Politics
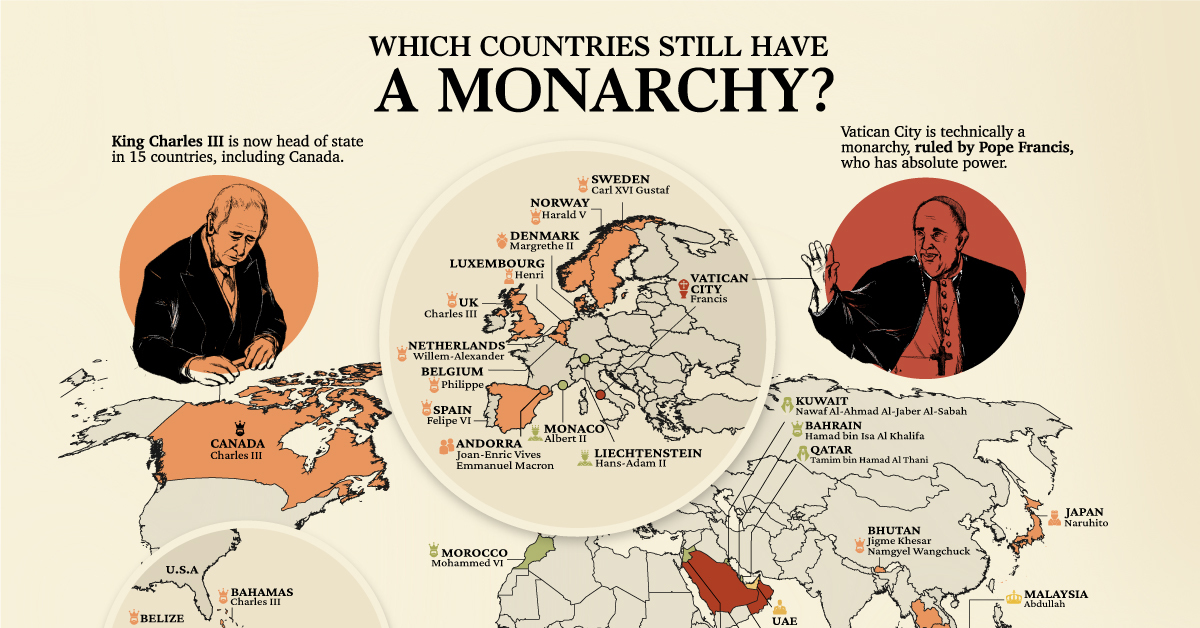
Mapped: Which Countries Still Have a Monarchy?
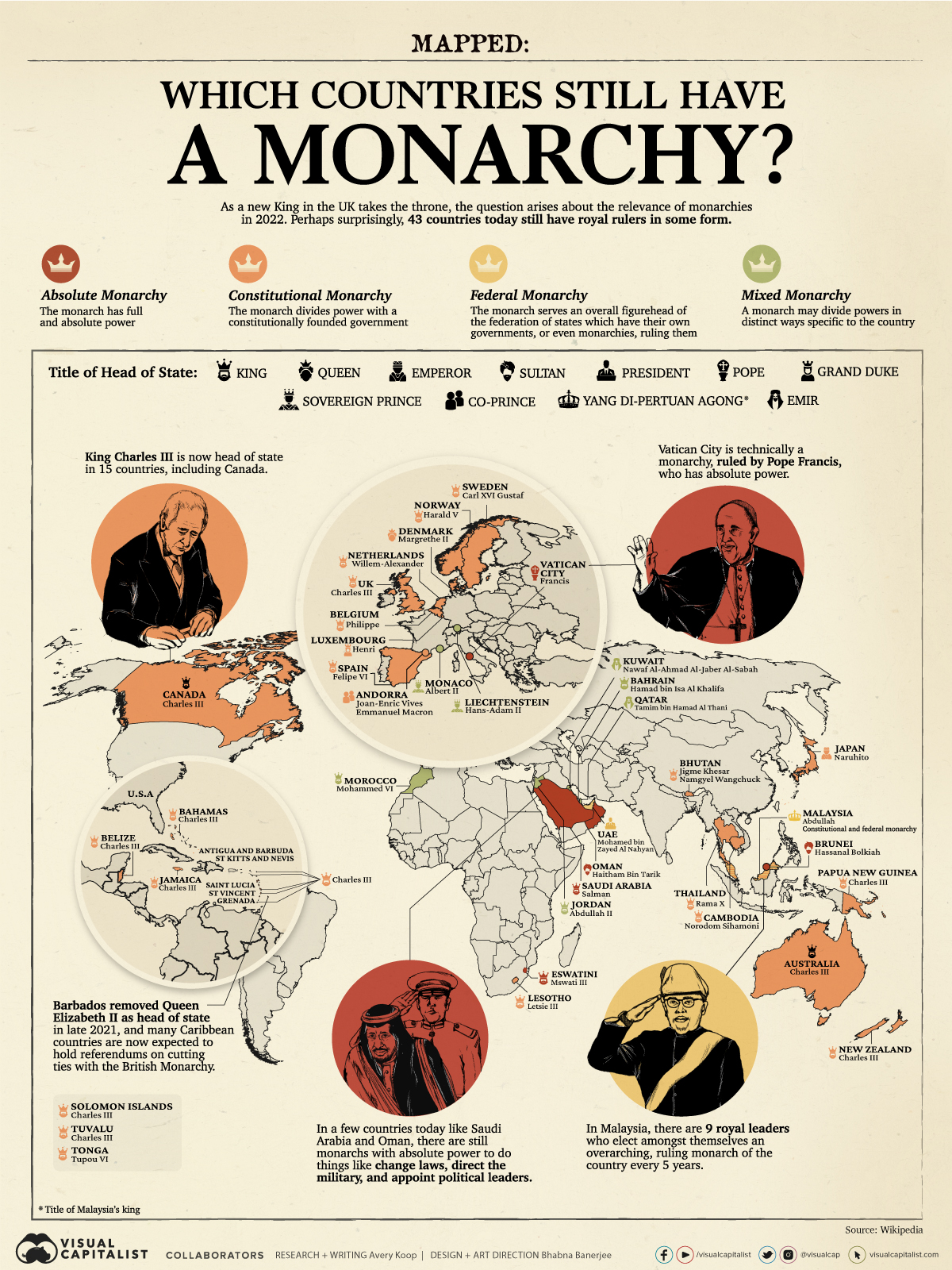
Mapped: Which Countries Still Have a Monarchy?
In the wake of Queen Elizabeth II’s death, the question of monarchy is brought sharply into focus.
However, a surprising number of countries have ruling monarchs, and in this visual we break down the kinds of royal leadership across the 43 countries that still have them.
Types of Monarchies
A monarch in the simplest sense is a country’s king, queen, emir, or sultan, and so on. But before diving in, it’s important to break down the distinctions between the types of monarchies that exist today. Generally, there are four kinds:
① Constitutional Monarchy
The monarch divides power with a constitutionally founded government. In this situation, the monarch, while having ceremonial duties and certain responsibilities, does not have any political power. For example, the UK’s monarch must sign all laws to make them official, but has no power to change or reject new laws.
Here are some examples of countries with constitutional monarchies:
🇯🇵 Japan
🇬🇧 United Kingdom
🇩🇰 Denmark
② Absolute Monarchy
The monarch has full and absolute political power. They can amend, reject, or create laws, represent the country’s interests abroad, appoint political leaders, and so on.
Here are some examples of countries with absolute monarchies:
🇸🇿 Eswatini
🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia
🇻🇦 Vatican City
③ Federal Monarchy
The monarch serves an overall figurehead of the federation of states which have their own governments, or even monarchies, ruling them.
Here are some examples of countries with federal monarchies:
🇦🇪 UAE
🇲🇾 Malaysia
Malaysia is a unique form of federal monarchy. Every five years, each state’s royal leaders choose amongst themselves who will be the monarch, or the Yang di-Pertuan Agong, of Malaysia and the respective states. Furthermore, the monarchy is also constitutional, allowing a democratically elected body to govern.
④ Mixed Monarchy
This is a situation wherein an absolute monarch may divide powers in distinct ways specific to the country.
Here are some examples of countries with mixed monarchies:
🇯🇴 Jordan
🇱🇮 Liechtenstein
🇲🇦 Morocco
Interestingly, Liechtenstein is the only European monarchy that still practises strict agnatic primogeniture. Under agnatic primogeniture, the degree of kinship is determined by tracing descent from the nearest common ancestor through male ancestors.
Kings, Queens, Emperors, and Sultans Around the Globe
Now let’s break down the different monarchies country by country:
| Country | Type of Monarchy | Title of Head of State | Monarch | Title of Head of Government |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 🇦🇩 Andorra | Constitutional | Co-Princes | Joan-Enric Vives, Emmanuel Macron | Prime Minister |
| 🇦🇬 Antigua and Barbuda | Constitutional | King | Charles III | Prime Minister |
| 🇦🇺 Australia | Constitutional | King | Charles III | Prime Minister |
| 🇧🇭 Bahrain | Mixed | King | Hamad bin Isa Al Khalifa | Prime Minister |
| 🇧🇪 Belgium | Constitutional | King | Philippe | Prime Minister |
| 🇧🇿 Belize | Constitutional | King | Charles III | Prime Minister |
| 🇧🇹 Bhutan | Constitutional | King | Jigme Khesar Namgyel Wangchuck | Prime Minister |
| 🇧🇳 Brunei Darussalam | Absolute | Sultan | Hassanal Bolkiah | Sultan |
| 🇰🇭 Cambodia | Constitutional | King | Norodom Sihamoni | Prime Minister |
| 🇨🇦 Canada | Constitutional | King | Charles III | Prime Minister |
| 🇩🇰 Denmark | Constitutional | Queen | Margrethe II | Prime Minister |
| 🇸🇿 Eswatini | Absolute | King | Mswati III | Prime Minister |
| 🇬🇩 Grenada | Constitutional | King | Charles III | Prime Minister |
| 🇯🇲 Jamaica | Constitutional | King | Charles III | Prime Minister |
| 🇯🇵 Japan | Constitutional | Emperor | Naruhito | Prime Minister |
| 🇯🇴 Jordan | Mixed | King | Abdullah II | Prime Minister |
| 🇰🇼 Kuwait | Mixed | Emir | Nawaf Al-Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah | Prime Minister |
| 🇱🇸 Lesotho | Constitutional | King | Letsie III | Prime Minister |
| 🇱🇮 Liechtenstein | Mixed | Sovereign Prince | Hans-Adam II | Prime Minister |
| 🇱🇺 Luxembourg | Constitutional | Grand Duke | Henri | Prime Minister |
| 🇲🇾 Malaysia | Constitutional & Federal | Yang di-Pertuan Agong | Abdullah | Prime Minister |
| 🇲🇨 Monaco | Mixed | Sovereign Prince | Albert II | Minister of State |
| 🇲🇦 Morocco | Mixed | King | Mohammed VI | Prime Minister |
| 🇳🇱 Netherlands | Constitutional | King | Willem-Alexander | Prime Minister |
| 🇳🇿 New Zealand | Constitutional | King | Charles III | Prime Minister |
| 🇳🇴 Norway | Constitutional | King | Harald V | Prime Minister |
| 🇴🇲 Oman | Absolute | Sultan | Haitham bin Tarik | Sultan |
| 🇵🇬 Papua New Guinea | Constitutional | King | Charles III | Prime Minister |
| 🇶🇦 Qatar | Mixed | Emir | Tamim bin Hamad Al Thani | Prime Minister |
| 🇰🇳 Saint Kitts and Nevis | Constitutional | King | Charles III | Prime Minister |
| 🇱🇨 Saint Lucia | Constitutional | King | Charles III | Prime Minister |
| 🇻🇨 Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | Constitutional | King | Charles III | Prime Minister |
| 🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia | Absolute | King | Salman | Prime Minister |
| 🇸🇧 Solomon Islands | Constitutional | King | Charles III | Prime Minister |
| 🇪🇸 Spain | Constitutional | King | Felipe VI | President of the Government |
| 🇸🇪 Sweden | Constitutional | King | Carl XVI Gustaf | Prime Minister |
| 🇹🇭 Thailand | Constitutional | King | Rama X | Prime Minister |
| 🇧🇸 The Bahamas | Constitutional | King | Charles III | Prime Minister |
| 🇹🇴 Tonga | Constitutional | King | Tupou VI | Prime Minister |
| 🇹🇻 Tuvalu | Constitutional | King | Charles III | Prime Minister |
| 🇦🇪 UAE | Federal | President | Mohamed bin Zayed Al Nahyan | Prime Minister |
| 🇬🇧 UK | Constitutional | King | Charles III | Prime Minister |
| 🇻🇦 Vatican City | Absolute | Pope | Francis | President of the Pontifical Commission |
Constitutional monarchies are undoubtedly the most popular form of royal leadership in the modern era, making up close to 70% of all monarchies. This situation allows for democratically elected governments to rule the country, while the monarch performs ceremonial duties.
Most monarchs are hereditary, inheriting their position by luck of their birth, but interestingly, French president, Emmanuel Macron, technically serves as a Co-Prince of Andorra.
Another unique case is the Vatican’s Pope Francis, who has absolute power in the small independent city—he gained his role thanks to an election process known as a papal conclave.
The Role of Monarchies
One of the most notable and famous ruling monarchies is the United Kingdom’s House of Windsor—also known as Queen Elizabeth II’s family. King Charles III has now ascended to the country’s throne, making him head of state in 15 nations total, including Canada, Australia, and New Zealand.
Many see the benefit in having a stable and consistent form of tradition and decorum at the country’s head of state.
“The Crown is an integral part of the institution of Parliament. The Queen [now King] plays a constitutional role in opening and dissolving Parliament and approving Bills before they become law.” – British Parliament
Japan’s royal family has been a prime example of stability, having reigned in the country for more than 2,600 years under the same hereditary line.
Critiques and the Future of Monarchy
Some claim, however, that there is no function of monarchy in the modern day, and complaints of monarchies’ immense wealth and power are rampant.
For example, according to the Dutch government, King Willem-Alexander’s budget for 2022, funded by the state and thus, taxpayers, comes out to more than €48 million.
Beyond tax dollars, with absolute monarchies there is typically a lack of political freedoms and certain rights. Saudi Arabia, for example, has no national elections. Rather its king, Salman bin Abdulaziz Al Saud, stays in power for life, appoints the cabinet himself, and passes laws by royal decree.
The death of Queen Elizabeth, though, may bring about change though for many of the world’s royally-governed. Since Barbados’ removal of her as head of state in 2021, six other Caribbean nations have expressed the desire to do the same, namely:
🇧🇿 Belize
🇧🇸 The Bahamas
🇯🇲 Jamaica
🇬🇩 Grenada
🇦🇬 Antigua and Barbuda
🇰🇳 St. Kitts and Nevis
The future of monarchy in the 21st century is certainly not a guarantee.
Economy
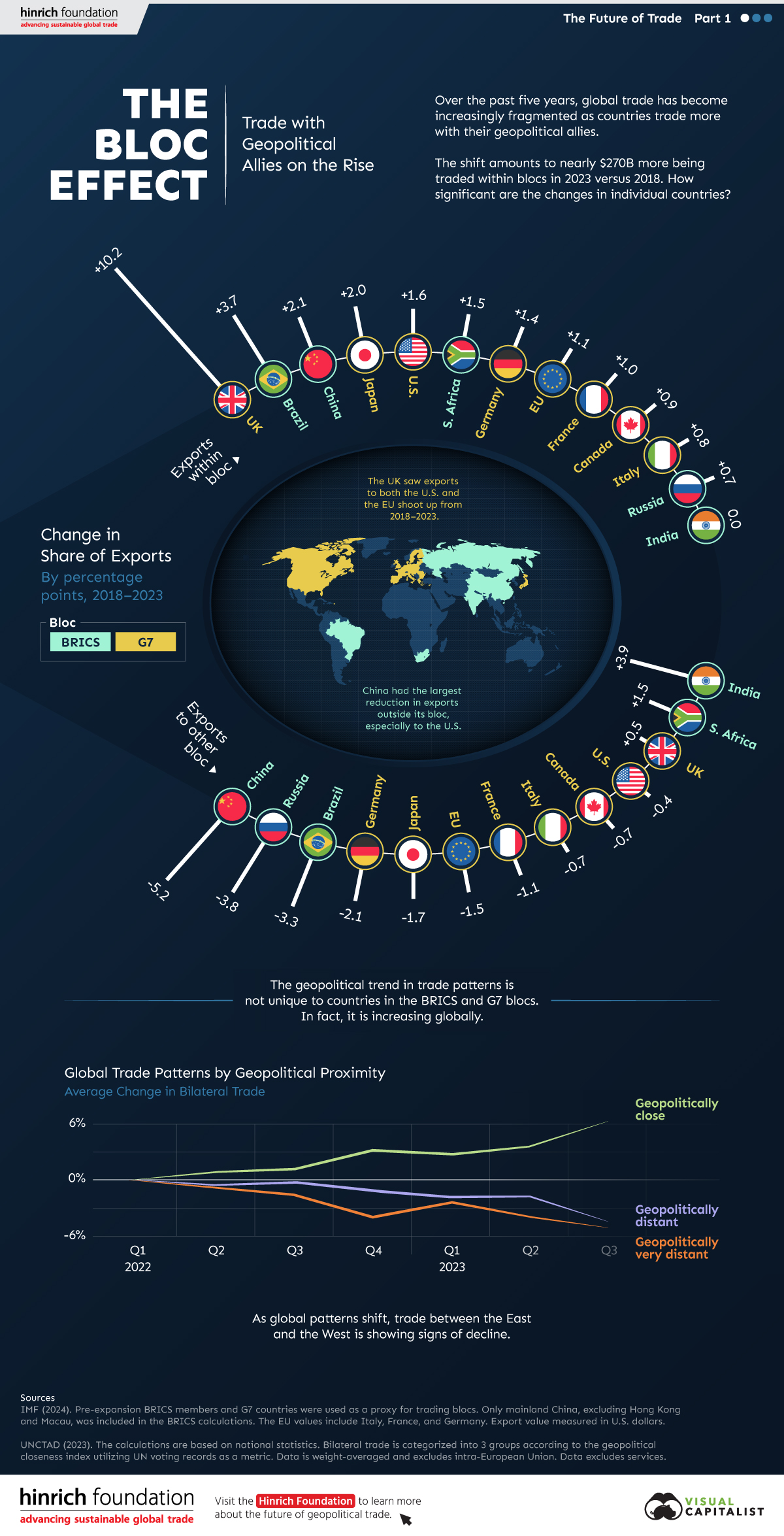
The Bloc Effect: International Trade with Geopolitical Allies on the Rise
Rising geopolitical tensions are shaping the future of international trade, but what is the effect on trading among G7 and BRICS countries?

The Bloc Effect: International Trade with Allies on the Rise
International trade has become increasingly fragmented over the last five years as countries have shifted to trading more with their geopolitical allies.
This graphic from The Hinrich Foundation, the first in a three-part series covering the future of trade, provides visual context to the growing divide in trade in G7 and pre-expansion BRICS countries, which are used as proxies for geopolitical blocs.
Trade Shifts in G7 and BRICS Countries
This analysis uses IMF data to examine differences in shares of exports within and between trading blocs from 2018 to 2023. For example, we looked at the percentage of China’s exports with other BRICS members as well as with G7 members to see how these proportions shifted in percentage points (pp) over time.
Countries traded nearly $270 billion more with allies in 2023 compared to 2018. This shift came at the expense of trade with rival blocs, which saw a decline of $314 billion.
Country Change in Exports Within Bloc (pp) Change in Exports With Other Bloc (pp)
🇮🇳 India 0.0 3.9
🇷🇺 Russia 0.7 -3.8
🇮🇹 Italy 0.8 -0.7
🇨🇦 Canada 0.9 -0.7
🇫🇷 France 1.0 -1.1
🇪🇺 EU 1.1 -1.5
🇩🇪 Germany 1.4 -2.1
🇿🇦 South Africa 1.5 1.5
🇺🇸 U.S. 1.6 -0.4
🇯🇵 Japan 2.0 -1.7
🇨🇳 China 2.1 -5.2
🇧🇷 Brazil 3.7 -3.3
🇬🇧 UK 10.2 0.5
All shifts reported are in percentage points. For example, the EU saw its share of exports to G7 countries rise from 74.3% in 2018 to 75.4% in 2023, which equates to a 1.1 percentage point increase.
The UK saw the largest uptick in trading with other countries within the G7 (+10.2 percentage points), namely the EU, as the post-Brexit trade slump to the region recovered.
Meanwhile, the U.S.-China trade dispute caused China’s share of exports to the G7 to fall by 5.2 percentage points from 2018 to 2023, the largest decline in our sample set. In fact, partly as a result of the conflict, the U.S. has by far the highest number of harmful tariffs in place.
The Russia-Ukraine War and ensuing sanctions by the West contributed to Russia’s share of exports to the G7 falling by 3.8 percentage points over the same timeframe.
India, South Africa, and the UK bucked the trend and continued to witness advances in exports with the opposing bloc.
Average Trade Shifts of G7 and BRICS Blocs
Though results varied significantly on a country-by-country basis, the broader trend towards favoring geopolitical allies in international trade is clear.
Bloc Change in Exports Within Bloc (pp) Change in Exports With Other Bloc (pp)
Average 2.1 -1.1
BRICS 1.6 -1.4
G7 incl. EU 2.4 -1.0
Overall, BRICS countries saw a larger shift away from exports with the other bloc, while for G7 countries the shift within their own bloc was more pronounced. This implies that though BRICS countries are trading less with the G7, they are relying more on trade partners outside their bloc to make up for the lost G7 share.
A Global Shift in International Trade and Geopolitical Proximity
The movement towards strengthening trade relations based on geopolitical proximity is a global trend.
The United Nations categorizes countries along a scale of geopolitical proximity based on UN voting records.
According to the organization’s analysis, international trade between geopolitically close countries rose from the first quarter of 2022 (when Russia first invaded Ukraine) to the third quarter of 2023 by over 6%. Conversely, trade with geopolitically distant countries declined.
The second piece in this series will explore China’s gradual move away from using the U.S. dollar in trade settlements.

Visit the Hinrich Foundation to learn more about the future of geopolitical trade

-

 Economy3 hours ago
Economy3 hours agoEconomic Growth Forecasts for G7 and BRICS Countries in 2024
The IMF has released its economic growth forecasts for 2024. How do the G7 and BRICS countries compare?
-

 United States1 week ago
United States1 week agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
We visualized the top U.S. companies by employees, revealing the massive scale of retailers like Walmart, Target, and Home Depot.
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
We visualized product categories that saw the highest % increase in price due to U.S. inflation as of March 2024.
-

 Economy4 weeks ago
Economy4 weeks agoG20 Inflation Rates: Feb 2024 vs COVID Peak
We visualize inflation rates across G20 countries as of Feb 2024, in the context of their COVID-19 pandemic peak.
-

 Economy1 month ago
Economy1 month agoMapped: Unemployment Claims by State
This visual heatmap of unemployment claims by state highlights New York, California, and Alaska leading the country by a wide margin.
-
 Economy2 months ago
Economy2 months agoConfidence in the Global Economy, by Country
Will the global economy be stronger in 2024 than in 2023?
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023