Technology
Charts: Visualizing the Bear Market in FAANG Stocks
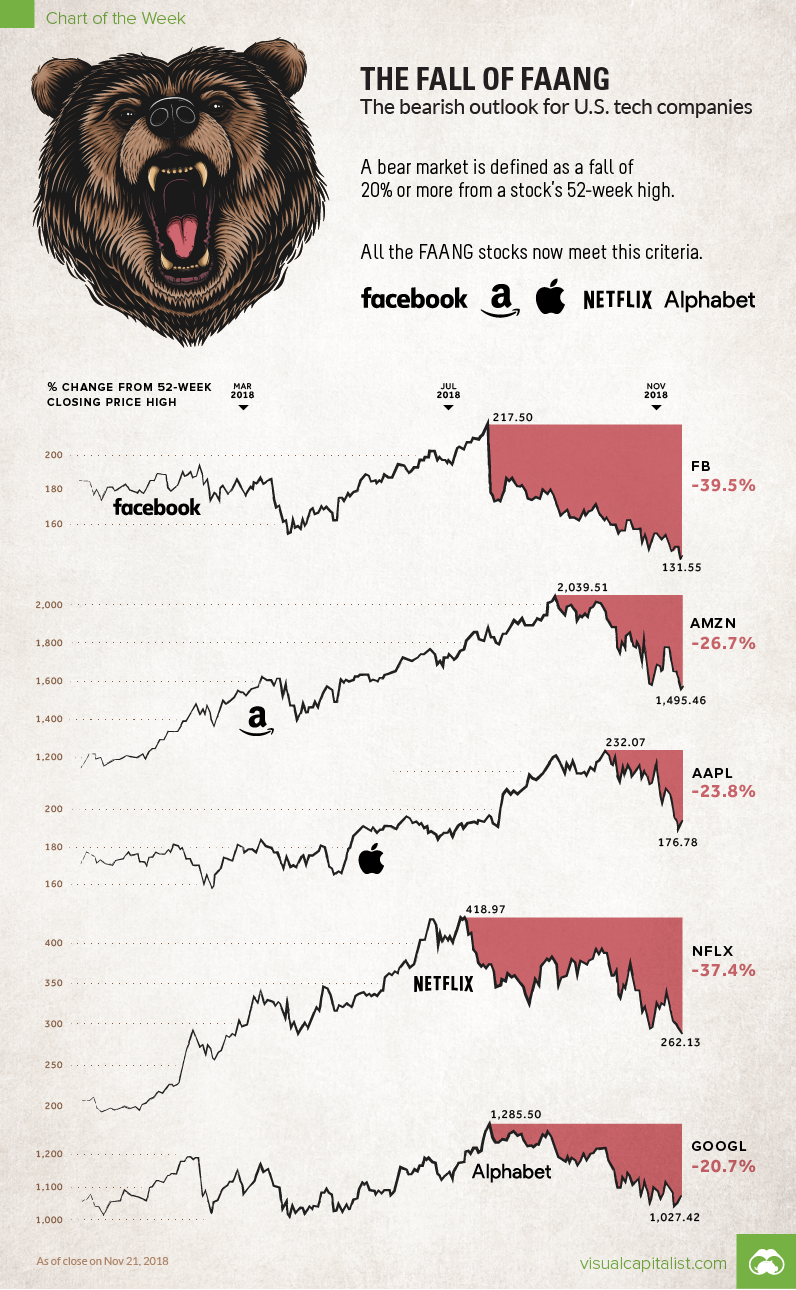
Visualizing the Bear Market in FAANG Stocks
The Chart of the Week is a weekly Visual Capitalist feature on Fridays.
What goes up, must come down.
Over recent years, there hasn’t been a safer bet than big tech – specifically the FAANG stocks, which include Facebook, Apple, Amazon, Netflix, and Google’s parent company Alphabet.
But in the financial world, this feeling of euphoria can be turned upside-down very quickly.
Since the summer, the five tech giants combined have lost close to $1 trillion in market capitalization from their peaks. Now the FAANG stocks have officially slipped into a bear market, with investors blaming rising interest rates, slumping sales forecasts, possible government intervention, and bubble-like valuations as reasons for the reversal in fortune.
The Damage Done
The generally accepted definition of a bear market is a 20% or greater decline from recent market highs.
Facebook and Netflix have been in bear territory for months, but the remaining members of FAANG only just recently capitulated. Apple was the last to go – but with -24% in lost value since its peak on October 3, it is now in trouble as well.
| Company | Peak valuation ($B) | Current valuation ($B) | Difference ($B) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apple | $1,103 | $839 | $264 |
| Amazon | $982 | $750 | $232 |
| $628 | $385 | $243 | |
| Alphabet | $894 | $722 | $172 |
| Netflix | $182 | $115 | $67 |
| Total | $3,789 | $2,811 | $978 |
Data based on publication time on Nov 23, 2018
Interestingly, this is the first time that the FAANG stocks have been in a bear market together, meaning this is uncharted territory for big tech and the wider market as a whole.
After the Gold Rush
While FAANG represents a small fraction of tech stocks available on the market, they do make up a significant percent of indices like the S&P 500 or the Nasdaq Composite. As a result, this slump can impact the rest of the market – and it manifests a more general malaise that other, less-beloved tech stocks must deal with.
Unsurprisingly, the Nasdaq Composite – a technology bellwether – is feeling the pain as well:
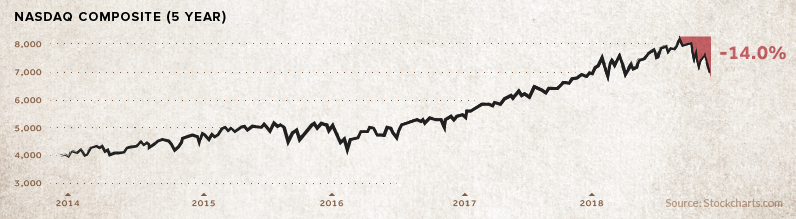
The sentiment can also be seen in other tech names, some which have been slumping for awhile and others which have fallen into a funk only recently:
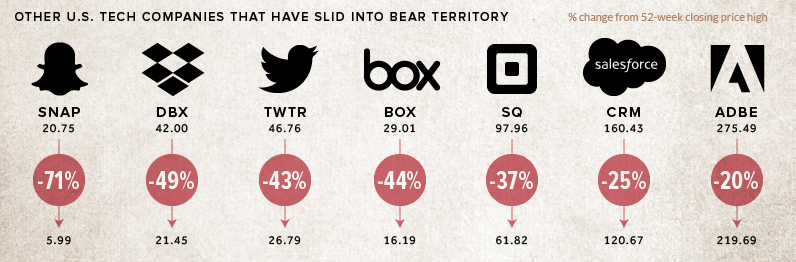
Even SaaS darlings like Salesforce.com can’t shake the trend – the stock entered bear territory itself on November 19th.
Tell Me Why
Why have investors soured, at least temporarily, on the tech stock universe?
There are multiple narratives floating around, but the general gist is something like this: the current bull market in stocks is nine years long, and at some point the party will come to an end. Because the FAANG stocks traditionally trade at very generous valuations, they are likely to come back down to earth as economic conditions deteriorate.
Further, the fears around FAANG stocks are seemingly being confirmed by recent news. For example, there are reports of Apple slicing orders for iPhones, a stagnant Facebook userbase, and other growth hurdles being experienced by these companies – and these reports are helping to fan the flames.
Some experts see the slump as an opportunity to load up on discounted tech heavyweights – while others, such as early Facebook investor Jason Calacanis, say it is possible that the social network has already experienced its “Yahoo peak” in terms of relevance and valuation.
Technology
Charting the Next Generation of Internet
In this graphic, Visual Capitalist has partnered with MSCI to explore the potential of satellite internet as the next generation of internet innovation.
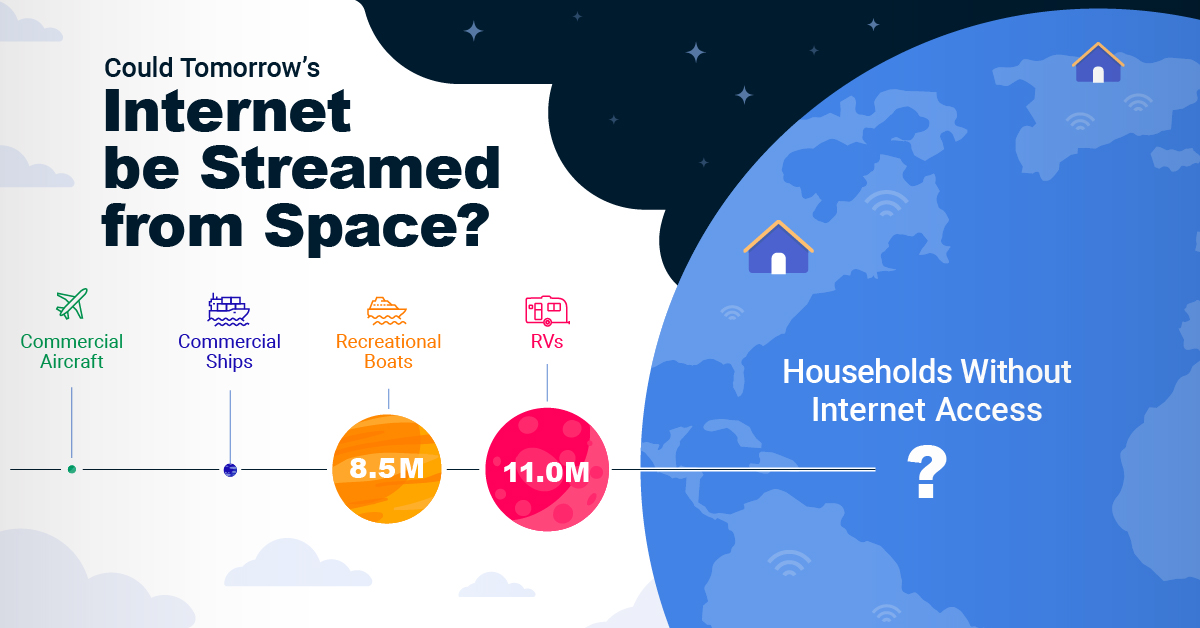
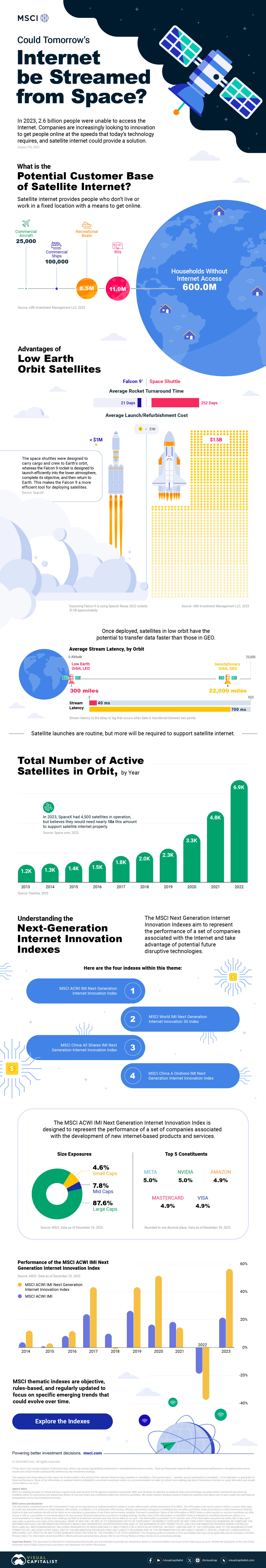
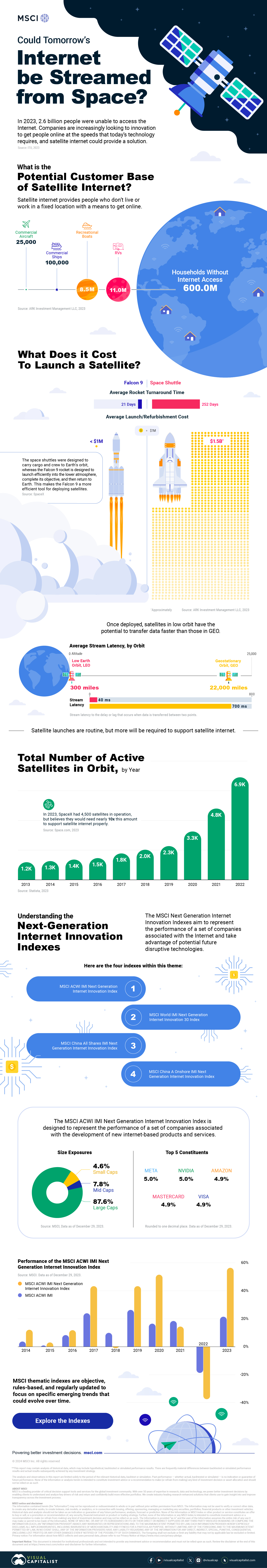
Could Tomorrow’s Internet be Streamed from Space?
In 2023, 2.6 billion people could not access the internet. Today, companies worldwide are looking to innovative technology to ensure more people are online at the speed of today’s technology.
Could satellite internet provide the solution?
In collaboration with MSCI, we embarked on a journey to explore whether tomorrow’s internet could be streamed from space.
Satellite Internet’s Potential Customer Base
Millions of people live in rural communities or mobile homes, and many spend much of their lives at sea or have no fixed abode. So, they cannot access the internet simply because the technology is unavailable.
Satellite internet gives these communities access to the internet without requiring a fixed location. Consequently, the volume of people who could get online using satellite internet is significant:
| Area | Potential Subscribers |
|---|---|
| Households Without Internet Access | 600,000,000 |
| RVs | 11,000,000 |
| Recreational Boats | 8,500,000 |
| Ships | 100,000 |
| Commercial Aircraft | 25,000 |
Advances in Satellite Technology
Satellite internet is not a new concept. However, it has only recently been that roadblocks around cost and long turnaround times have been overcome.
NASA’s space shuttle, until it was retired in 2011, was the only reusable means of transporting crew and cargo into orbit. It cost over $1.5 billion and took an average of 252 days to launch and refurbish.
In stark contrast, SpaceX’s Falcon 9 can now launch objects into orbit and maintain them at a fraction of the time and cost, less than 1% of the space shuttle’s cost.
| Average Rocket Turnaround Time | Average Launch/Refurbishment Cost | |
|---|---|---|
| Falcon 9* | 21 days | < $1,000,000 |
| Space Shuttle | 252 days | $1,500,000,000 (approximately) |
Satellites are now deployed 300 miles in low Earth orbit (LEO) rather than 22,000 miles above Earth in Geostationary Orbit (GEO), previously the typical satellite deployment altitude.
What this means for the consumer is that satellite internet streamed from LEO has a latency of 40 ms, which is an optimal internet connection. Especially when compared to the 700 ms stream latency experienced with satellite internet streamed from GEO.
What Would it Take to Build a Satellite Internet?
SpaceX, the private company that operates Starlink, currently has 4,500 satellites. However, the company believes it will require 10 times this number to provide comprehensive satellite internet coverage.
Charting the number of active satellites reveals that, despite the increasing number of active satellites, many more must be launched to create a comprehensive satellite internet.
| Year | Number of Active Satellites |
|---|---|
| 2022 | 6,905 |
| 2021 | 4,800 |
| 2020 | 3,256 |
| 2019 | 2,272 |
| 2018 | 2,027 |
| 2017 | 1,778 |
| 2016 | 1,462 |
| 2015 | 1,364 |
| 2014 | 1,262 |
| 2013 | 1,187 |
Next-Generation Internet Innovation
Innovation is at the heart of the internet’s next generation, and the MSCI Next Generation Innovation Index exposes investors to companies that can take advantage of potentially disruptive technologies like satellite internet.
You can gain exposure to companies advancing access to the internet with four indexes:
- MSCI ACWI IMI Next Generation Internet Innovation Index
- MSCI World IMI Next Generation Internet Innovation 30 Index
- MSCI China All Shares IMI Next Generation Internet Innovation Index
- MSCI China A Onshore IMI Next Generation Internet Innovation Index
MSCI thematic indexes are objective, rules-based, and regularly updated to focus on specific emerging trends that could evolve.

Click here to explore the MSCI thematic indexes

-
 Technology2 weeks ago
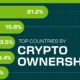
Technology2 weeks agoCountries With the Highest Rates of Crypto Ownership
While the U.S. is a major market for cryptocurrencies, two countries surpass it in terms of their rates of crypto ownership.
-
 Technology2 weeks ago
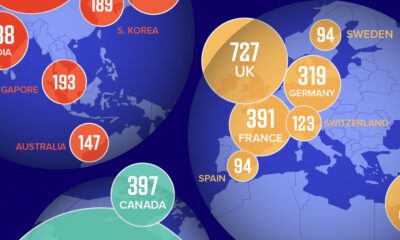
Technology2 weeks agoMapped: The Number of AI Startups By Country
Over the past decade, thousands of AI startups have been funded worldwide. See which countries are leading the charge in this map graphic.
-

 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks agoAll of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
Intel, TSMC, and more have received billions in subsidies from the U.S. CHIPS Act in 2024.
-

 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks agoVisualizing AI Patents by Country
See which countries have been granted the most AI patents each year, from 2012 to 2022.
-

 Technology4 weeks ago
Technology4 weeks agoHow Tech Logos Have Evolved Over Time
From complete overhauls to more subtle tweaks, these tech logos have had quite a journey. Featuring: Google, Apple, and more.
-

 AI1 month ago
AI1 month agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
Nvidia is coming for Intel’s crown. Samsung is losing ground. AI is transforming the space. We break down revenue for semiconductor companies.
-

 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week agoVisualizing the Tax Burden of Every U.S. State
-
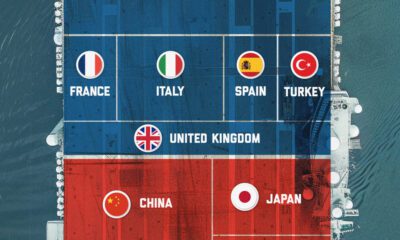
 Misc7 days ago
Misc7 days agoVisualized: Aircraft Carriers by Country
-

 Culture7 days ago
Culture7 days agoHow Popular Snack Brand Logos Have Changed
-

 Mining1 week ago
Mining1 week agoVisualizing Copper Production by Country in 2023
-
 Misc1 week ago
Misc1 week agoCharted: How Americans Feel About Federal Government Agencies
-
 Healthcare1 week ago
Healthcare1 week agoWhich Countries Have the Highest Infant Mortality Rates?
-
 Demographics1 week ago
Demographics1 week agoMapped: U.S. Immigrants by Region
-
 Maps1 week ago
Maps1 week agoMapped: Southeast Asia’s GDP Per Capita, by Country