Energy
Visualizing the Power Consumption of Bitcoin Mining

Visualizing the Power Consumption of Bitcoin Mining
Cryptocurrencies have been some of the most talked-about assets in recent months, with bitcoin and ether prices reaching record highs. These gains were driven by a flurry of announcements, including increased adoption by businesses and institutions.
Lesser known, however, is just how much electricity is required to power the Bitcoin network. To put this into perspective, we’ve used data from the University of Cambridge’s Bitcoin Electricity Consumption Index (CBECI) to compare Bitcoin’s power consumption with a variety of countries and companies.
Why Does Bitcoin Mining Require So Much Power?
When people mine bitcoins, what they’re really doing is updating the ledger of Bitcoin transactions, also known as the blockchain. This requires them to solve numerical puzzles which have a 64-digit hexadecimal solution known as a hash.
Miners may be rewarded with bitcoins, but only if they arrive at the solution before others. It is for this reason that Bitcoin mining facilities—warehouses filled with computers—have been popping up around the world.
These facilities enable miners to scale up their hashrate, also known as the number of hashes produced each second. A higher hashrate requires greater amounts of electricity, and in some cases can even overload local infrastructure.
Putting Bitcoin’s Power Consumption Into Perspective
On March 18, 2021, the annual power consumption of the Bitcoin network was estimated to be 129 terawatt-hours (TWh). Here’s how this number compares to a selection of countries, companies, and more.
| Name | Population | Annual Electricity Consumption (TWh) |
|---|---|---|
| China | 1,443M | 6,543 |
| United States | 330.2M | 3,989 |
| All of the world’s data centers | - | 205 |
| State of New York | 19.3M | 161 |
| Bitcoin network | - | 129 |
| Norway | 5.4M | 124 |
| Bangladesh | 165.7M | 70 |
| - | 12 | |
| - | 5 | |
| Walt Disney World Resort (Florida) | - | 1 |
Note: A terawatt hour (TWh) is a measure of electricity that represents 1 trillion watts sustained for one hour.
Source: Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance, Science Mag, New York ISO, Forbes, Facebook, Reedy Creek Improvement District, Worldometer
If Bitcoin were a country, it would rank 29th out of a theoretical 196, narrowly exceeding Norway’s consumption of 124 TWh. When compared to larger countries like the U.S. (3,989 TWh) and China (6,543 TWh), the cryptocurrency’s energy consumption is relatively light.
For further comparison, the Bitcoin network consumes 1,708% more electricity than Google, but 39% less than all of the world’s data centers—together, these represent over 2 trillion gigabytes of storage.
Where Does This Energy Come From?
In a 2020 report by the University of Cambridge, researchers found that 76% of cryptominers rely on some degree of renewable energy to power their operations. There’s still room for improvement, though, as renewables account for just 39% of cryptomining’s total energy consumption.
Here’s how the share of cryptominers that use each energy type vary across four global regions.
| Energy Source | Asia-Pacific | Europe | Latin America and the Caribbean | North America |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydroelectric | 65% | 60% | 67% | 61% |
| Natural gas | 38% | 33% | 17% | 44% |
| Coal | 65% | 2% | 0% | 28% |
| Wind | 23% | 7% | 0% | 22% |
| Oil | 12% | 7% | 33% | 22% |
| Nuclear | 12% | 7% | 0% | 22% |
| Solar | 12% | 13% | 17% | 17% |
| Geothermal | 8% | 0% | 0% | 6% |
Source: University of Cambridge
Editor’s note: Numbers in each column are not meant to add to 100%
Hydroelectric energy is the most common source globally, and it gets used by at least 60% of cryptominers across all four regions. Other types of clean energy such as wind and solar appear to be less popular.
Coal energy plays a significant role in the Asia-Pacific region, and was the only source to match hydroelectricity in terms of usage. This can be largely attributed to China, which is currently the world’s largest consumer of coal.
Researchers from the University of Cambridge noted that they weren’t surprised by these findings, as the Chinese government’s strategy to ensure energy self-sufficiency has led to an oversupply of both hydroelectric and coal power plants.
Towards a Greener Crypto Future
As cryptocurrencies move further into the mainstream, it’s likely that governments and other regulators will turn their attention to the industry’s carbon footprint. This isn’t necessarily a bad thing, however.
Mike Colyer, CEO of Foundry, a blockchain financing provider, believes that cryptomining can support the global transition to renewable energy. More specifically, he believes that clustering cryptomining facilities near renewable energy projects can mitigate a common issue: an oversupply of electricity.
“It allows for a faster payback on solar projects or wind projects… because they would [otherwise] produce too much energy for the grid in that area”
– Mike Colyer, CEO, Foundry
This type of thinking appears to be taking hold in China as well. In April 2020, Ya’an, a city located in China’s Sichuan province, issued a public guidance encouraging blockchain firms to take advantage of its excess hydroelectricity.

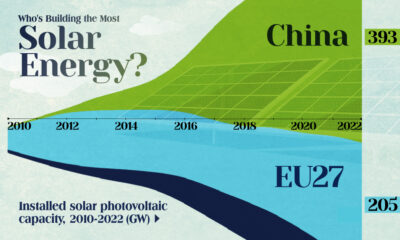
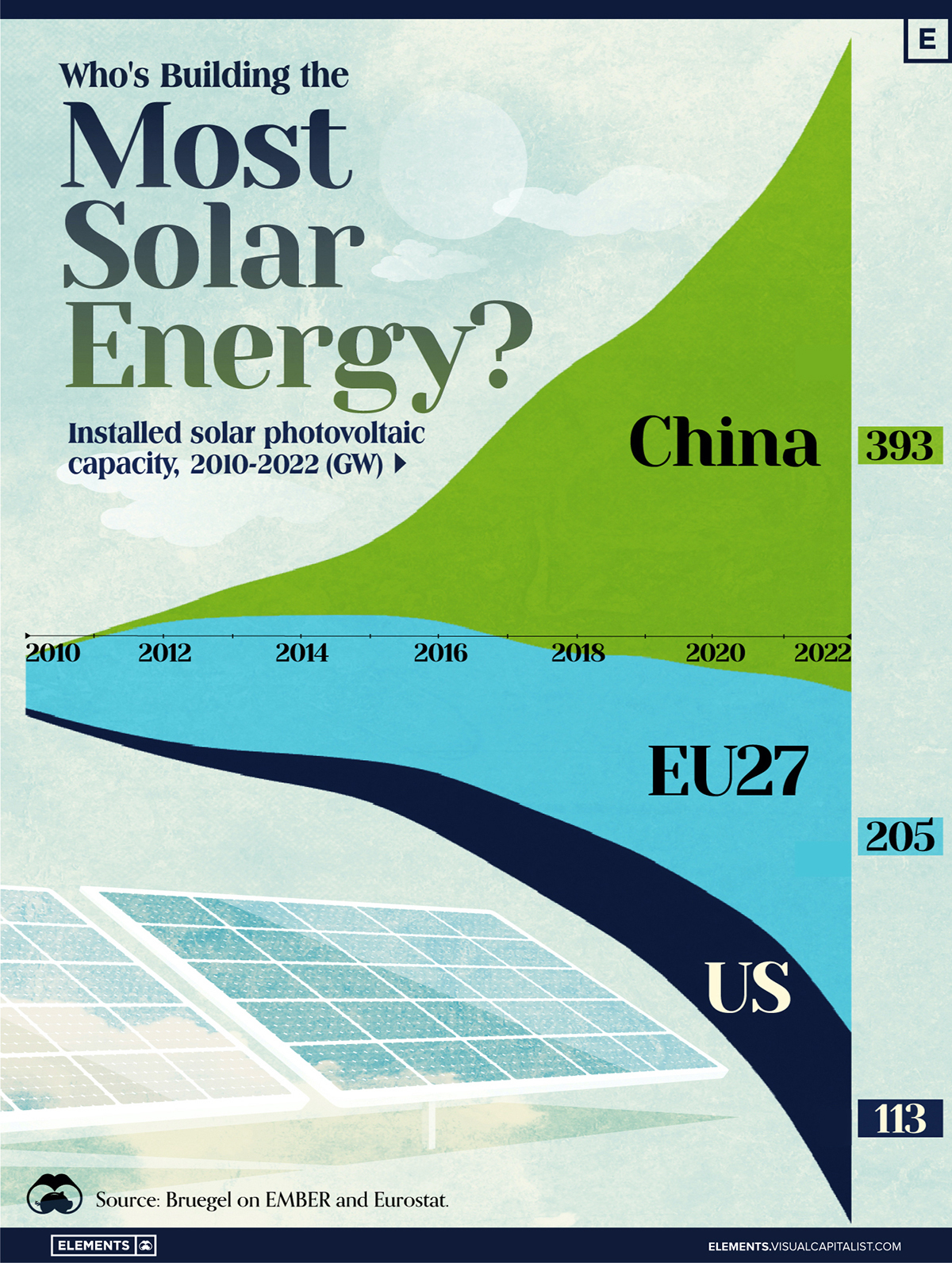
Who’s Building the Most Solar Energy?
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
In 2023, solar energy accounted for three-quarters of renewable capacity additions worldwide. Most of this growth occurred in Asia, the EU, and the U.S., continuing a trend observed over the past decade.
In this graphic, we illustrate the rise in installed solar photovoltaic (PV) capacity in China, the EU, and the U.S. between 2010 and 2022, measured in gigawatts (GW). Bruegel compiled the data..
Chinese Dominance
As of 2022, China’s total installed capacity stands at 393 GW, nearly double that of the EU’s 205 GW and surpassing the USA’s total of 113 GW by more than threefold in absolute terms.
| Installed solar capacity (GW) | China | EU27 | U.S. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | 393.0 | 205.5 | 113.0 |
| 2021 | 307.0 | 162.7 | 95.4 |
| 2020 | 254.0 | 136.9 | 76.4 |
| 2019 | 205.0 | 120.1 | 61.6 |
| 2018 | 175.3 | 104.0 | 52.0 |
| 2017 | 130.8 | 96.2 | 43.8 |
| 2016 | 77.8 | 91.5 | 35.4 |
| 2015 | 43.6 | 87.7 | 24.2 |
| 2014 | 28.4 | 83.6 | 18.1 |
| 2013 | 17.8 | 79.7 | 13.3 |
| 2012 | 6.7 | 71.1 | 8.6 |
| 2011 | 3.1 | 53.3 | 5.6 |
| 2010 | 1.0 | 30.6 | 3.4 |
Since 2017, China has shown a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 25% in installed PV capacity, while the USA has seen a CAGR of 21%, and the EU of 16%.
Additionally, China dominates the production of solar power components, currently controlling around 80% of the world’s solar panel supply chain.
In 2022, China’s solar industry employed 2.76 million individuals, with manufacturing roles representing approximately 1.8 million and the remaining 918,000 jobs in construction, installation, and operations and maintenance.
The EU industry employed 648,000 individuals, while the U.S. reached 264,000 jobs.
According to the IEA, China accounts for almost 60% of new renewable capacity expected to become operational globally by 2028.
Despite the phasing out of national subsidies in 2020 and 2021, deployment of solar PV in China is accelerating. The country is expected to reach its national 2030 target for wind and solar PV installations in 2024, six years ahead of schedule.
-
 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoCountries With the Highest Rates of Crypto Ownership
-

 Mining7 days ago
Mining7 days agoVisualizing Copper Production by Country in 2023
-
 Politics7 days ago
Politics7 days agoCharted: How Americans Feel About Federal Government Agencies
-
 Healthcare1 week ago
Healthcare1 week agoWhich Countries Have the Highest Infant Mortality Rates?
-
 Demographics1 week ago
Demographics1 week agoMapped: U.S. Immigrants by Region
-
 Economy1 week ago
Economy1 week agoMapped: Southeast Asia’s GDP Per Capita, by Country
-
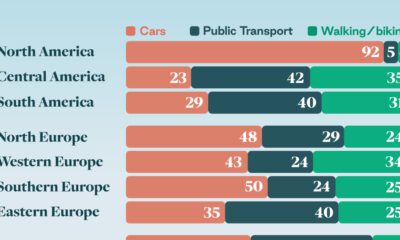
 Automotive1 week ago
Automotive1 week agoHow People Get Around in America, Europe, and Asia
-

 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week agoVisualizing the Tax Burden of Every U.S. State