5 Drivers Behind the Growth of the GPU Cloud Computing Market
5 Drivers Behind the Growth of the GPU Cloud Computing Market
Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) are specialized computer chips originally designed for use in gaming, but have recently found a second life on the cloud because of their capabilities in high performance computing.
GPUs use parallel processing to efficiently and effectively solve complex problems across a wide range of domains, much faster than the serial processing approach of CPUs.
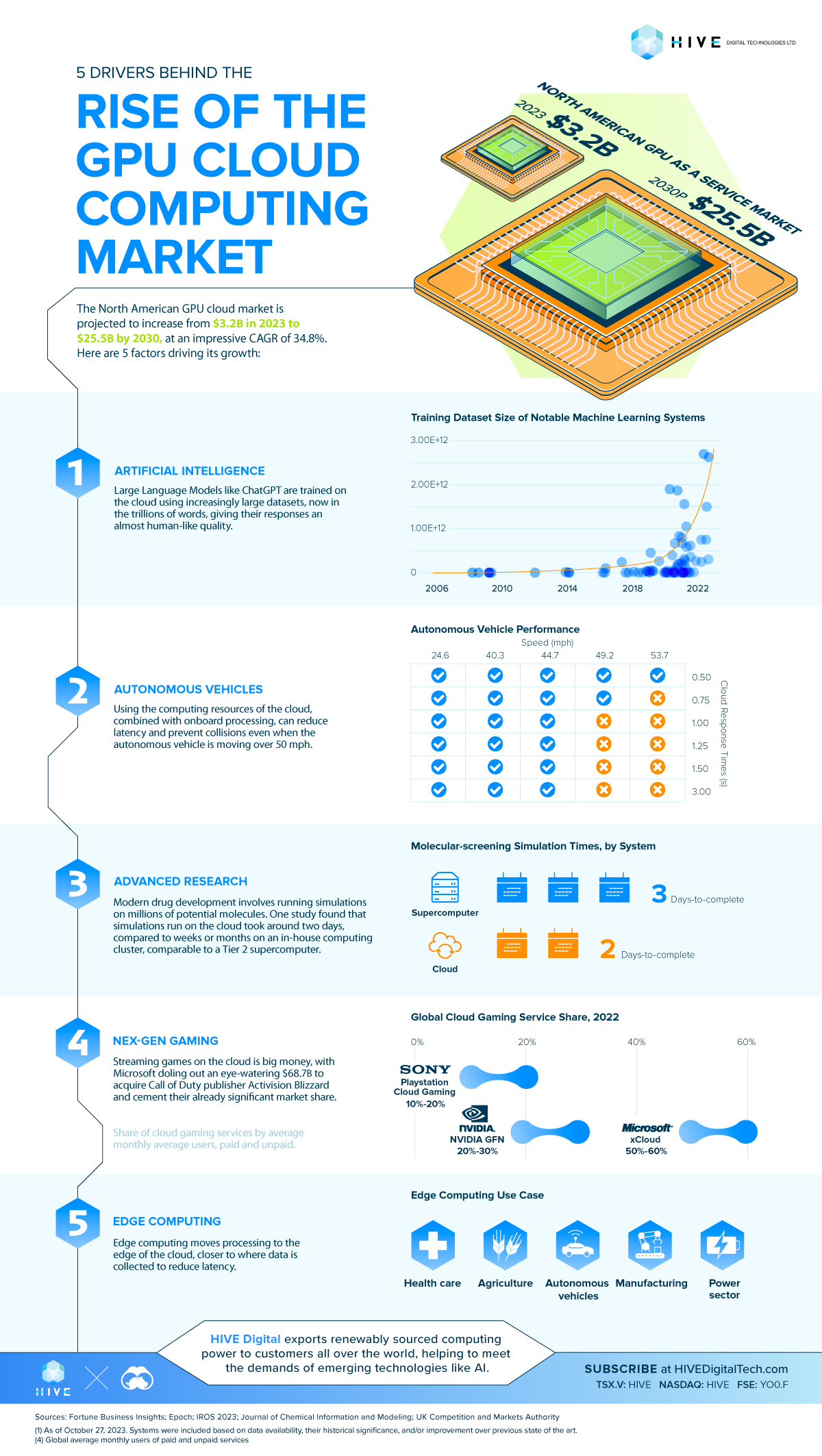
In this visualization for HIVE Digital, we look at five drivers behind the growth of the GPU cloud computing market.
1. Artificial Intelligence
Large Language Models, like OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Google’s Bard, have surpassed human performance on a variety of tasks in part because of increasingly large training datasets.
In 2008, a NEC Laboratories model used a training package with 6.33 x 108 (633 million) datapoints. By 2023, an Abu-Dhabi-based lab used a training dataset with 2.63 x 1012 (2.63 trillion) datapoints, 10,000 times larger than 15 years earlier.
2. Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles collect huge amounts of data from a host of onboard sensors—potentially between 380 and 5,100 terabytes every year—and finding an effective and efficient way of processing that information has been a key focus for carmakers.
One approach, which combines onboard processing power with the resources of the cloud, prevented collisions in simulations of vehicles moving up to 45 mph, even when network lag was as high as 3 seconds. That improved to 50 mph when cloud response time was reduced to half a second.
3. Advanced Research
Modern drug development typically begins by running computer simulations on millions of candidate molecules to look for potential matches to advance to expensive, lab-based testing.
Normally these operations run on scarce high-performance computing resources that can take weeks or months to complete. A recent study that used the cloud was able to complete a typical dataset in around two days, comparable to a Tier 2 supercomputer.
4. Next-Gen Gaming
Streaming games on the cloud is big money, with Microsoft recently doling out an eye-watering $68.7 billion to acquire Call of Duty publisher Activision Blizzard and cement their already significant market share.
According to papers filed with the U.K. Competition and Markets Authority, Microsoft’s xCloud held 50-60% of the global cloud gaming market in 2022, twice that of second-place Nvidia. Google’s Stadia, on the other hand, had less than 5% of the market when they wound down operations in January 2023.
5. Edge Computing
When latency is critical for an application, the shorter the distance between the cloud and the user, the better.
That’s why edge computing—so named because processing happens at the ‘edge’ of the network—has become critical in industries as varied as health care and autonomous vehicles, where every fraction of a second counts.
Conclusion
So it’s no surprise that the global GPU cloud market is projected to increase from $3.2 billion in 2023 to $25.5 billion by 2030, at an impressive CAGR of 34.8%.
HIVE Digital exports renewably sourced computing power to customers all over the world, helping to meet the demands of emerging technologies like AI.

Subscribe to HIVE Digital’s newsletter to learn more.

-

 Technology1 day ago
Technology1 day agoAll of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
Intel, TSMC, and more have received billions in subsidies from the U.S. CHIPS Act in 2024.
-

 Technology3 days ago
Technology3 days agoVisualizing AI Patents by Country
See which countries have been granted the most AI patents each year, from 2012 to 2022.
-

 Brands5 days ago
Brands5 days agoHow Tech Logos Have Evolved Over Time
From complete overhauls to more subtle tweaks, these tech logos have had quite a journey. Featuring: Google, Apple, and more.
-

 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
Nvidia is coming for Intel’s crown. Samsung is losing ground. AI is transforming the space. We break down revenue for semiconductor companies.
-

 AI3 weeks ago
AI3 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
The Nvidia rocket ship is refusing to slow down, leading the pack of strong stock performance for most major U.S. chipmakers.
-

 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks agoRanked: The Most Popular Smartphone Brands in the U.S.
This graphic breaks down America’s most preferred smartphone brands, according to a December 2023 consumer survey.