The Recession Playbook: Three Strategies for Investors
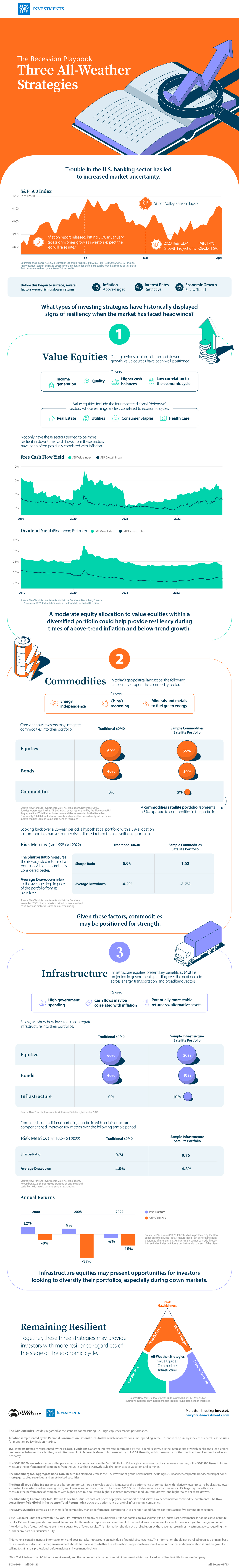
The Recession Playbook: Three Strategies for Investors
Concerns about the economy and trouble in the U.S. banking sector have led to increased market uncertainty.
Before this began to surface, several factors were driving slower returns:
- Inflation: Above-Target
- Interest Rates: Restrictive
- Economic Growth: Below Trend
In this graphic from New York Life Investments, we look at three recession investment strategies that have historically been resilient when the market has faced headwinds.
1. Value Equities
During periods of high inflation and slower growth, value equities have been well-positioned as a recession investment strategy, thanks to the following factors:
- Income generation
- Quality
- High cash balances
- Low correlation to the economic cycle
Value equities include the four most traditional “defensive” sectors, whose earnings are less correlated to economic cycles:
- Real Estate
- Utilities
- Consumer Staples
- Health Care
Not only have these sectors tended to be more resilient in downturns; cash flows from these sectors have been often positively correlated with inflation.
A moderate equity allocation to value equities within a diversified portfolio could help provide resiliency during times of above-trend inflation and below-trend growth.
2. Commodities
In today’s geopolitical landscape, there are a number of factors that may support the commodity sector, including:
- Energy independence
- China’s reopening
- Minerals and metals to fuel green energy
With this in mind, here’s how investors may integrate commodities into their portfolio.
| Traditional 60/40 | Sample Commodities Satellite Portfolio | |
|---|---|---|
| Equities | 60% | 55% |
| Bonds | 40% | 40% |
| Commodities | 0% | 5% |
As the above table shows, the commodities satellite portfolio represented a 5% exposure to commodity firms in the portfolio.
Next, when looking back over a 25-year period, a hypothetical portfolio with a 5% allocation to commodities had a stronger risk-adjusted return than a traditional portfolio. This can be seen in its Sharpe Ratio, which measures the risk-adjusted returns of a portfolio. A higher number is considered better.
| Risk Metrics (Jan 1998-Oct 2022) | Traditional 60/40 | Sample Commodities Satellite Portfolio |
|---|---|---|
| Sharpe Ratio | 0.96 | 1.02 |
| Average Drawdown | -4.2% | -3.7% |
Given these factors, commodities may be positioned for strength.
3. Infrastructure
Infrastructure equities present key benefits as $1.3 trillion is projected in government spending over the next decade across energy, transportation, and broadband sectors.
Here are a few key drivers supporting infrastructure as part of a recession investment strategy:
- High government spending
- Cash flows may be correlated with inflation
- Potentially more stable returns vs. alternative assets
Below, we show how investors can incorporate infrastructure into their portfolios.
| Traditional 60/40 | Sample Infrastructure Satellite Portfolio | |
|---|---|---|
| Equities | 60% | 50% |
| Bonds | 40% | 40% |
| Infrastructure Equities | 0% | 10% |
As we can see, the infrastructure portfolio included a 10% allocation to stocks in the sector. Compared to a traditional portfolio, a portfolio with an infrastructure component had improved risk metrics between the period of January 1998 and October 2022.
| Risk Metrics (Jan 1998-Oct 2022) | Traditional 60/40 | Sample Commodities Satellite Portfolio |
|---|---|---|
| Sharpe Ratio | 0.74 | 0.76 |
| Average Drawdown | -4.5% | -4.3% |
Moreover, the infrastructure sector has been resilient when the market slides. For instance, the Dow Jones Brookfield Global Infrastructure Index outperformed the S&P 500 Index by a wide margin in 2022, 2008, and 2000 when the market faced increased turmoil.
In this way, infrastructure equities may present opportunities for investors looking to diversify their portfolios, especially as a recession investment strategy.
Remaining Resilient With a Recession Investment Strategy
Together, these three strategies may provide investors with more resilience regardless of the stage of the economic cycle:
- Value Equities
- Commodities
- Infrastructure
Thanks to each of their specific attributes, investors can equip themselves with a recession investment strategy that may help offset the unexpected swings of the market cycle.

Learn more about all-weather strategies with New York Life Investments.

-

 Economy1 day ago
Economy1 day agoEconomic Growth Forecasts for G7 and BRICS Countries in 2024
The IMF has released its economic growth forecasts for 2024. How do the G7 and BRICS countries compare?
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
U.S. debt interest payments have surged past the $1 trillion dollar mark, amid high interest rates and an ever-expanding debt burden.
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
We visualized the top U.S. companies by employees, revealing the massive scale of retailers like Walmart, Target, and Home Depot.
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
This graphic shows the states with the highest real GDP growth rate in 2023, largely propelled by the oil and gas boom.
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
In this graphic, we show the highest earning flight routes globally as air travel continued to rebound in 2023.
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
The U.S. residential real estate market is worth a staggering $47.5 trillion. Here are the most valuable housing markets in the country.

