Technology
Six Problems Facing Driverless Cars and Their Track Record

Six Problems Facing Driverless Cars and Their Track Record
Driverless car technology is here to stay. Their track record so far is very impressive with Google cars driving over a million miles since 2009. During that time, 13 accidents have been recorded, but all of them were caused by other drivers or by human intervention. The robots themselves have been virtually flawless.
Right now, various vehicle manufacturers (Mercedes-Benz, General Motors, Toyota, Tesla, Audi, and more) have already built prototypes of driverless cars, and tech companies (Google, Uber, and potentially even Apple) are working on similar ambitions.
However, human nature seems to be innately suspicious of robots and artificial intelligence. Whether we’re talking about Skynet from “The Terminator” or Elon Musk’s concerns about AI, it’s clear that there will always be some pushback towards these kinds of ideas. It may take decades to convince people that autonomous cars will solve more problems than they create.
For these reasons, regulations around driverless cars are likely to move forward with a speed rivaling that of molasses. Policy makers do not want to be held responsible for potential hiccups, and much of the populace that is not in Silicon Valley will be slow to embrace ideas that could change the entire status quo.
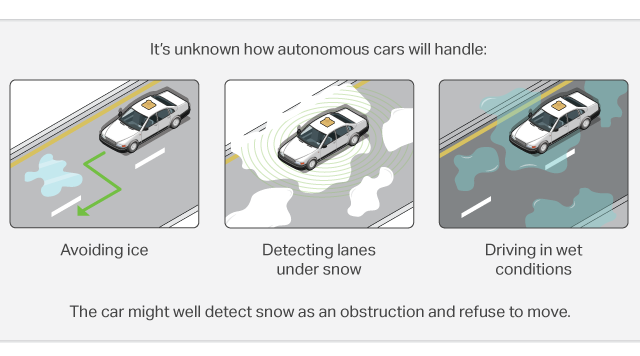
Beyond general human suspicion of robots, there are some legitimate obstacles that need to be solved before driverless cars become a reality. Today’s infographic highlights some of these issues that need to be addressed:
Firstly, driverless cars struggle to identify humans alongside the vehicle or walking in front of them. This could lead to situations where they fail to see police officers, pedestrians, or workers on the side of construction zones giving instructions. Next, autonomous cars have a tough time in bad weather conditions in which an entire new array of problems are created for the algorithms to solve. Driving in Silicon Valley may be relatively straightforward, but what happens when a car encounters a snow storm in the Northeast, or torrential rainfall in the tropics?
It is also not a surprise that making decisions based on morality, ethics, and the law are also problems for robots. When a car needs to make a decision between running over a pedestrian, and getting rear-ended from behind, what does it do? Further, who is accountable in a situation where a car performs an emergency stop where it stops as fast as possible, but still hits another person or vehicle?
There are also some conflicting directives that may hinder decision-making by autonomous vehicles. They have a directive to avoid collisions with objects, but also to obey the law by staying in lanes. At what point, if ever, does one of these directives override the other?
Lastly, even with the above issues and regulations sorted, cost is going to continue to be preventative measure for many consumers. Even in 2025, it will cost up to an extra $10k in vehicle add-ons to allow for driverless software and hardware. This is expected to decrease as time goes on, with costs dropping to roughly $3k in 2035.
The good news for driverless technology is that most of the problems highlighted in today’s infographic can be overcome with more research and time. Even with these issues identified, autonomous cars are still driving today with relatively flawless track records compared to human-controlled vehicles. They eliminate human error, which is the cause of most accidents: robots don’t drive under the influence, use unnecessary speed, or get distracted by text messages.
The bad news for the technology? If you thought the lobby against Uber was strong, wait until all truck drivers, taxi drivers, public transit employees, and limousine drivers are collectively put up against a wall.
Original graphic by: ClickMechanic
Technology
Visualizing AI Patents by Country
See which countries have been granted the most AI patents each year, from 2012 to 2022.
Visualizing AI Patents by Country
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
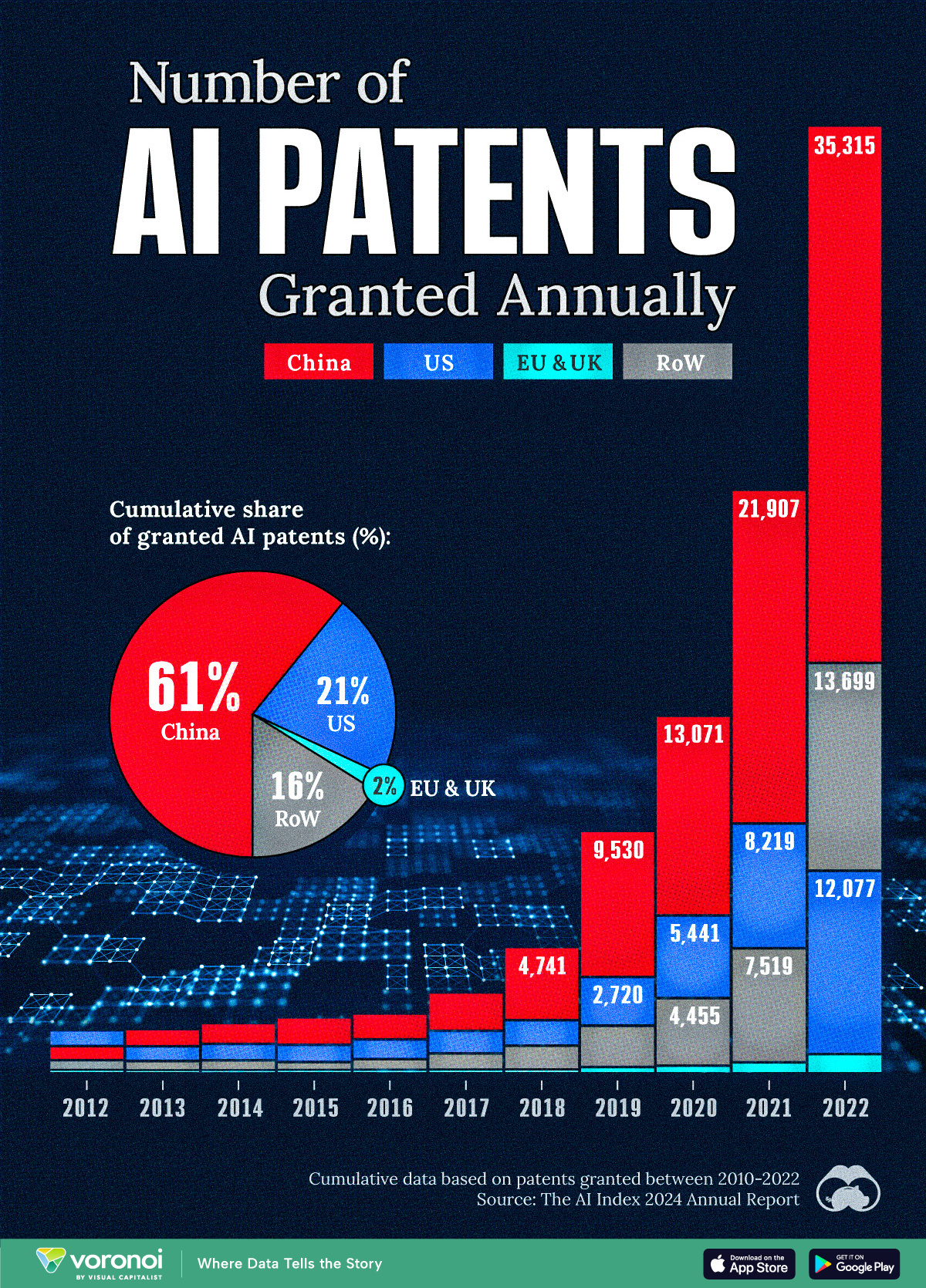
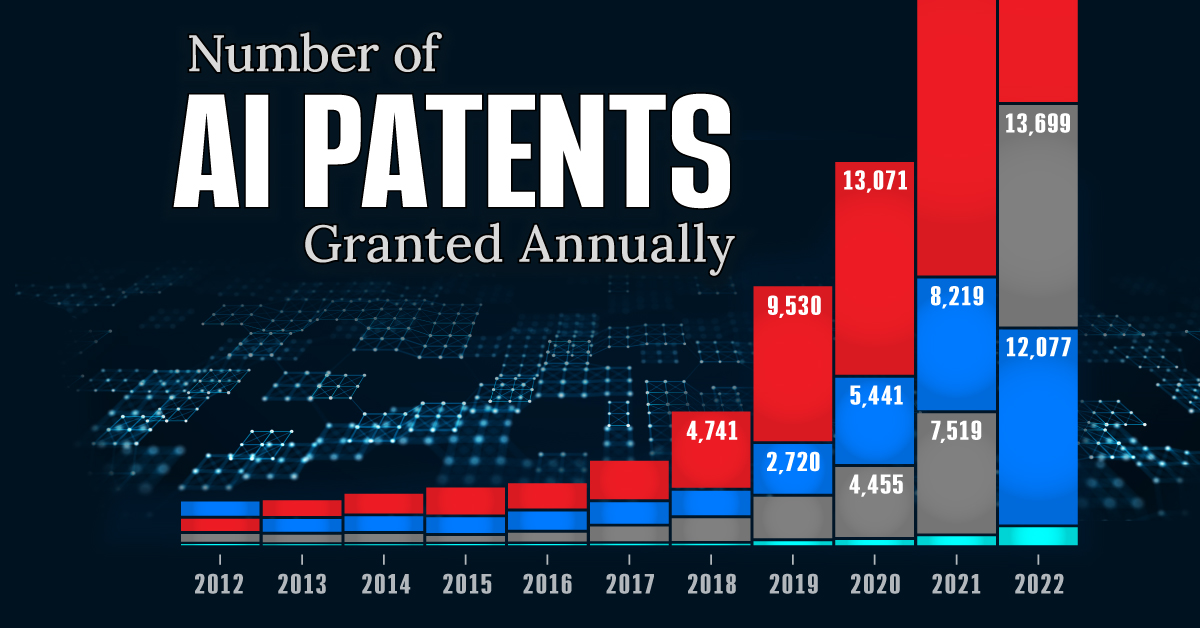
This infographic shows the number of AI-related patents granted each year from 2010 to 2022 (latest data available). These figures come from the Center for Security and Emerging Technology (CSET), accessed via Stanford University’s 2024 AI Index Report.
From this data, we can see that China first overtook the U.S. in 2013. Since then, the country has seen enormous growth in the number of AI patents granted each year.
| Year | China | EU and UK | U.S. | RoW | Global Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 307 | 137 | 984 | 571 | 1,999 |
| 2011 | 516 | 129 | 980 | 581 | 2,206 |
| 2012 | 926 | 112 | 950 | 660 | 2,648 |
| 2013 | 1,035 | 91 | 970 | 627 | 2,723 |
| 2014 | 1,278 | 97 | 1,078 | 667 | 3,120 |
| 2015 | 1,721 | 110 | 1,135 | 539 | 3,505 |
| 2016 | 1,621 | 128 | 1,298 | 714 | 3,761 |
| 2017 | 2,428 | 144 | 1,489 | 1,075 | 5,136 |
| 2018 | 4,741 | 155 | 1,674 | 1,574 | 8,144 |
| 2019 | 9,530 | 322 | 3,211 | 2,720 | 15,783 |
| 2020 | 13,071 | 406 | 5,441 | 4,455 | 23,373 |
| 2021 | 21,907 | 623 | 8,219 | 7,519 | 38,268 |
| 2022 | 35,315 | 1,173 | 12,077 | 13,699 | 62,264 |
In 2022, China was granted more patents than every other country combined.
While this suggests that the country is very active in researching the field of artificial intelligence, it doesn’t necessarily mean that China is the farthest in terms of capability.
Key Facts About AI Patents
According to CSET, AI patents relate to mathematical relationships and algorithms, which are considered abstract ideas under patent law. They can also have different meaning, depending on where they are filed.
In the U.S., AI patenting is concentrated amongst large companies including IBM, Microsoft, and Google. On the other hand, AI patenting in China is more distributed across government organizations, universities, and tech firms (e.g. Tencent).
In terms of focus area, China’s patents are typically related to computer vision, a field of AI that enables computers and systems to interpret visual data and inputs. Meanwhile America’s efforts are more evenly distributed across research fields.
Learn More About AI From Visual Capitalist
If you want to see more data visualizations on artificial intelligence, check out this graphic that shows which job departments will be impacted by AI the most.
-

 Mining1 week ago
Mining1 week agoGold vs. S&P 500: Which Has Grown More Over Five Years?
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries