Technology
This Paper Map Shows the Extent of the Entire Internet in 1973
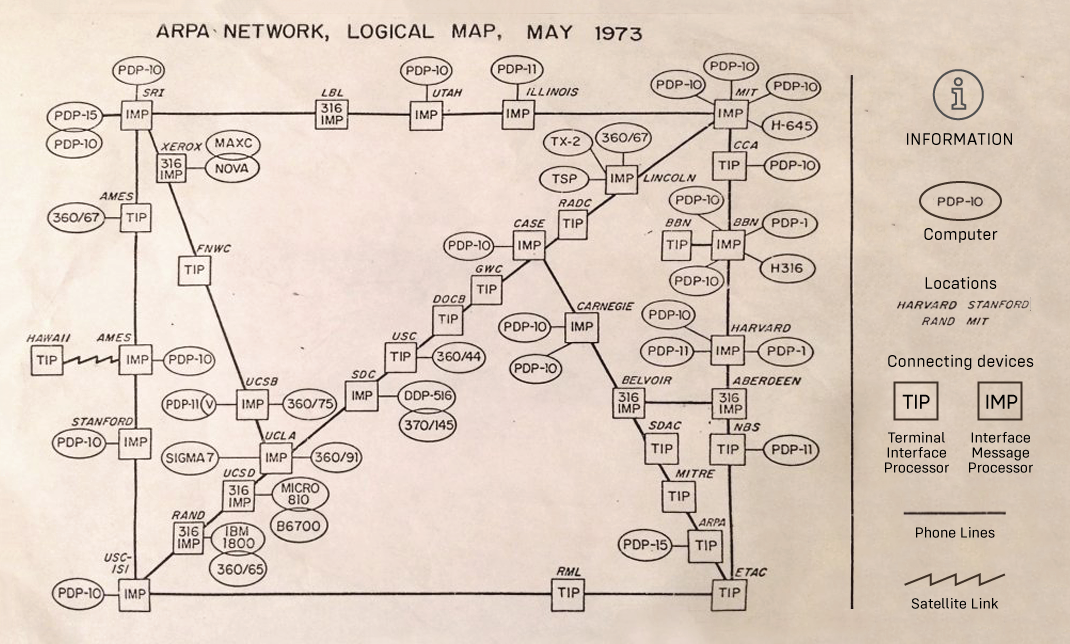
This Map Shows the Extent of the Entire Internet in 1973
Before the modern internet, there was ARPANET.
ARPANET was the first internet-like network, and it was developed to allow multiple computers to share data across vast geographical distances. Interestingly, the researchers that worked on ARPANET are credited with developing many of the communication protocols that the internet still uses today.
Today’s map comes from David Newbury, who shared a keepsake from his father’s time as a computer science business manager at Carnegie Mellon University in the 1970s. We added a legend to help explain the symbols on the map.
A Brief History of ARPANET
ARPANET was funded in the late 1960s by a branch of the U.S. Military called The Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA), with the original purpose being to allow researchers at different universities to use their limited computing resources more efficiently.
Before ARPANET, if a researcher at Harvard wanted to access a database at Stanford, they had to travel there and use it in person. ARPANET was used to test out a new communication technology known as packet-switching, which broke up data into smaller “packets” and allowed various computers on the network to access the data.
With ARPANET researchers could:
- Login to another computer miles away
- Transfer and save files across the network
- Send emails from one person to several others
On the map above, you can see the network only had computers in the United States, but later that same year, a satellite link connected the ARPANET to Norway, creating the beginnings of a global network.
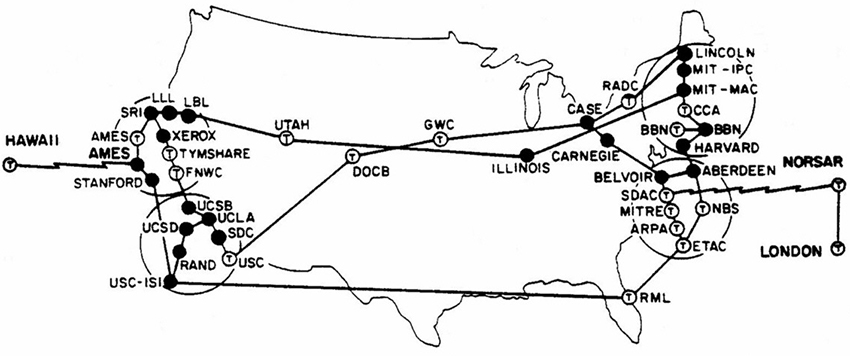
A Network of Networks
In 1983, ARPANET adopted the TCP/IP protocol standards which paved the way for a “network of networks”, and the internet was born. Several years later, ARPANET would be decommissioned and the new internet would begin to flourish.
Below you can see what the early internet looked like in 1984:
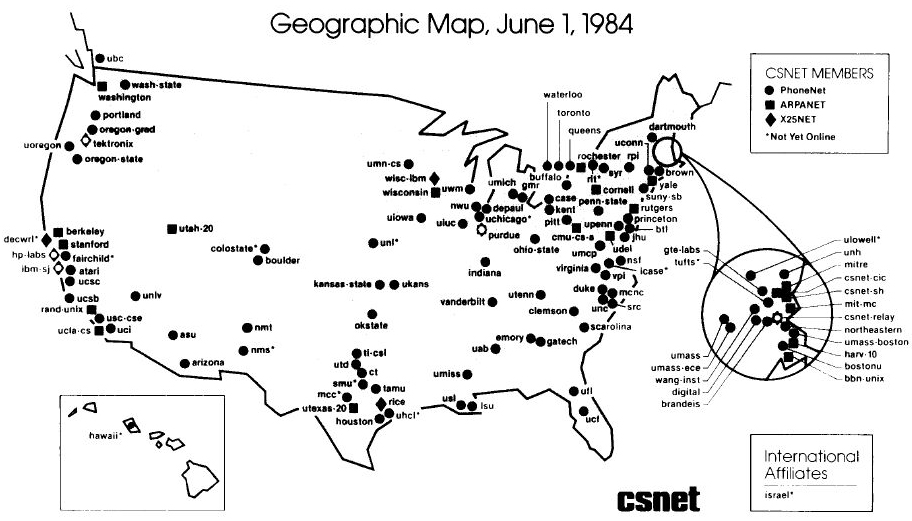
A Big Jump
These maps take us back to a simpler time when social networks, mobile phones, and unlimited access to the world’s information did not yet exist. Even 12 years after the first message was transmitted on the ARPANET, there were still only 213 computers on the network.
Fast forward a few decades later and the change in scale is mind-boggling – the modern internet has 1.94 billion websites and 4.1 billion internet users globally, resembling a digital universe.
One can only imagine how quaint the ARPANET will look a few more decades from now.
An earlier version of this article said the ARPANET was first connected internationally to the United Kingdom, but in fact, it was with Norway.
Technology
All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
Intel, TSMC, and more have received billions in subsidies from the U.S. CHIPS Act in 2024.

All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This visualization shows which companies are receiving grants from the U.S. CHIPS Act, as of April 25, 2024. The CHIPS Act is a federal statute signed into law by President Joe Biden that authorizes $280 billion in new funding to boost domestic research and manufacturing of semiconductors.
The grant amounts visualized in this graphic are intended to accelerate the production of semiconductor fabrication plants (fabs) across the United States.
Data and Company Highlights
The figures we used to create this graphic were collected from a variety of public news sources. The Semiconductor Industry Association (SIA) also maintains a tracker for CHIPS Act recipients, though at the time of writing it does not have the latest details for Micron.
| Company | Federal Grant Amount | Anticipated Investment From Company |
|---|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 Intel | $8,500,000,000 | $100,000,000,000 |
| 🇹🇼 TSMC | $6,600,000,000 | $65,000,000,000 |
| 🇰🇷 Samsung | $6,400,000,000 | $45,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Micron | $6,100,000,000 | $50,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 GlobalFoundries | $1,500,000,000 | $12,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Microchip | $162,000,000 | N/A |
| 🇬🇧 BAE Systems | $35,000,000 | N/A |
BAE Systems was not included in the graphic due to size limitations
Intel’s Massive Plans
Intel is receiving the largest share of the pie, with $8.5 billion in grants (plus an additional $11 billion in government loans). This grant accounts for 22% of the CHIPS Act’s total subsidies for chip production.
From Intel’s side, the company is expected to invest $100 billion to construct new fabs in Arizona and Ohio, while modernizing and/or expanding existing fabs in Oregon and New Mexico. Intel could also claim another $25 billion in credits through the U.S. Treasury Department’s Investment Tax Credit.
TSMC Expands its U.S. Presence
TSMC, the world’s largest semiconductor foundry company, is receiving a hefty $6.6 billion to construct a new chip plant with three fabs in Arizona. The Taiwanese chipmaker is expected to invest $65 billion into the project.
The plant’s first fab will be up and running in the first half of 2025, leveraging 4 nm (nanometer) technology. According to TrendForce, the other fabs will produce chips on more advanced 3 nm and 2 nm processes.
The Latest Grant Goes to Micron
Micron, the only U.S.-based manufacturer of memory chips, is set to receive $6.1 billion in grants to support its plans of investing $50 billion through 2030. This investment will be used to construct new fabs in Idaho and New York.
-

 Debt1 week ago
Debt1 week agoHow Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees



