Politics
A Visual Guide to Europe’s Member States
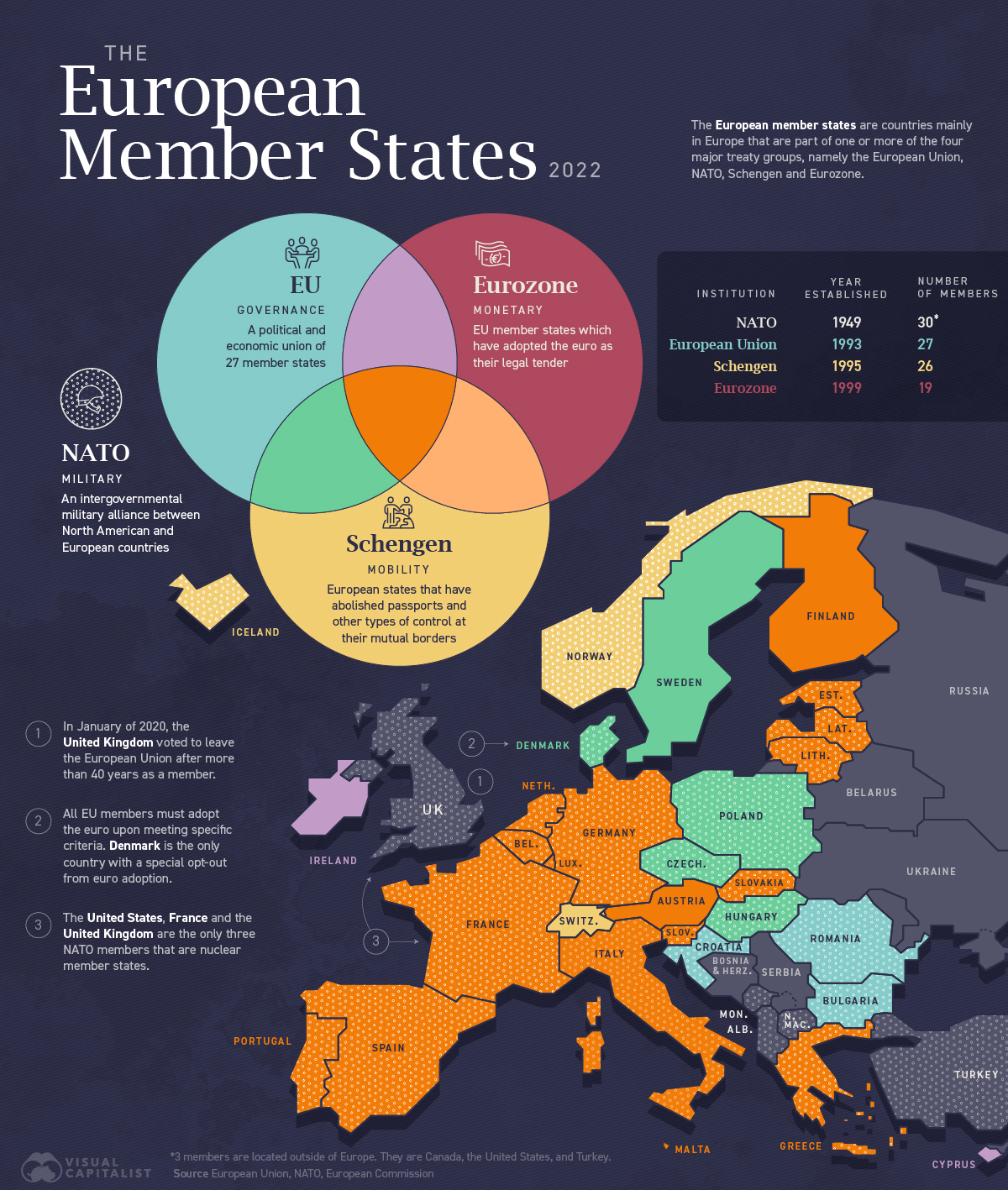
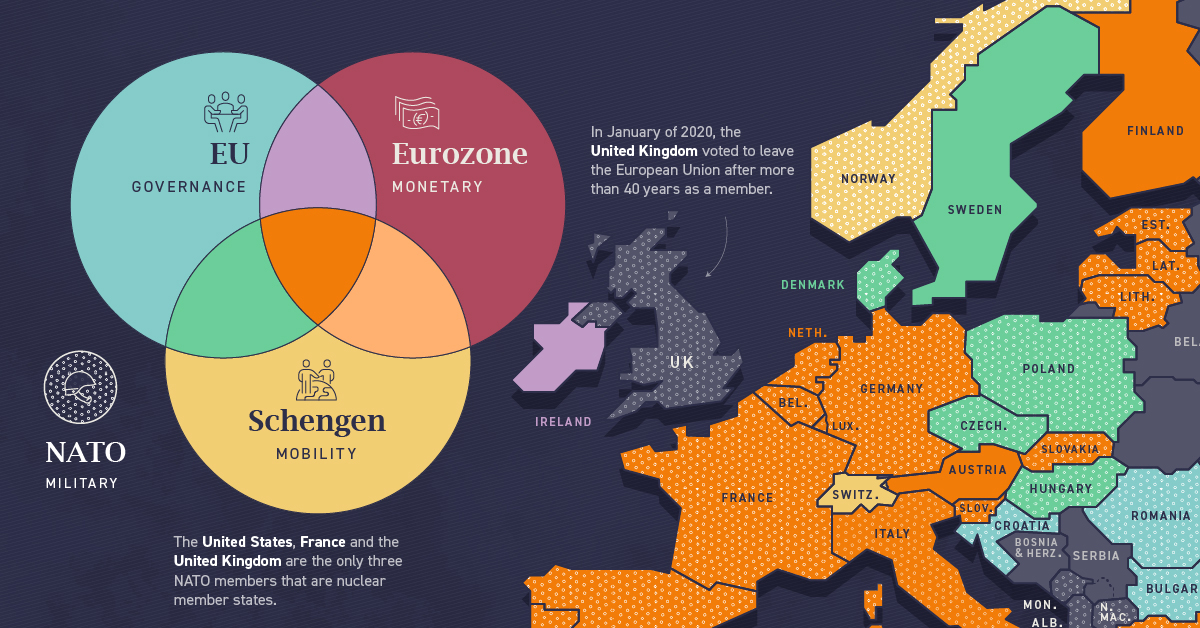
Who are Europe’s Member States?
With Ukraine’s recent bid to join the European Union (EU), the current status of Europe’s member states is back in the fray.
The European member states are countries mainly in Europe, and three outside, that are part of one or more of the four major treaty groups, namely the European Union (EU), NATO, Schengen, and eurozone.
Each of these institutions governs a different aspect of the region’s infrastructure.
Let’s take a look at each of them.
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a unique economic and political union between 27 European countries.
First created as the European Economic Community in the aftermath of WW2, the organization’s main focus was to foster economic cooperation. The idea was simple: countries that trade with one another and become economically interdependent are more likely to avoid conflict.
Beginning with six countries in 1958, the European Economic Community has since added 21 more countries (the UK left the EU in 2020), with a primary focus on single or internal markets.
Here are the countries that comprise the European Union:
| Number | Countries | Year of Accession |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇦🇹 Austria | 1995 |
| 2 | 🇧🇪 Belgium | Founder |
| 3 | 🇧🇬 Bulgaria | 2007 |
| 4 | 🇭🇷 Croatia | 2013 |
| 5 | 🇨🇾 Cyprus | 2004 |
| 6 | 🇨🇿 Czech Republic | 2004 |
| 7 | 🇩🇰 Denmark | 1973 |
| 8 | 🇪🇪 Estonia | 2004 |
| 9 | 🇫🇮 Finland | 1995 |
| 10 | 🇫🇷 France | Founder |
| 11 | 🇩🇪 Germany | Founder |
| 12 | 🇬🇷 Greece | 1981 |
| 13 | 🇭🇺 Hungary | 2004 |
| 14 | 🇮🇪 Ireland | 1973 |
| 15 | 🇮🇹 Italy | Founder |
| 16 | 🇱🇻 Latvia | 2004 |
| 17 | 🇱🇹 Lithuania | 2004 |
| 18 | 🇱🇺 Luxembourg | Founder |
| 19 | 🇲🇹 Malta | 2004 |
| 20 | 🇳🇱 Netherlands | Founder |
| 21 | 🇵🇱 Poland | 2004 |
| 22 | 🇵🇹 Portugal | 1986 |
| 23 | 🇷🇴 Romania | 2007 |
| 24 | 🇸🇰 Slovakia | 2004 |
| 25 | 🇸🇮 Slovenia | 2004 |
| 26 | 🇪🇸 Spain | 1986 |
| 27 | 🇸🇪 Sweden | 1995 |
What began as a purely economic union has evolved into an organization pioneering the development of many different policy areas. A name change from the European Economic Community to the European Union in 1993 reflected this.
NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) exists for the sole purpose of facilitating a political and military alliance between its 30 member countries.
Established in 1949 in response to post-WW2 Soviet aggression, NATO exists for the collective defense and security of the group. Members share few laws and regulations. An attack on one constitutes an attack on all, and member states are obligated to defend one another.
The chronological timeline of NATO’s expansion since its establishment paints a fascinating picture.
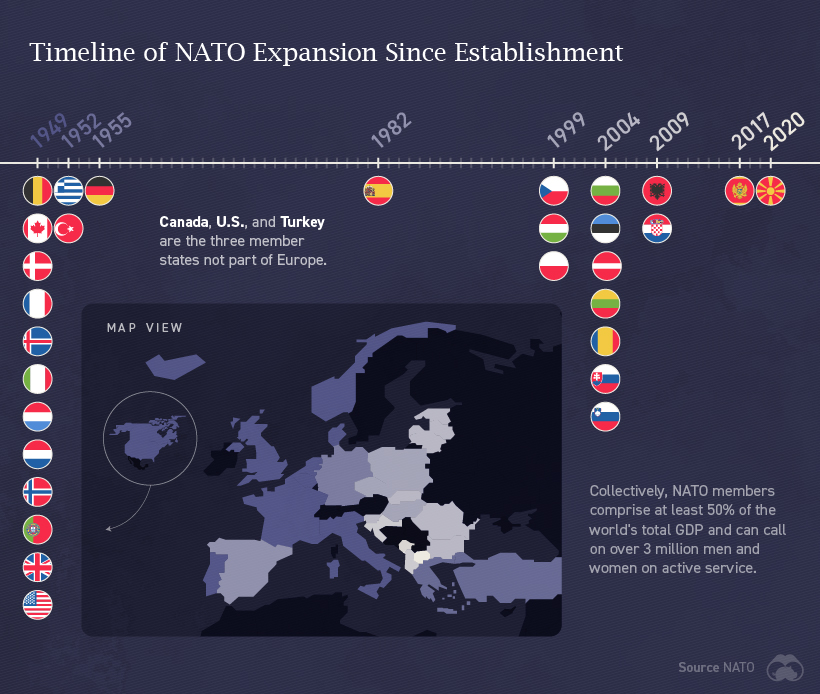
As of 2021, NATO officially recognizes three aspiring NATO members: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Georgia, and Ukraine. Ukraine has voiced its desire to join NATO since 2014 but hasn’t met its political and military criteria.
Eurozone
The eurozone is a geographic and economic region that consists of countries that have adopted the euro as their national currency. Approximately 340 million people live in the euro area.
Today, the eurozone consists of 19 countries of the European Union. Here they are:
| Number | Countries | Year of Adoption |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇦🇹 Austria | 1999 |
| 2 | 🇧🇪 Belgium | 1999 |
| 3 | 🇨🇾 Cyprus | 2008 |
| 4 | 🇪🇪 Estonia | 2011 |
| 5 | 🇫🇮 Finland | 1999 |
| 6 | 🇫🇷 France | 1999 |
| 7 | 🇩🇪 Germany | 1999 |
| 8 | 🇬🇷 Greece | 2001 |
| 9 | 🇮🇪 Ireland | 1999 |
| 10 | 🇮🇹 Italy | 1999 |
| 11 | 🇱🇻 Latvia | 2014 |
| 12 | 🇱🇹 Lithuania | 2015 |
| 13 | 🇱🇺 Luxembourg | 1999 |
| 14 | 🇲🇹 Malta | 2008 |
| 15 | 🇳🇱 Netherlands | 1999 |
| 16 | 🇵🇹 Portugal | 1999 |
| 17 | 🇸🇰 Slovakia | 2009 |
| 18 | 🇸🇮 Slovenia | 2007 |
| 19 | 🇪🇸 Spain | 1999 |
European Union nations that decide to participate in the eurozone must meet a multitude of financial requirements. They include price stability, sound public finances, the durability of convergence, and exchange rate stability.
Not all countries have to adopt the currency, though. For example, Denmark has a special opt-out clause to use its own currency and maintain its financial independence.
Schengen
The Schengen Area comprises 26 European countries that agreed to create common entry and exit requirements to remove the need for internal borders. This allows travellers up to 90 days of visa-free travel to any of the countries in the Schengen Area.
The border-free Schengen Area guarantees free movement to more than 400 million EU citizens, along with non-EU nationals living in the EU or visiting as tourists, exchange students, or for business purposes.
Here’s a list of the 26 countries that are a part of the Schengen Area:
| Number | Countries | Year of Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇦🇹 Austria | 1997 |
| 2 | 🇧🇪 Belgium | 1995 |
| 3 | 🇨🇿 Czech Republic | 2007 |
| 4 | 🇩🇰 Denmark | 2001 |
| 5 | 🇪🇪 Estonia | 2007 |
| 6 | 🇫🇮 Finland | 2001 |
| 7 | 🇫🇷 France | 1995 |
| 8 | 🇩🇪 Germany | 1995 |
| 9 | 🇬🇷 Greece | 2000 |
| 10 | 🇭🇺 Hungary | 2007 |
| 11 | 🇮🇸 Iceland | 2001 |
| 12 | 🇮🇹 Italy | 1997 |
| 13 | 🇱🇻 Latvia | 2007 |
| 14 | 🇱🇮 Liechtenstein | 2011 |
| 15 | 🇱🇹 Lithuania | 2007 |
| 16 | 🇱🇺 Luxembourg | 1995 |
| 17 | 🇲🇹 Malta | 2007 |
| 18 | 🇳🇱 Netherlands | 1995 |
| 19 | 🇳🇴 Norway | 2001 |
| 20 | 🇵🇱 Poland | 2007 |
| 21 | 🇵🇹 Portugal | 1995 |
| 22 | 🇸🇰 Slovakia | 2007 |
| 23 | 🇸🇮 Slovenia | 2007 |
| 24 | 🇪🇸 Spain | 1995 |
| 25 | 🇸🇪 Sweden | 2001 |
| 26 | 🇨🇭 Switzerland | 2008 |
Monaco, Vatican City, and San Marino also have open borders with Schengen area countries even though they aren’t part of the treaty.
China
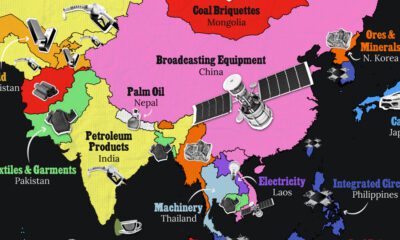
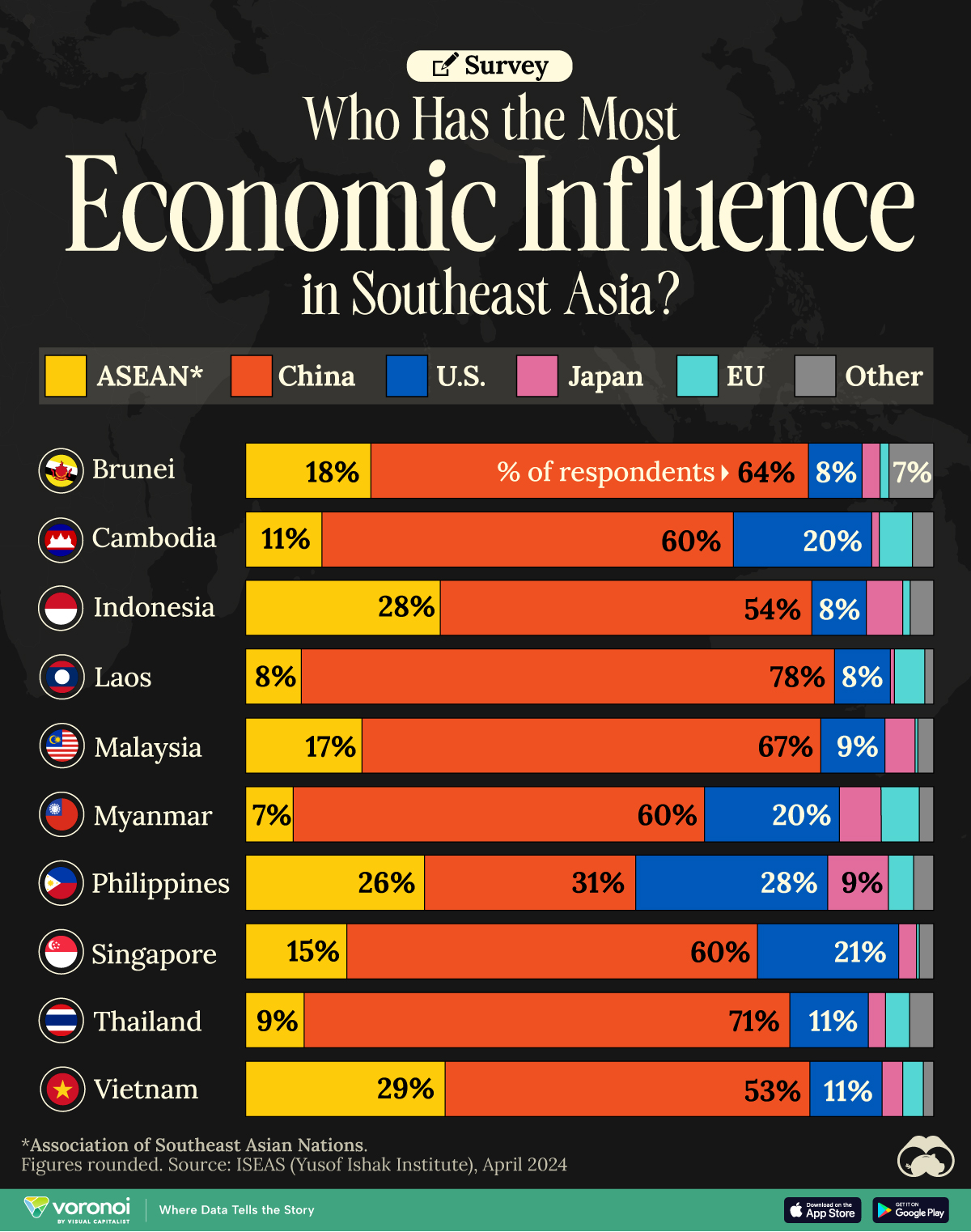
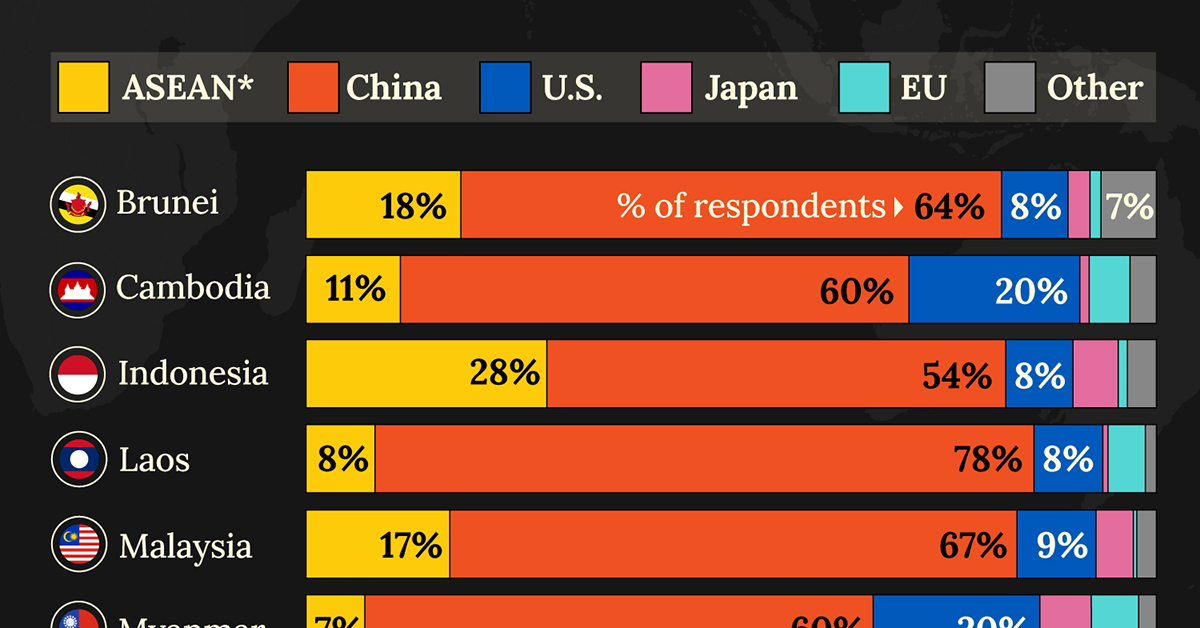
Which Countries Have the Most Economic Influence in Southeast Asia?
One country dominates this survey of who has the most economic influence in the region.
Countries With the Most Economic Influence in Southeast Asia
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This chart visualizes the results of a 2024 survey conducted by the ASEAN Studies Centre at the ISEAS-Yusof Ishak Institute.
Nearly 2,000 respondents from 10 countries were asked to select which country/region they believe has the most influential economic power in Southeast Asia.
The countries surveyed are all member states of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), a political and economic union of 10 countries in Southeast Asia.
Southeast Asia Perceptions: Who’s Got Economic Influence?
Across all ASEAN nations, China is regarded as the region’s most influential economic power.
Laos and Thailand had the highest share of respondents picking China, at 78% and 71% respectively. As the report points out, China is Laos’ largest foreign investor as well as its top export market.
| Country | 🇨🇳 China | 🌏 ASEAN | 🇺🇸 U.S. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🇧🇳 Brunei | 64% | 18% | 8% |
| 🇰🇭 Cambodia | 60% | 11% | 20% |
| 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 54% | 28% | 8% |
| 🇱🇦 Laos | 78% | 8% | 8% |
| 🇲🇾 Malaysia | 67% | 17% | 9% |
| 🇲🇲 Myanmar | 60% | 7% | 20% |
| 🇵🇭 Philippines | 31% | 26% | 28% |
| 🇸🇬 Singapore | 60% | 15% | 21% |
| 🇹🇭 Thailand | 71% | 9% | 11% |
| 🇻🇳 Vietnam | 53% | 29% | 11% |
Note: Percentages are rounded.
Other ASEAN countries usually score highly as well, along with the United States.
It’s only in the Philippines, where China (31%), the U.S. (28%) and ASEAN (26%) were perceived as having a similar amount of influence.
ASEAN, Japan, and the EU
Filipinos also rated Japan’s economic influence the highest (9%) compared to those surveyed in other ASEAN countries. In 2023, the Southeast Asian bloc celebrated 50 years of friendship with Japan, marking it as one of their most important “dialogue partners.”
| Country | 🇯🇵 Japan | 🇪🇺 EU | 🌐 Other |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🇧🇳 Brunei | 3% | 1% | 7% |
| 🇰🇭 Cambodia | 1% | 5% | 3% |
| 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 5% | 1% | 3% |
| 🇱🇦 Laos | 1% | 4% | 1% |
| 🇲🇾 Malaysia | 4% | 0% | 2% |
| 🇲🇲 Myanmar | 6% | 6% | 2% |
| 🇵🇭 Philippines | 9% | 4% | 3% |
| 🇸🇬 Singapore | 3% | 0% | 2% |
| 🇹🇭 Thailand | 3% | 4% | 4% |
| 🇻🇳 Vietnam | 3% | 3% | 2% |
Note: Percentages are rounded. Other countries include: Australia, South Korea, India, and the UK.
The EU also received single-percentage responses, its highest share coming from Myanmar (6%), Cambodia (5%), and Laos (4%).
Finally, the report contrasted China’s robust economic influence with concerns about its growing impact in the region. Respondents from Vietnam (88%), Myanmar (88%), and Thailand (80%) had the highest levels of concern, despite their countries’ strong trade ties with China.
-

 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week agoVisualizing the Tax Burden of Every U.S. State
-
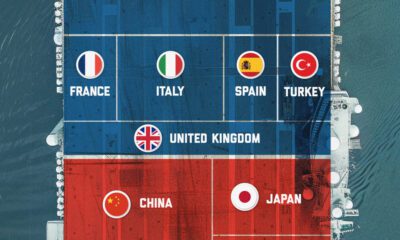
 Misc6 days ago
Misc6 days agoVisualized: Aircraft Carriers by Country
-

 Culture6 days ago
Culture6 days agoHow Popular Snack Brand Logos Have Changed
-

 Mining1 week ago
Mining1 week agoVisualizing Copper Production by Country in 2023
-
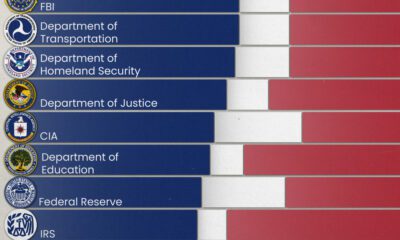
 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoCharted: How Americans Feel About Federal Government Agencies
-
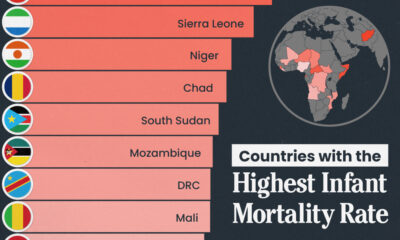
 Healthcare1 week ago
Healthcare1 week agoWhich Countries Have the Highest Infant Mortality Rates?
-
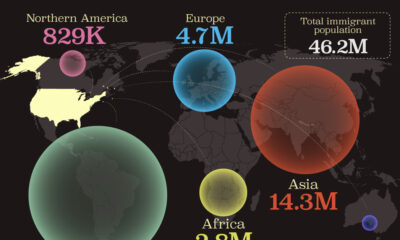
 Demographics1 week ago
Demographics1 week agoMapped: U.S. Immigrants by Region
-
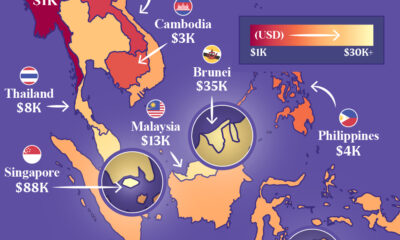
 Economy1 week ago
Economy1 week agoMapped: Southeast Asia’s GDP Per Capita, by Country