Technology
The Future of Homes: From Smart to Autonomous
For years, consumers have been promised that their homes will be connected and smart, integrating the latest technology to optimize and control lighting, heating, energy consumption, electronic devices, and security features.
However, the future has come a little slower than expected. By the end of 2017, it’s estimated that only 16.3% of Americans will live in a smart home, though this percentage will increase to 35.6% by 2021.
Examining the Smart Home Market
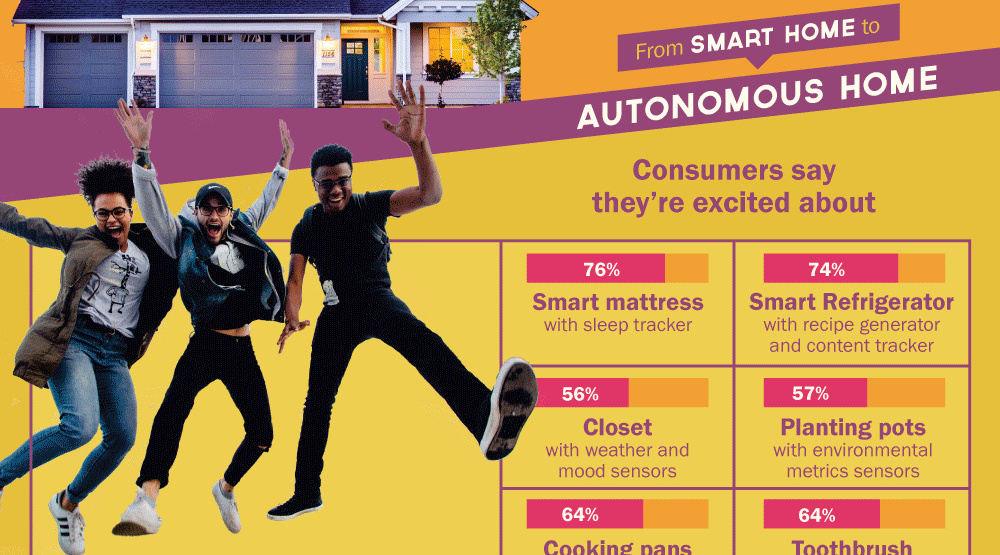
Today’s infographic comes from Insurance Quotes, and it helps to give an overview of the current market as well as the reasons for hesitation in the switch to smart homes.
The infographic also provides a future outlook, including the impending movement to “autonomous” smart homes.

In 2016, smart systems were installed in about 45% of all homes in the U.S. that got renovated.
However, they are far from ubiquitous yet – many consumers still have concerns that are holding the market back from reaching its full potential.
Top Trepidations
The largest hindrance to smart homes for now is cost, which is cited by 42% of consumers as an obstacle.
However, there is also evidence that a fear of devices being hacked is also a challenge for many wanting to adopt the technology – in fact, 17% prospective buyers cite privacy and security concerns as a top hindrance. Further, about 10% of consumers have already had smart home devices hacked, and 87% of them had to shell out money to solve the issue.
Paradoxically, even though technologically superior security systems are a top reason that homeowners want to have smarter homes in the first place, the vast majority of IT experts say that IoT apps such as those used at home are far harder to secure than regular mobile apps.
Autonomous Smart Homes
After smart homes, the next logical step is an autonomous smart home that can learn based on your habits and behaviors. Such a home would recognize you and other family members, adapting things like temperature, lighting, or recommendations to you automatically based on your lifestyle and activities.
For this to work – everything would need to be truly connected: your mattress would assess how you sleep, your alarm would connect to your coffee maker, and the morning lighting would be shifted to match your evolving preferences.
While there are many uncertainties about what an autonomous smart home would mean, the inevitability of their rise is clear.
Technology
All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
Intel, TSMC, and more have received billions in subsidies from the U.S. CHIPS Act in 2024.

All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This visualization shows which companies are receiving grants from the U.S. CHIPS Act, as of April 25, 2024. The CHIPS Act is a federal statute signed into law by President Joe Biden that authorizes $280 billion in new funding to boost domestic research and manufacturing of semiconductors.
The grant amounts visualized in this graphic are intended to accelerate the production of semiconductor fabrication plants (fabs) across the United States.
Data and Company Highlights
The figures we used to create this graphic were collected from a variety of public news sources. The Semiconductor Industry Association (SIA) also maintains a tracker for CHIPS Act recipients, though at the time of writing it does not have the latest details for Micron.
| Company | Federal Grant Amount | Anticipated Investment From Company |
|---|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 Intel | $8,500,000,000 | $100,000,000,000 |
| 🇹🇼 TSMC | $6,600,000,000 | $65,000,000,000 |
| 🇰🇷 Samsung | $6,400,000,000 | $45,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Micron | $6,100,000,000 | $50,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 GlobalFoundries | $1,500,000,000 | $12,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Microchip | $162,000,000 | N/A |
| 🇬🇧 BAE Systems | $35,000,000 | N/A |
BAE Systems was not included in the graphic due to size limitations
Intel’s Massive Plans
Intel is receiving the largest share of the pie, with $8.5 billion in grants (plus an additional $11 billion in government loans). This grant accounts for 22% of the CHIPS Act’s total subsidies for chip production.
From Intel’s side, the company is expected to invest $100 billion to construct new fabs in Arizona and Ohio, while modernizing and/or expanding existing fabs in Oregon and New Mexico. Intel could also claim another $25 billion in credits through the U.S. Treasury Department’s Investment Tax Credit.
TSMC Expands its U.S. Presence
TSMC, the world’s largest semiconductor foundry company, is receiving a hefty $6.6 billion to construct a new chip plant with three fabs in Arizona. The Taiwanese chipmaker is expected to invest $65 billion into the project.
The plant’s first fab will be up and running in the first half of 2025, leveraging 4 nm (nanometer) technology. According to TrendForce, the other fabs will produce chips on more advanced 3 nm and 2 nm processes.
The Latest Grant Goes to Micron
Micron, the only U.S.-based manufacturer of memory chips, is set to receive $6.1 billion in grants to support its plans of investing $50 billion through 2030. This investment will be used to construct new fabs in Idaho and New York.
-

 Brands6 days ago
Brands6 days agoHow Tech Logos Have Evolved Over Time
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoThe Largest Earthquakes in the New York Area (1970-2024)
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: The Countries With the Most Air Pollution in 2023
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanking the Top 15 Countries by Carbon Tax Revenue