Markets
Where the World’s Banks Make the Most Money

Where the World’s Banks Make the Most Money
Profits in banking have been steadily on the rise since the financial crisis.
Just last year, the global banking industry cashed in an impressive $1.36 trillion in after-tax profits — the highest total in the sector seen in the last 20 years.
What are the drivers behind revenue and profits in the financial services sector, and where do the biggest opportunities exist in the future?
Following the Money
Today’s infographic comes to us from McKinsey & Company, and it leverages proprietary insights from their Panorama database.
Using data stemming from more than 60 countries, we’ve broken down historical banking profits by region, while also visualizing key ratios that help demonstrate why specific countries are more profitable for the industry.
Finally, we’ve also looked at the particular geographic regions that may present the biggest opportunities in the future, and why they are relevant today.
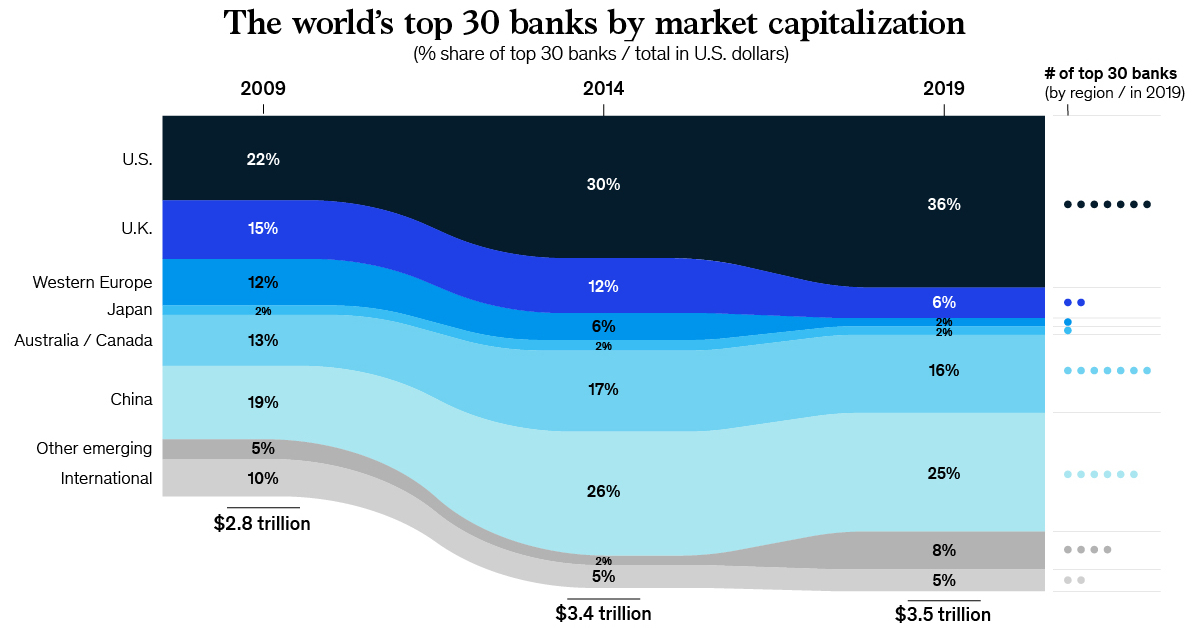
Banking Profits, by Region
Before we look at what’s driving banking profits, let’s start with a breakdown of annual after-tax profits by region over time.
Banking Profit by Year and Region ($B)
| 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | $19 | $118 | $176 | $263 | $268 | $263 | $291 | $275 | $270 | $403 |
| China | $95 | $135 | $174 | $225 | $255 | $278 | $278 | $270 | $301 | $333 |
| Western Europe | $78 | $34 | $21 | -$70 | $28 | $95 | $154 | $159 | $186 | $198 |
| Rest of World | $196 | $243 | $265 | $285 | $309 | $327 | $348 | $361 | $387 | $421 |
| Global ($B) | $388 | $530 | $635 | $703 | $859 | $963 | $1,070 | $1,065 | $1,144 | $1,356 |
In 2018, the United States accounted for $403 billion of after-tax profits in the banking sector — however, China sits in a very close second place, raking in $333 billion.
What’s Under the Hood?
While there’s no doubt that financial services can be profitable in almost any corner of the globe, what is less obvious is where this profit actually comes from.
The truth is that banking can vary greatly depending on location — and what drives value for banks in one country may be completely different from what drives value in another.
Let’s look at data and ratios from four very different places to get a sense of how financial services markets can vary.
| Country | RARC/GDP | Loans Penetration/GDP | Margins (RBRC/Total Loans) | Risk Cost Margin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 5.4% | 121% | 5.0% | 0.4% |
| China | 6.6% | 147% | 6.0% | 1.4% |
| Singapore | 13.0% | 316% | 4.6% | 0.4% |
| Finland | 3.4% | 133% | 2.8% | 0.2% |
| Global Average | 5.1% | 124% | 5.0% | 0.8% |
1. RARC / GDP (Revenues After Risk Costs / GDP)
This ratio shows compares a country’s banking revenues to overall economic production, giving a sense of how important banking is to the economy. Using this, you can see that banking is far more important to Singapore’s economy than others in the table.
2. Loans Penetration / GDP
Loans penetration can be further broken up into retail loans and wholesale loans. The difference can be immediately seen when looking at data on China and the United States:
| Country | Retail Loans | Wholesale Loans | Loan Penetration (Total) |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 73% | 48% | 121% |
| China | 34% | 113% | 147% |
In America, banks make loans primarily to the retail sector. In China, there’s a higher penetration on a wholesale basis — usually loans being made to corporations or other such entities.
3. Margins (Revenues Before Risk Costs / Total Loans)
Margins made on lending is one way for bankers to gauge the potential of a market, and as you can see above, margins in the United States and China are both at (or above) the global average. Meanwhile, for comparison, Finland has margins that are closer to half of the global average.
4. Risk Cost Margin (Risk Cost / Total Loans)
Not surprisingly, China still holds higher risk cost margins than the global average. On the flipside, established markets like Singapore, Finland, and the U.S. all have risk margins below the global average.
Future Opportunities in Banking
While this data is useful at breaking down existing markets, it can also help to give us a sense of future opportunities as well.
Here are some of the geographic markets that have the potential to grow into key financial services markets in the future:
- Sub-Saharan Africa
Despite having 16x the population of South Africa, the rest of Sub-Saharan Africa still generates fewer banking profits. With lower loan penetration rates and RARC/GDP ratios, there is significant potential to be found throughout the continent. - India and Indonesia
Compared to similar economies in Asia, both India and Indonesia present an interesting banking opportunity because of their high margins and low loan penetration rates. - China
While China has a high overall loan penetration rate, the retail loan category still holds much potential given the country’s population and growing middle class.
A Changing Landscape in Banking
As banks shift focus to face new market challenges, the next chapter of banking may be even more interesting than the last.
Add in the high stakes around digital transformation, aging populations, and new service opportunities, and the distance between winners and losers could lengthen even more.
Where will the money in banking be in the future?
Markets
U.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
U.S. debt interest payments have surged past the $1 trillion dollar mark, amid high interest rates and an ever-expanding debt burden.

U.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
The cost of paying for America’s national debt crossed the $1 trillion dollar mark in 2023, driven by high interest rates and a record $34 trillion mountain of debt.
Over the last decade, U.S. debt interest payments have more than doubled amid vast government spending during the pandemic crisis. As debt payments continue to soar, the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) reported that debt servicing costs surpassed defense spending for the first time ever this year.
This graphic shows the sharp rise in U.S. debt payments, based on data from the Federal Reserve.
A $1 Trillion Interest Bill, and Growing
Below, we show how U.S. debt interest payments have risen at a faster pace than at another time in modern history:
| Date | Interest Payments | U.S. National Debt |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | $1.0T | $34.0T |
| 2022 | $830B | $31.4T |
| 2021 | $612B | $29.6T |
| 2020 | $518B | $27.7T |
| 2019 | $564B | $23.2T |
| 2018 | $571B | $22.0T |
| 2017 | $493B | $20.5T |
| 2016 | $460B | $20.0T |
| 2015 | $435B | $18.9T |
| 2014 | $442B | $18.1T |
| 2013 | $425B | $17.2T |
| 2012 | $417B | $16.4T |
| 2011 | $433B | $15.2T |
| 2010 | $400B | $14.0T |
| 2009 | $354B | $12.3T |
| 2008 | $380B | $10.7T |
| 2007 | $414B | $9.2T |
| 2006 | $387B | $8.7T |
| 2005 | $355B | $8.2T |
| 2004 | $318B | $7.6T |
| 2003 | $294B | $7.0T |
| 2002 | $298B | $6.4T |
| 2001 | $318B | $5.9T |
| 2000 | $353B | $5.7T |
| 1999 | $353B | $5.8T |
| 1998 | $360B | $5.6T |
| 1997 | $368B | $5.5T |
| 1996 | $362B | $5.3T |
| 1995 | $357B | $5.0T |
| 1994 | $334B | $4.8T |
| 1993 | $311B | $4.5T |
| 1992 | $306B | $4.2T |
| 1991 | $308B | $3.8T |
| 1990 | $298B | $3.4T |
| 1989 | $275B | $3.0T |
| 1988 | $254B | $2.7T |
| 1987 | $240B | $2.4T |
| 1986 | $225B | $2.2T |
| 1985 | $219B | $1.9T |
| 1984 | $205B | $1.7T |
| 1983 | $176B | $1.4T |
| 1982 | $157B | $1.2T |
| 1981 | $142B | $1.0T |
| 1980 | $113B | $930.2B |
| 1979 | $96B | $845.1B |
| 1978 | $84B | $789.2B |
| 1977 | $69B | $718.9B |
| 1976 | $61B | $653.5B |
| 1975 | $55B | $576.6B |
| 1974 | $50B | $492.7B |
| 1973 | $45B | $469.1B |
| 1972 | $39B | $448.5B |
| 1971 | $36B | $424.1B |
| 1970 | $35B | $389.2B |
| 1969 | $30B | $368.2B |
| 1968 | $25B | $358.0B |
| 1967 | $23B | $344.7B |
| 1966 | $21B | $329.3B |
Interest payments represent seasonally adjusted annual rate at the end of Q4.
At current rates, the U.S. national debt is growing by a remarkable $1 trillion about every 100 days, equal to roughly $3.6 trillion per year.
As the national debt has ballooned, debt payments even exceeded Medicaid outlays in 2023—one of the government’s largest expenditures. On average, the U.S. spent more than $2 billion per day on interest costs last year. Going further, the U.S. government is projected to spend a historic $12.4 trillion on interest payments over the next decade, averaging about $37,100 per American.
Exacerbating matters is that the U.S. is running a steep deficit, which stood at $1.1 trillion for the first six months of fiscal 2024. This has accelerated due to the 43% increase in debt servicing costs along with a $31 billion dollar increase in defense spending from a year earlier. Additionally, a $30 billion increase in funding for the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation in light of the regional banking crisis last year was a major contributor to the deficit increase.
Overall, the CBO forecasts that roughly 75% of the federal deficit’s increase will be due to interest costs by 2034.
-

 Green1 week ago
Green1 week agoRanked: The Countries With the Most Air Pollution in 2023
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Travel2 weeks ago
Travel2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue