Markets
Interest Rate Hikes vs. Inflation Rate, by Country
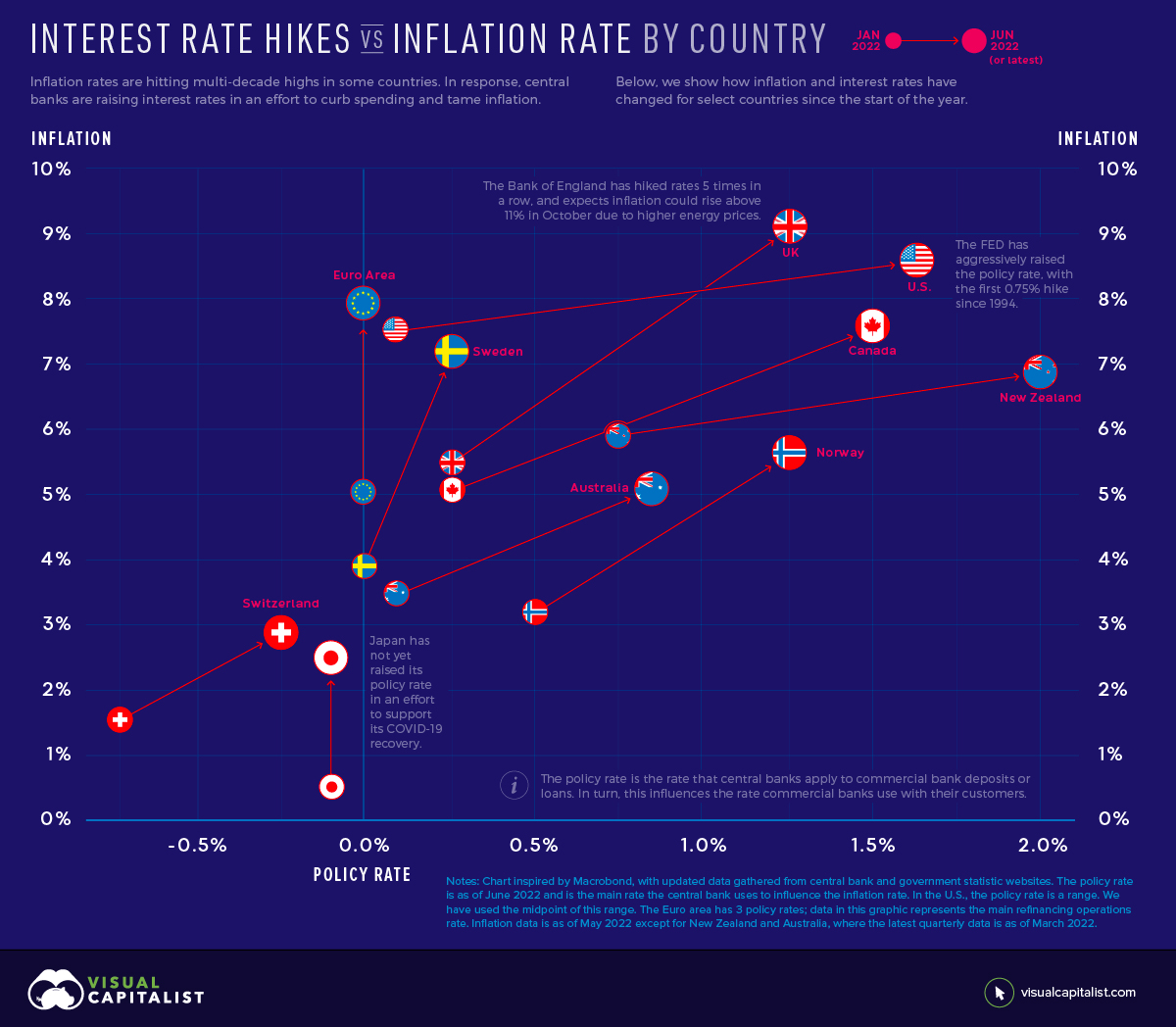
Interest Rate Hikes vs. Inflation Rate, by Country
Imagine today’s high inflation like a car speeding down a hill. In order to slow it down, you need to hit the brakes. In this case, the “brakes” are interest rate hikes intended to slow spending. However, some central banks are hitting the brakes faster than others.
This graphic uses data from central banks and government websites to show how policy interest rates and inflation rates have changed since the start of the year. It was inspired by a chart created by Macrobond.
How Do Interest Rate Hikes Combat Inflation?
To understand how interest rates influence inflation, we need to understand how inflation works. Inflation is the result of too much money chasing too few goods. Over the last several months, this has occurred amid a surge in demand and supply chain disruptions worsened by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
In an effort to combat inflation, central banks will raise their policy rate. This is the rate they charge commercial banks for loans or pay commercial banks for deposits. Commercial banks pass on a portion of these higher rates to their customers, which reduces the purchasing power of businesses and consumers. For example, it becomes more expensive to borrow money for a house or car.
Ultimately, interest rate hikes act to slow spending and encourage saving. This motivates companies to increase prices at a slower rate, or lower prices, to stimulate demand.
Rising Interest Rates and Inflation
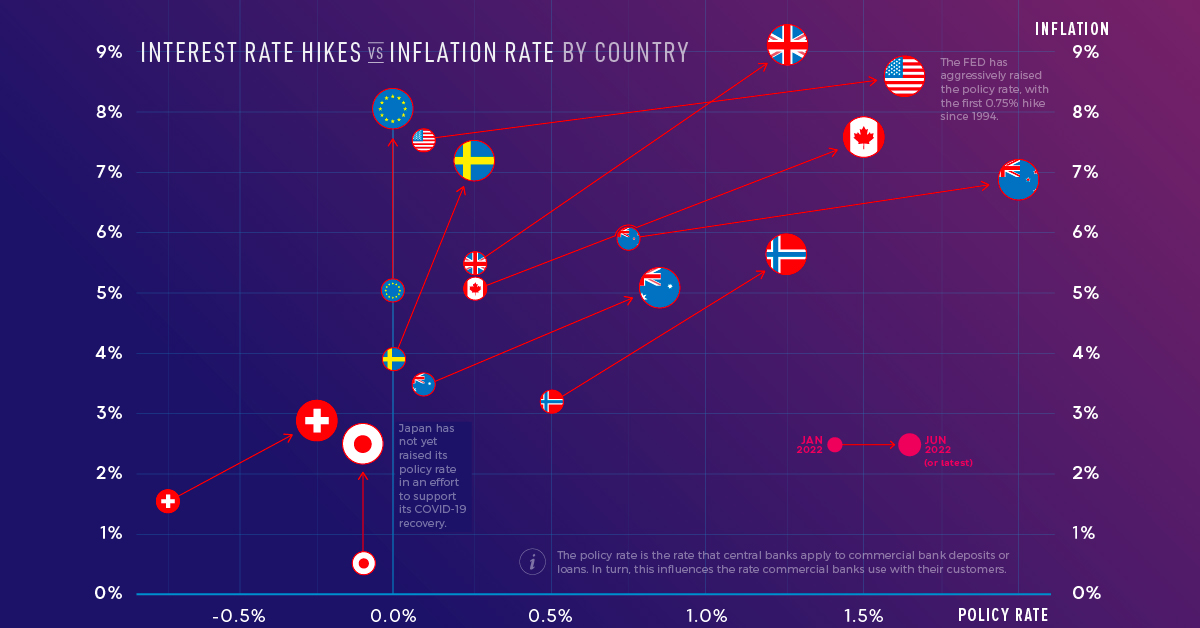
With inflation rates hitting multi-decade highs in some countries, many central banks have announced interest rate hikes. Below, we show how the inflation rate and policy interest rate have changed for select countries and regions since January 2022. The jurisdictions are ordered from highest to lowest current inflation rate.
| Jurisdiction | Jan 2022 Inflation | May 2022 Inflation | Jan 2022 Policy Rate | Jun 2022 Policy Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UK | 5.50% | 9.10% | 0.25% | 1.25% |
| U.S. | 7.50% | 8.60% | 0.00%-0.25% | 1.50%-1.75% |
| Euro Area | 5.10% | 8.10% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| Canada | 5.10% | 7.70% | 0.25% | 1.50% |
| Sweden | 3.90% | 7.20% | 0.00% | 0.25% |
| New Zealand | 5.90% | 6.90% | 0.75% | 2.00% |
| Norway | 3.20% | 5.70% | 0.50% | 1.25% |
| Australia | 3.50% | 5.10% | 0.10% | 0.85% |
| Switzerland | 1.60% | 2.90% | -0.75% | -0.25% |
| Japan | 0.50% | 2.50% | -0.10% | -0.10% |
The Euro area has 3 policy rates; the data above represents the main refinancing operations rate. Inflation data is as of May 2022 except for New Zealand and Australia, where the latest quarterly data is as of March 2022.
The U.S. Federal Reserve has been the most aggressive with its interest rate hikes. It has raised its policy rate by 1.5% since January, with half of that increase occurring at the June 2022 meeting. Jerome Powell, the Federal Reserve chair, said the committee would like to “do a little more front-end loading” to bring policy rates to normal levels. The action comes as the U.S. faces its highest inflation rate in 40 years.
On the other hand, the European Union is experiencing inflation of 8.1% but has not yet raised its policy rate. The European Central Bank has, however, provided clear forward guidance. It intends to raise rates by 0.25% in July, by a possibly larger increment in September, and with gradual but sustained increases thereafter. Clear forward guidance is intended to help people make spending and investment decisions, and avoid surprises that could disrupt markets.
Pacing Interest Rate Hikes
Raising interest rates is a fine balancing act. If central banks raise rates too quickly, it’s like slamming the brakes on that car speeding downhill: the economy could come to a standstill. This occurred in the U.S. in the 1980’s when the Federal Reserve, led by Chair Paul Volcker, raised the policy rate to 20%. The economy went into a recession, though the aggressive monetary policy did eventually tame double digit inflation.
However, if rates are raised too slowly, inflation could gather enough momentum that it becomes difficult to stop. The longer high price increases linger, the more future inflation expectations build. This can result in people buying more in anticipation of prices rising further, perpetuating high demand.
“There’s always a risk of going too far or not going far enough, and it’s going to be a very difficult judgment to make.” — Jerome Powell, U.S. Federal Reserve Chair
It’s worth noting that while central banks can influence demand through policy rates, this is only one side of the equation. Inflation is also being caused by supply chain issues, a problem that is more or less outside of the control of central banks.
AI
Ranked: The 20 Biggest Tech Companies by Market Cap
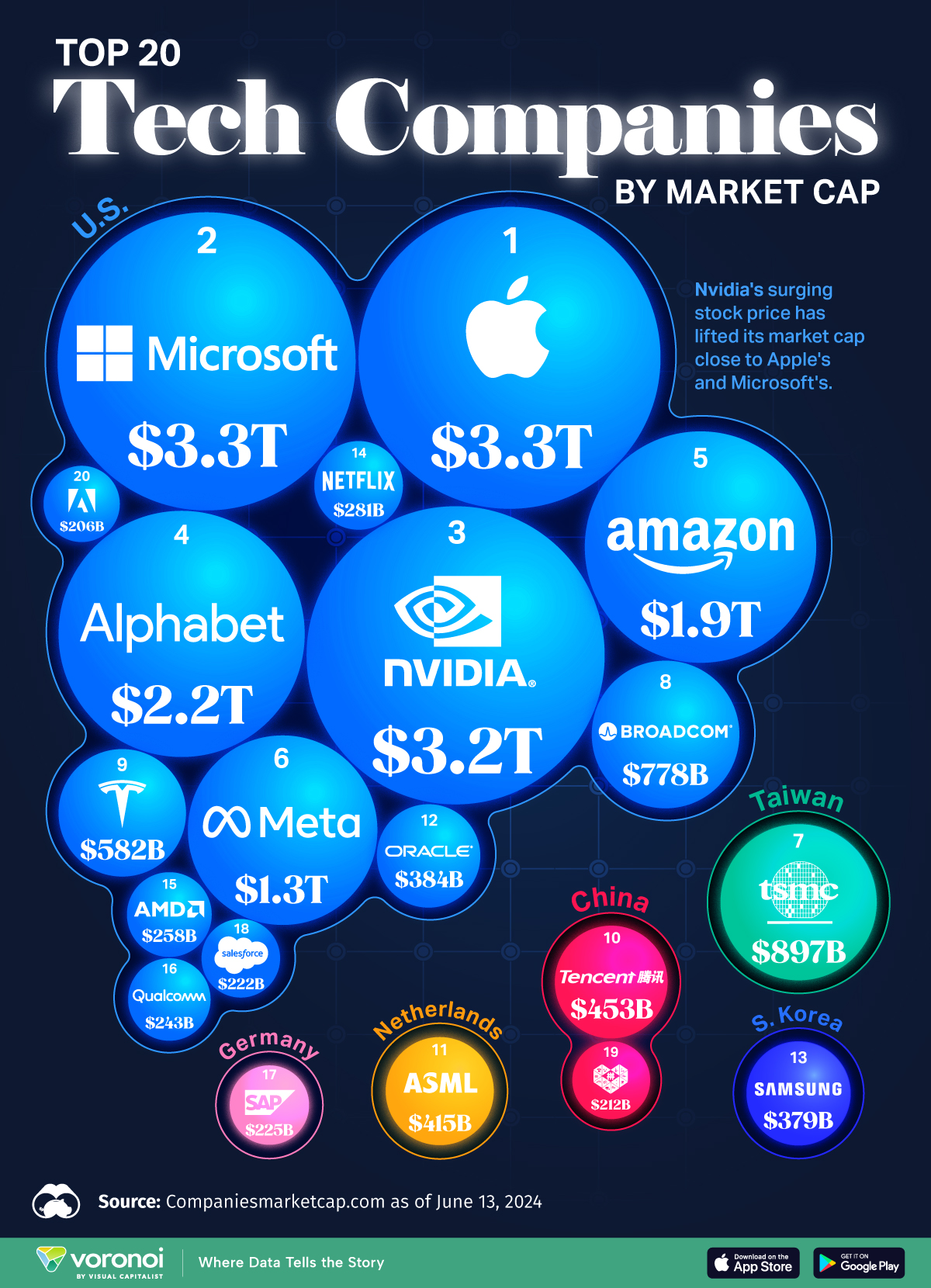
In total, the 20 biggest tech companies are worth over $20 trillion—nearly 18% of the stock market value globally.

Ranked: The 20 Biggest Tech Companies by Market Cap
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
The world’s 20 biggest tech companies are worth over $20 trillion in total. To put this in perspective, this is nearly 18% of the stock market value globally.
This graphic shows which companies top the ranks, using data from Companiesmarketcap.com.
A Closer Look at The Top 20
Market capitalization (market cap) measures what a company is worth by taking the current share price and multiplying it by the number of shares outstanding. Here are the biggest tech companies according to their market cap on June 13, 2024.
| Rank | Company | Country/Region | Market Cap |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Apple | U.S. | $3.3T |
| 2 | Microsoft | U.S. | $3.3T |
| 3 | Nvidia | U.S. | $3.2T |
| 4 | Alphabet | U.S. | $2.2T |
| 5 | Amazon | U.S. | $1.9T |
| 6 | Meta | U.S. | $1.3T |
| 7 | TSMC | Taiwan | $897B |
| 8 | Broadcom | U.S. | $778B |
| 9 | Tesla | U.S. | $582B |
| 10 | Tencent | China | $453B |
| 11 | ASML | Netherlands | $415B |
| 12 | Oracle | U.S. | $384B |
| 13 | Samsung | South Korea | $379B |
| 14 | Netflix | U.S. | $281B |
| 15 | AMD | U.S. | $258B |
| 16 | Qualcomm | U.S. | $243B |
| 17 | SAP | Germany | $225B |
| 18 | Salesforce | U.S. | $222B |
| 19 | PDD Holdings (owns Pinduoduo) | China | $212B |
| 20 | Adobe | U.S. | $206B |
Note: PDD Holdings says its headquarters remain in Shanghai, China, and Ireland is used for legal registration for its overseas business.
Apple is the largest tech company at the moment, having competed with Microsoft for the top of the leaderboard for many years. The company saw its market cap soar after announcing its generative AI, Apple Intelligence. Analysts believe people will upgrade their devices over the next few years, since the new features are only available on the iPhone 15 Pro or newer.
Microsoft is in second place in the rankings, partly thanks to enthusiasm for its AI software which is already generating revenue. Rising profits also contributed to the company’s value. For the quarter ended March 31, 2024, Microsoft increased its net income by 20% compared to the same quarter last year.
Nvidia follows closely behind with the third-highest market cap, rising more than eight times higher compared to its value at the start of 2023. The company has recently announced higher profits, introduced a higher dividend, and reported that its next-generation GPU chip will start generating revenue later this year.
AI a Driver of the Biggest Tech Companies
It’s clear from the biggest tech companies that involvement in AI can contribute to investor confidence.
Among S&P 500 companies, AI has certainly become a focus topic. In fact, 199 companies cited the term “AI” during their first quarter earnings calls, the highest on record. The companies who mentioned AI the most were Meta (95 times), Nvidia (86 times), and Microsoft (74 times).
-
 United States6 days ago
United States6 days agoRanked: U.S. Cities with the Highest Rent in 2024
-

 Globalization2 weeks ago
Globalization2 weeks agoCharted: Countries Offering Digital Nomad Visas
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoMapped: Unauthorized Immigrants by State
-

 Bitcoin2 weeks ago
Bitcoin2 weeks agoVisualizing the 15 Most Valuable Bitcoin Addresses
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoWhich Countries Have the Most and Least Women in the Workforce?
-
 Mining1 week ago
Mining1 week agoVisualizing Raw Steel Production in 2023
-

 Misc1 week ago
Misc1 week agoCharted: The World’s Highest Homicide Rates, in Each Region
-

 Environment1 week ago
Environment1 week agoWildfire Area Burned by U.S. State in 2023