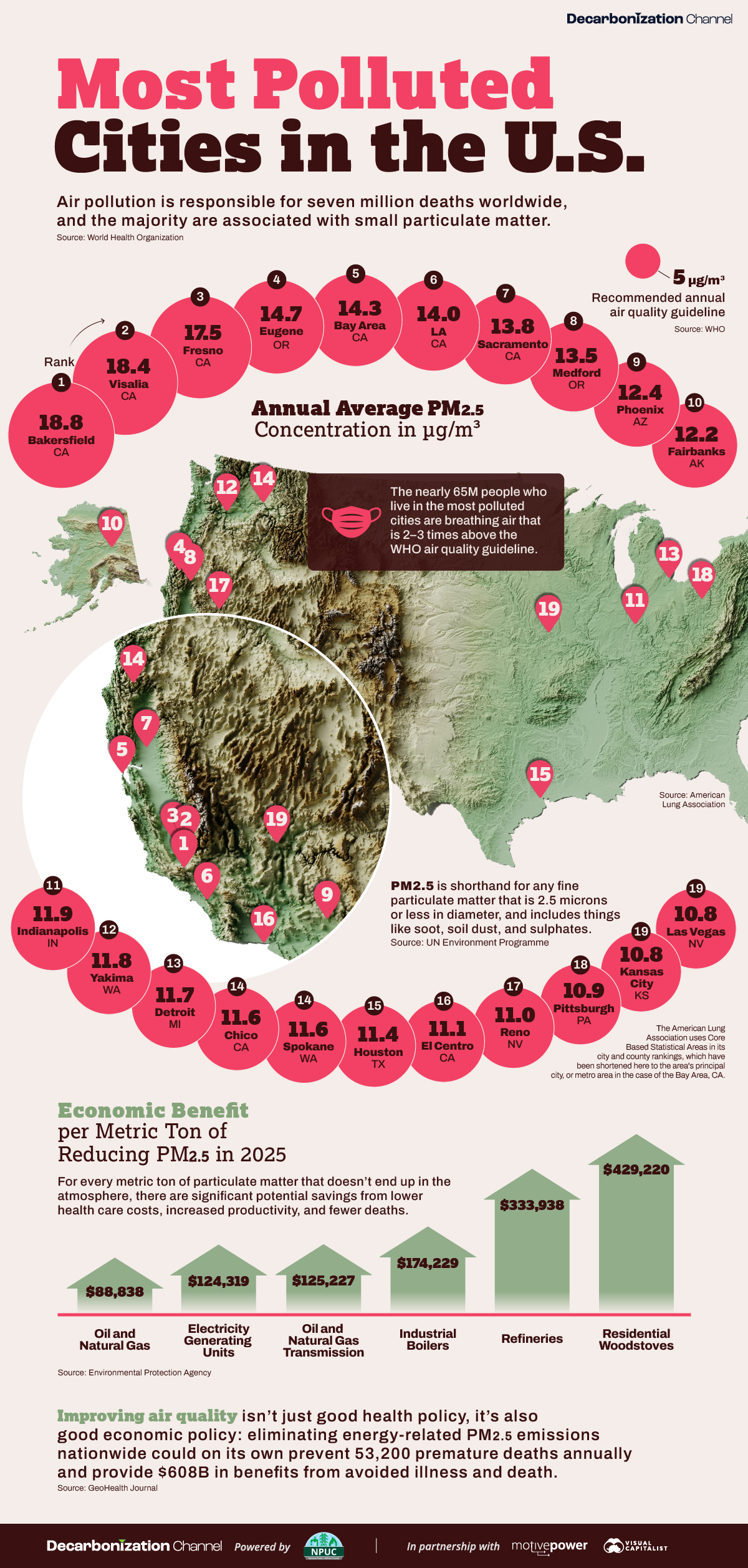
The Most Polluted Cities in the U.S.
What are the most polluted cities in the U.S. according to data from the American Lung Association’s 2024 State of the Air Report?
The Most Polluted U.S. Cities in 2024
According to the World Health Organization, air pollution is responsible for 7 million deaths annually, and could cost the global economy between $18–25 trillion by 2060 in annual welfare costs, or roughly 4–6% of world GDP.
And with predictions that 7 in 10 people will make their homes in urban centers by mid-century, cities are fast becoming one of the frontlines in the global effort to clear the air.
In this visualization, we use 2024 data from the State of the Air report from the American Lung Association to show the most polluted cities in the United States.
What is Air Pollution?
Air pollution is a complex mixture of gases, particles, and liquid droplets and can have a variety of sources, including wildfires and cookstoves in rural areas, and road dust and diesel exhaust in cities.
There are a few kinds of air pollution that are especially bad for human health, including ozone and carbon monoxide, but here we’re concerned with fine particulate matter that is smaller than 2.5 microns, or PM2.5 for short.
The reason for the focus is because at that small size, particulate matter can penetrate the bloodstream and cause all manner of havoc, including cardiovascular disease, lung cancer, and chronic pulmonary disease.
The American Lung Association has set an annual average guideline of 9 µg/m³ for PM2.5, however, the World Health Organization has set a much more stringent limit of 5 µg/m³.
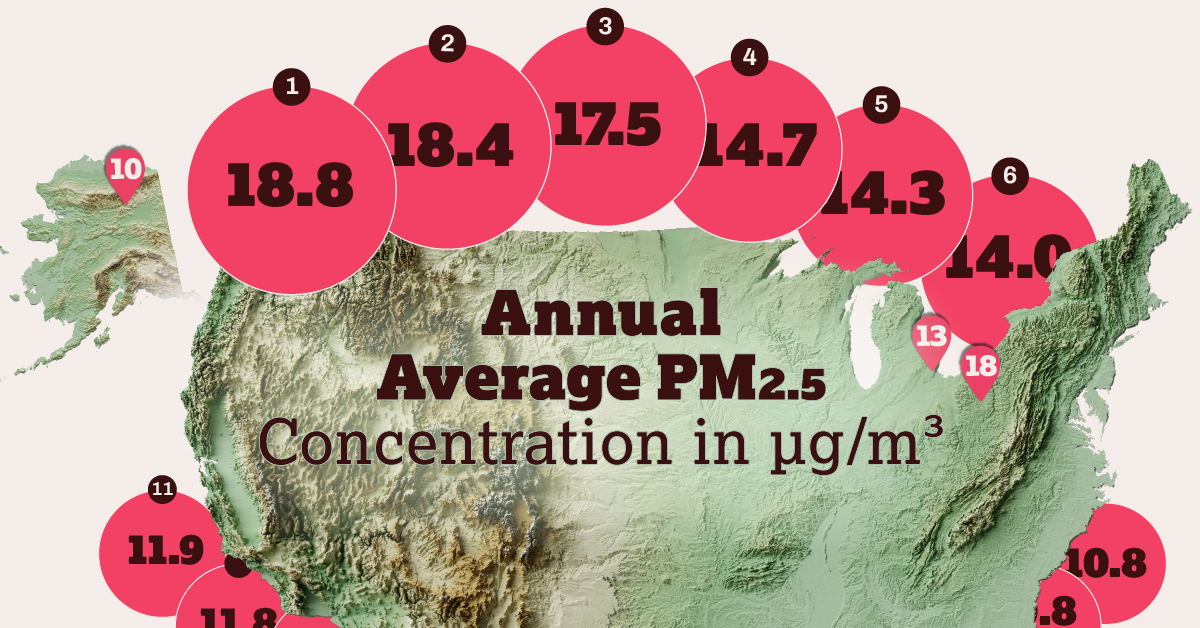
The 21 Worst Polluted Cities in the U.S.
Here are the top 21 most polluted cities in the U.S., according to their annual average PM2.5 concentrations:
| Rank | City, State | Annual average concentration, 2020-2022 (µg/m3) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bakersfield, CA | 18.8 |
| 2 | Visalia, CA | 18.4 |
| 3 | Fresno, CA | 17.5 |
| 4 | Eugene, OR | 14.7 |
| 5 | Bay Area, CA | 14.3 |
| 6 | Los Angeles, CA | 14.0 |
| 7 | Sacramento, CA | 13.8 |
| 8 | Medford, OR | 13.5 |
| 9 | Phoenix, AZ | 12.4 |
| 10 | Fairbanks, AK | 12.2 |
| 11 | Indianapolis, IN | 11.9 |
| 12 | Yakima, WA | 11.8 |
| 13 | Detroit, MI | 11.7 |
| T14 | Chico, CA | 11.6 |
| T14 | Spokane, WA | 11.6 |
| 15 | Houston, TX | 11.4 |
| 16 | El Centro, CA | 11.1 |
| 17 | Reno, NV | 11.0 |
| 18 | Pittsburgh, PA | 10.9 |
| T19 | Kansas City, KS | 10.8 |
| T19 | Las Vegas, NV | 10.8 |
Note: The American Lung Association uses Core Based Statistical Areas in its city and county rankings, which have been shortened here to the area’s principal city, or metro area in the case of the Bay Area, CA.
Six of the top seven cities are in California, and four in the state’s Central Valley, a 450-mile flat valley that runs parallel to the Pacific coast, and bordered by the Coast and Sierra Nevada mountain ranges. As a result, when pollution from the big population centers on the coast is carried inland by the wind—cities #5 and #6 on the list—it tends to get trapped in the valley.
Bakersfield (#1), Visalia (#2), and Fresno (#3) are located at the drier and hotter southern end of the valley, which is worse for air quality. The top three local sources of PM2.5 emissions in 2023 were farms (20%), forest management / agricultural waste burning (20%), and road dust (14%).
Benefit to Economy
While the health impacts are generally well understood, less well known are the economic impacts.
Low air quality negatively affects worker productivity, increases absenteeism, and adds both direct and indirect health care costs. But the flip side of that equation is that improving air quality has measurable impacts to the wider economy. The EPA published a study that calculated the economic benefits of each metric ton of particulate matter that didn’t end up in the atmosphere, broken down by sector.
| Sector | Benefits per metric ton |
|---|---|
| Residential Woodstoves | $429,220 |
| Refineries | $333,938 |
| Industrial Boilers | $174,229 |
| Oil and Natural Gas Transmission | $125,227 |
| Electricity Generating Units | $124,319 |
| Oil and Natural Gas | $88,838 |
At the same time, the EPA recently updated a cost-benefit analysis of the Clean Air Act, the main piece of federal legislation governing air quality, and found that between 1990 and 2020 it cost the economy roughly $65 billion, but also provided $2 trillion in benefits.
Benefit to Business
But that’s at the macroeconomic level, so what about for individual businesses?
For one, employees like to breathe clean air and will choose to work somewhere else, given a choice. A 2022 Deloitte case study revealed that nearly 70% of highly-skilled workers said air quality was a significant factor in choosing which city to live and work in.
At the same time, air quality can impact employer-sponsored health care premiums, by reducing the overall health of the risk pool. And since insurance premiums averaged $7,590 per year in 2022 for a single employee, and rose to $21,931 for a family, that can add up fast.
Consumers are also putting their purchase decisions through a green lens, while ESG, triple-bottom-line, and impact investing are putting the environment front and center for many investors.
And if the carrot isn’t enough for some businesses, there is the stick. The EPA recently gave vehicle engine manufacturer Cummins nearly two billion reasons to help improve air quality, in a settlement the agency is calling “the largest civil penalty in the history of the Clean Air Act and the second largest environmental penalty ever.”

Learn how the National Public Utilities Council is working toward the future of sustainable electricity.

-

 Environment1 month ago
Environment1 month agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
The country with the most forest loss since 2001 lost as much forest cover as the next four countries combined.
-

 Environment3 months ago
Environment3 months agoCharted: Share of World Forests by Country
We visualize which countries have the biggest share of world forests by area—and while country size plays a factor, so too, does the environment.
-
 Environment4 months ago
Environment4 months agoWhich Countries Have the Largest Forests?
Together, the top five countries with the largest forests account for more than half of the world’s entire forest cover.
-
 Environment5 months ago
Environment5 months agoVisualized: What Lives in Your Gut Microbiome?
The human gut microbiome contains a world of microbes. We look at the the bacteria that deeply affect our health and well-being.
-

 Environment5 months ago
Environment5 months agoMapped: Global Temperature Rise by Country (2022-2100P)
In this set of three maps, we show the global temperature rise on a national level for 2022, 2050, and 2100 based on an analysis by…
-
 Environment5 months ago
Environment5 months agoRanked: Per Capita Carbon Emissions by Country
Which countries rank the highest in per capita carbon emissions, and how do they impact the world’s total carbon emissions?
-
 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoCountries With the Highest Rates of Crypto Ownership
-

 Mining6 days ago
Mining6 days agoVisualizing Copper Production by Country in 2023
-
 Politics7 days ago
Politics7 days agoCharted: How Americans Feel About Federal Government Agencies
-
 Healthcare1 week ago
Healthcare1 week agoWhich Countries Have the Highest Infant Mortality Rates?
-
 Demographics1 week ago
Demographics1 week agoMapped: U.S. Immigrants by Region
-
 Economy1 week ago
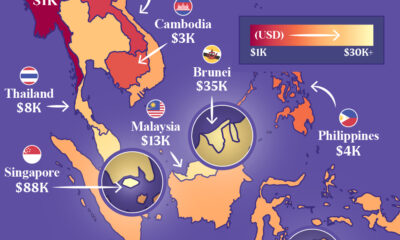
Economy1 week agoMapped: Southeast Asia’s GDP Per Capita, by Country
-
 Automotive1 week ago
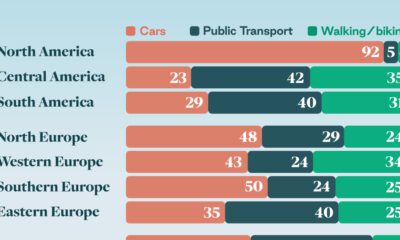
Automotive1 week agoHow People Get Around in America, Europe, and Asia
-

 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week agoVisualizing the Tax Burden of Every U.S. State