Technology
This Chart Reveals Google’s True Dominance Over the Web
This Chart Reveals Google’s True Dominance Over the Web
The Chart of the Week is a weekly Visual Capitalist feature on Fridays.
Yes, we all know that Google is dominant in the realm of search.
But at the same time, the internet is also a huge place – and building a decent searching algorithm can’t be that hard, right?
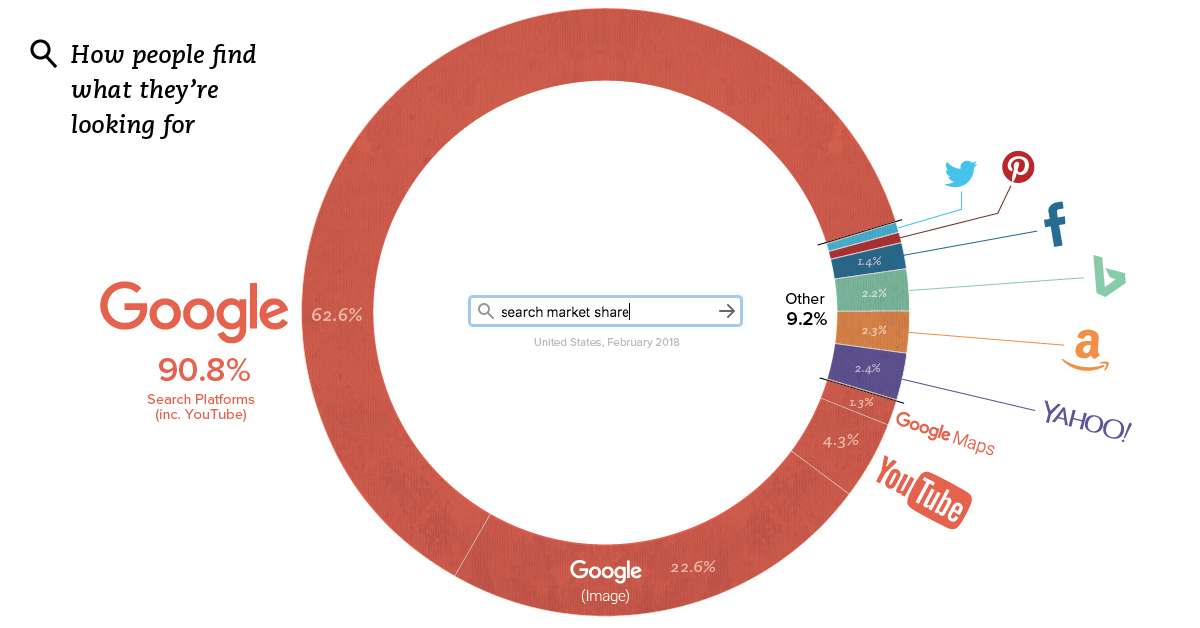
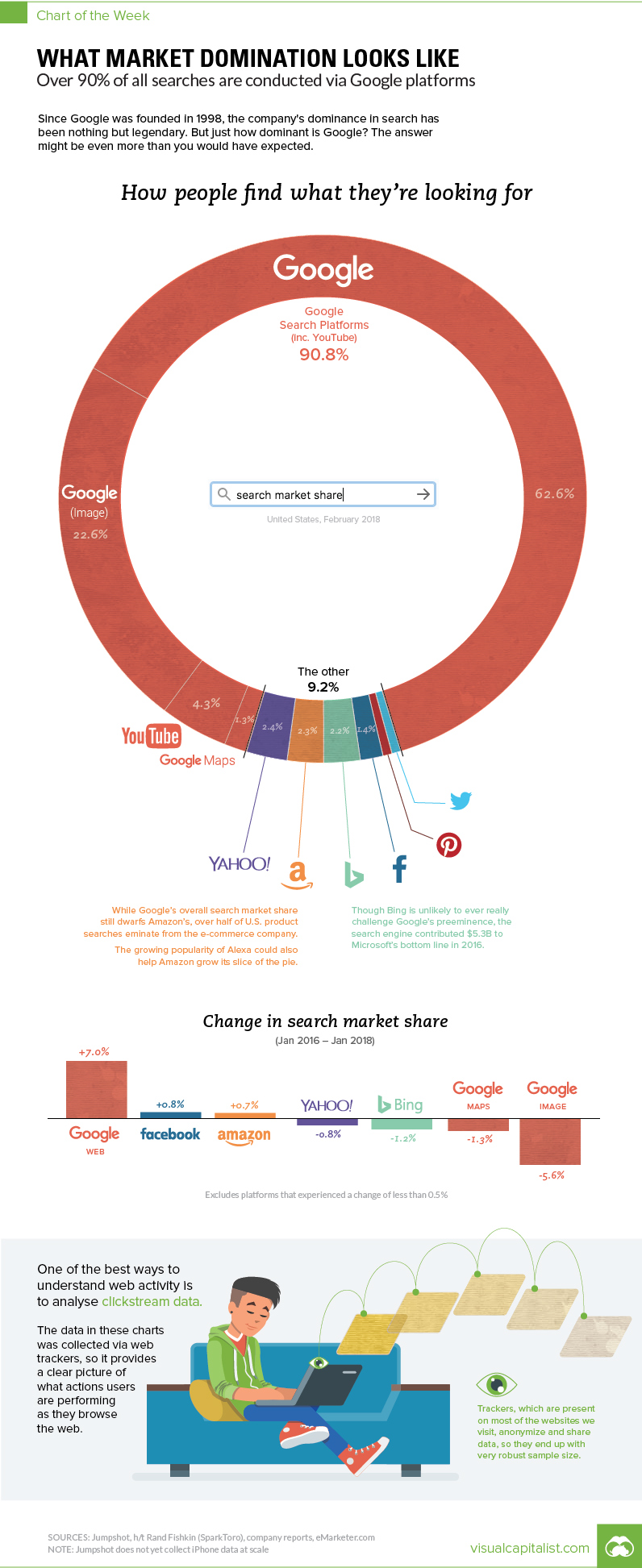
This week’s chart is a bit mind-boggling, because it makes the case that Google is even more dominant than you may have guessed. Between all Google features and the search giant’s YouTube subsidiary, more than 90% of all internet searches are taking place through the company.
The Hard Data
According to Jumpshot (via SparkToro), a marketing analytics firm that licenses anonymous ClickStream data from hundreds of millions of users, about 62.6% of all searches online are through Google’s core function.
But that’s just the beginning, as that number doesn’t include other Google functions like image search or Google Maps, or properties such as YouTube:
| Search Platform | % of Searches |
|---|---|
| 62.6% | |
| Google (image) | 22.6% |
| YouTube | 4.3% |
| Google Maps | 1.3% |
| Google Total | 90.8% |
Together, Google holds onto an impressive 90.8% market share of web, mobile, and in-app searches – though it should be noted that the above source does not include iPhone data at scale yet.
The Google-opoly
How does Google keep up such a massive market share, and why can’t a real competitor in search emerge?
The answer has to do with platforms and apps. Google’s strategy is to go where the users are, and to ensure that wherever they go, a Google search is not hard to do.
Over a decade ago, this meant being the home page on every internet browser – but more recently, it’s taken the form of internet browser market share (Chrome), mobile OS market share (Android), owning the dominant video platform (YouTube), and even venturing into your dwelling with Google Home.
As a result of these efforts, whenever users are searching, Google has never been far away.
Low Bids from Competition
There are competitors that dare to pluck away at Google’s market share in search and ad revenue.
Microsoft’s Bing is the most known one, and it has the advantage of being integrated into Microsoft products all over the globe. Meanwhile, DuckDuckGo is another name worth mentioning – the privacy-focused search engine doesn’t have anywhere near the same kind of financial backing as Microsoft, but it does differentiate its product considerably.
Yet, here’s a picture of U.S. search ad revenues. Bing is small, but others are smaller. DuckDuckGo doesn’t even register.

Why can no one match Google?
Part of the reason lies in the math. Google operates at an insane level, processing 3.5 billion searches per day. To get millions of people to try a different search algorithm is expensive – and to get them to keep that behavior permanently is even more expensive.
The only way such change becomes feasible is if a product comes out that is 10x better than Google, and at this point, such an event seems unlikely – at least in the current ecosystem.
Technology
Charting the Next Generation of Internet
In this graphic, Visual Capitalist has partnered with MSCI to explore the potential of satellite internet as the next generation of internet innovation.
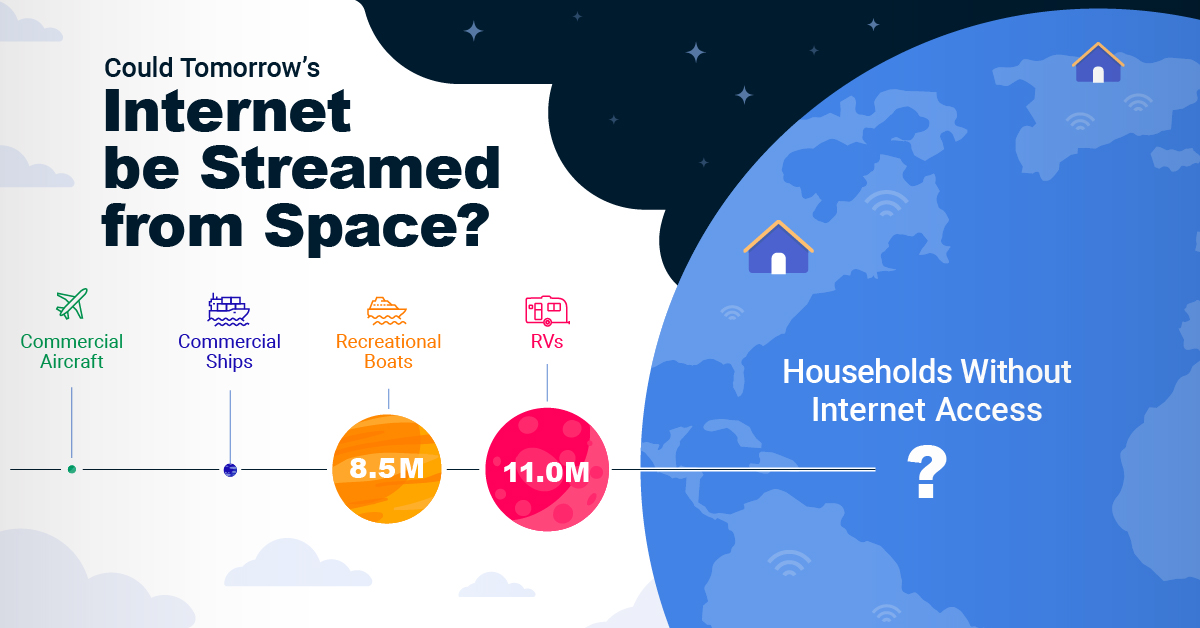
Could Tomorrow’s Internet be Streamed from Space?
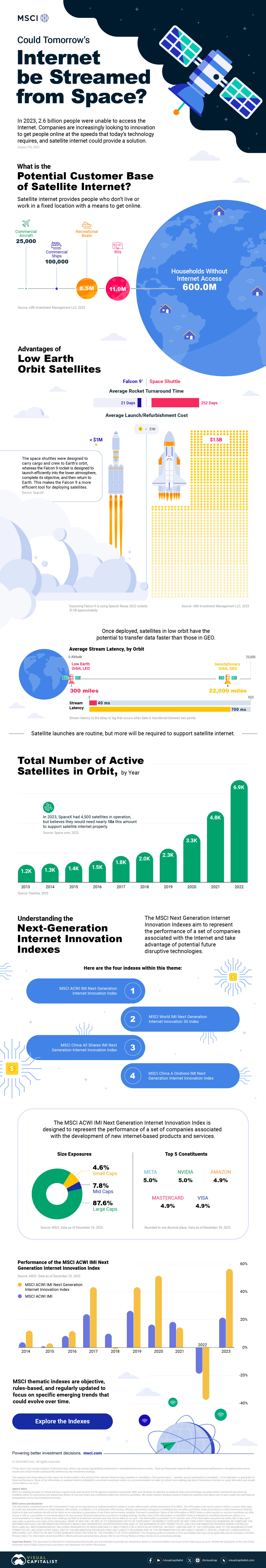
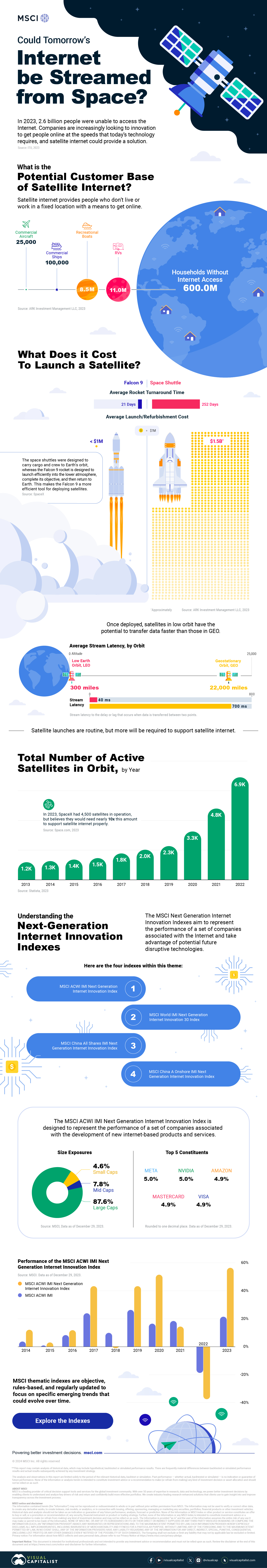
In 2023, 2.6 billion people could not access the internet. Today, companies worldwide are looking to innovative technology to ensure more people are online at the speed of today’s technology.
Could satellite internet provide the solution?
In collaboration with MSCI, we embarked on a journey to explore whether tomorrow’s internet could be streamed from space.
Satellite Internet’s Potential Customer Base
Millions of people live in rural communities or mobile homes, and many spend much of their lives at sea or have no fixed abode. So, they cannot access the internet simply because the technology is unavailable.
Satellite internet gives these communities access to the internet without requiring a fixed location. Consequently, the volume of people who could get online using satellite internet is significant:
| Area | Potential Subscribers |
|---|---|
| Households Without Internet Access | 600,000,000 |
| RVs | 11,000,000 |
| Recreational Boats | 8,500,000 |
| Ships | 100,000 |
| Commercial Aircraft | 25,000 |
Advances in Satellite Technology
Satellite internet is not a new concept. However, it has only recently been that roadblocks around cost and long turnaround times have been overcome.
NASA’s space shuttle, until it was retired in 2011, was the only reusable means of transporting crew and cargo into orbit. It cost over $1.5 billion and took an average of 252 days to launch and refurbish.
In stark contrast, SpaceX’s Falcon 9 can now launch objects into orbit and maintain them at a fraction of the time and cost, less than 1% of the space shuttle’s cost.
| Average Rocket Turnaround Time | Average Launch/Refurbishment Cost | |
|---|---|---|
| Falcon 9* | 21 days | < $1,000,000 |
| Space Shuttle | 252 days | $1,500,000,000 (approximately) |
Satellites are now deployed 300 miles in low Earth orbit (LEO) rather than 22,000 miles above Earth in Geostationary Orbit (GEO), previously the typical satellite deployment altitude.
What this means for the consumer is that satellite internet streamed from LEO has a latency of 40 ms, which is an optimal internet connection. Especially when compared to the 700 ms stream latency experienced with satellite internet streamed from GEO.
What Would it Take to Build a Satellite Internet?
SpaceX, the private company that operates Starlink, currently has 4,500 satellites. However, the company believes it will require 10 times this number to provide comprehensive satellite internet coverage.
Charting the number of active satellites reveals that, despite the increasing number of active satellites, many more must be launched to create a comprehensive satellite internet.
| Year | Number of Active Satellites |
|---|---|
| 2022 | 6,905 |
| 2021 | 4,800 |
| 2020 | 3,256 |
| 2019 | 2,272 |
| 2018 | 2,027 |
| 2017 | 1,778 |
| 2016 | 1,462 |
| 2015 | 1,364 |
| 2014 | 1,262 |
| 2013 | 1,187 |
Next-Generation Internet Innovation
Innovation is at the heart of the internet’s next generation, and the MSCI Next Generation Innovation Index exposes investors to companies that can take advantage of potentially disruptive technologies like satellite internet.
You can gain exposure to companies advancing access to the internet with four indexes:
- MSCI ACWI IMI Next Generation Internet Innovation Index
- MSCI World IMI Next Generation Internet Innovation 30 Index
- MSCI China All Shares IMI Next Generation Internet Innovation Index
- MSCI China A Onshore IMI Next Generation Internet Innovation Index
MSCI thematic indexes are objective, rules-based, and regularly updated to focus on specific emerging trends that could evolve.

Click here to explore the MSCI thematic indexes

-
 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoCountries With the Highest Rates of Crypto Ownership
While the U.S. is a major market for cryptocurrencies, two countries surpass it in terms of their rates of crypto ownership.
-
 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoMapped: The Number of AI Startups By Country
Over the past decade, thousands of AI startups have been funded worldwide. See which countries are leading the charge in this map graphic.
-

 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks agoAll of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
Intel, TSMC, and more have received billions in subsidies from the U.S. CHIPS Act in 2024.
-

 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks agoVisualizing AI Patents by Country
See which countries have been granted the most AI patents each year, from 2012 to 2022.
-

 Technology4 weeks ago
Technology4 weeks agoHow Tech Logos Have Evolved Over Time
From complete overhauls to more subtle tweaks, these tech logos have had quite a journey. Featuring: Google, Apple, and more.
-

 AI1 month ago
AI1 month agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
Nvidia is coming for Intel’s crown. Samsung is losing ground. AI is transforming the space. We break down revenue for semiconductor companies.
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoCountries With the Highest Rates of Crypto Ownership
-

 Mining6 days ago
Mining6 days agoVisualizing Copper Production by Country in 2023
-
 Politics7 days ago
Politics7 days agoCharted: How Americans Feel About Federal Government Agencies
-
 Healthcare1 week ago
Healthcare1 week agoWhich Countries Have the Highest Infant Mortality Rates?
-
 Demographics1 week ago
Demographics1 week agoMapped: U.S. Immigrants by Region
-
 Economy1 week ago
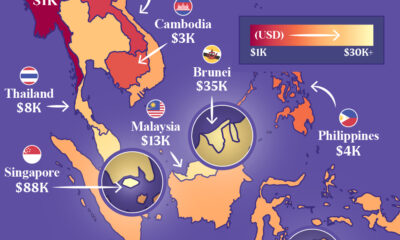
Economy1 week agoMapped: Southeast Asia’s GDP Per Capita, by Country
-
 Automotive1 week ago
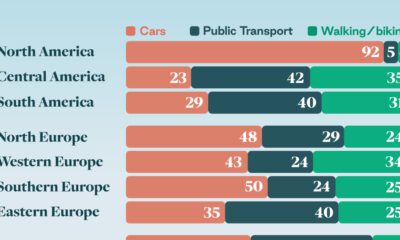
Automotive1 week agoHow People Get Around in America, Europe, and Asia
-

 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week agoVisualizing the Tax Burden of Every U.S. State