Technology
Visualizing the Critical Metals in a Smartphone
![]() Subscribe to the Elements free mailing list for more like this
Subscribe to the Elements free mailing list for more like this
Visualizing the Critical Metals in a Smartphone
In an increasingly connected world, smartphones have become an inseparable part of our lives.
Over 60% of the world’s population owns a mobile phone and smartphone adoption continues to rise in developing countries around the world.
While each brand has its own mix of components, whether it’s a Samsung or an iPhone, most smartphones can carry roughly 80% of the stable elements on the periodic table.
But some of the vital metals to build these devices are considered at risk due to geological scarcity, geopolitical issues, and other factors.
| Smartphone Part | Critical Metal |
|---|---|
| Touch Screen | indium |
| Display | lanthanum; gadolinium; praseodymium; europium; terbium; dysprosium |
| Electronics | nickel, gallium, tantalum |
| Casing | nickel, magnesium |
| Battery | lithium, nickel, cobalt |
| Microphone, speakers, vibration unit | nickel, praseodymium, neodymium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium |
What’s in Your Pocket?
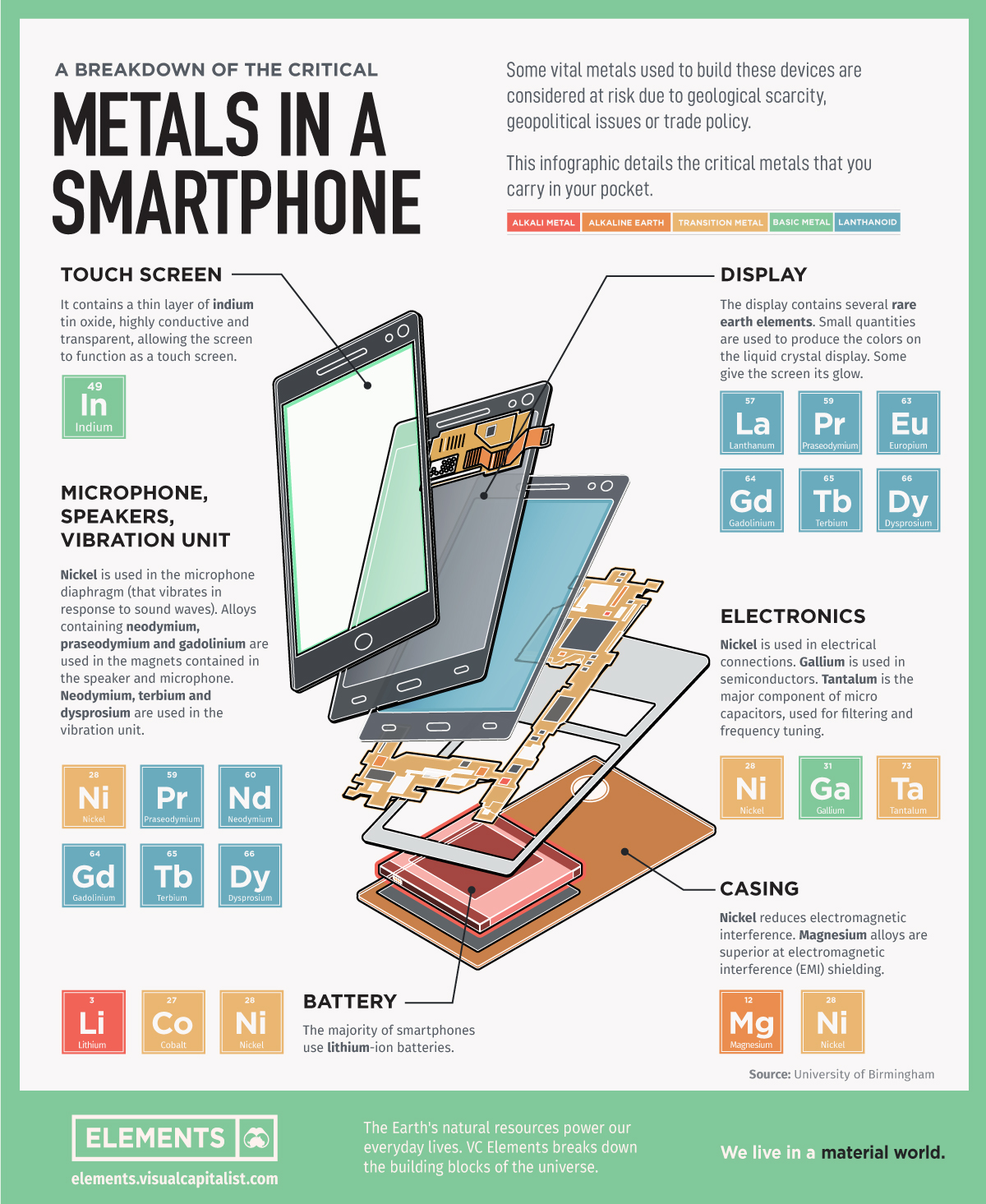
This infographic based on data from the University of Birmingham details all the critical metals that you carry in your pocket with your smartphone.
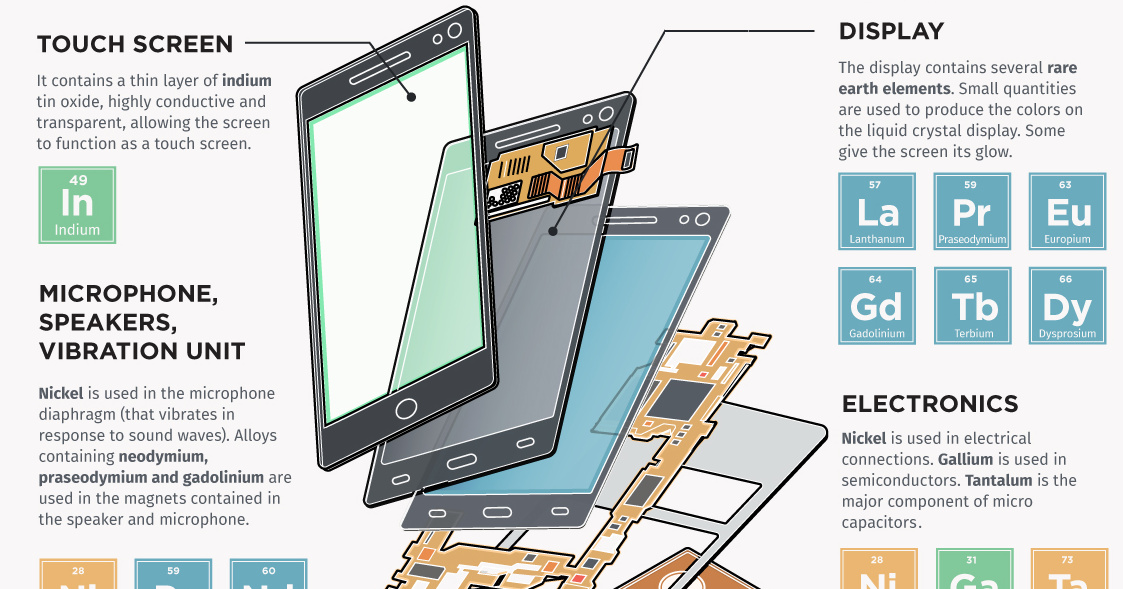
1. Touch Screen
Screens are made up of multiple layers of glass and plastic, coated with a conductor material called indium which is highly conductive and transparent.
Indium responds when contacted by another electrical conductor, like our fingers.
When we touch the screen, an electric circuit is completed where the finger makes contact with the screen, changing the electrical charge at this location. The device registers this electrical charge as a “touch event”, then prompting a response.
2. Display
Smartphones screens display images on a liquid crystal display (LCD). Just like in most TVs and computer monitors, a phone LCD uses an electrical current to adjust the color of each pixel.
Several rare earth elements are used to produce the colors on screen.
3. Electronics
Smartphones employ multiple antenna systems, such as Bluetooth, GPS, and WiFi.
The distance between these antenna systems is usually small making it extremely difficult to achieve flawless performance. Capacitors made of the rare, hard, blue-gray metal tantalum are used for filtering and frequency tuning.
Nickel is also used in capacitors and in mobile phone electrical connections. Another silvery metal, gallium, is used in semiconductors.
4. Microphone, Speakers, Vibration Unit
Nickel is used in the microphone diaphragm (that vibrates in response to sound waves).
Alloys containing rare earths neodymium, praseodymium and gadolinium are used in the magnets contained in the speaker and microphone. Neodymium, terbium and dysprosium are also used in the vibration unit.
5. Casing
There are many materials used to make phone cases, such as plastic, aluminum, carbon fiber, and even gold. Commonly, the cases have nickel to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and magnesium alloys for EMI shielding.
6. Battery
Unless you bought your smartphone a decade ago, your device most likely carries a lithium-ion battery, which is charged and discharged by lithium ions moving between the negative (anode) and positive (cathode) electrodes.
What’s Next?
Smartphones will naturally evolve as consumers look for ever-more useful features. Foldable phones, 5G technology with higher download speeds, and extra cameras are just a few of the changes expected.
As technology continues to improve, so will the demand for the metals necessary for the next generation of smartphones.
This post was originally featured on Elements
Technology
Ranked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
Nvidia is coming for Intel’s crown. Samsung is losing ground. AI is transforming the space. We break down revenue for semiconductor companies.
Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Did you know that some computer chips are now retailing for the price of a new BMW?
As computers invade nearly every sphere of life, so too have the chips that power them, raising the revenues of the businesses dedicated to designing them.
But how did various chipmakers measure against each other last year?
We rank the biggest semiconductor companies by their percentage share of the industry’s revenues in 2023, using data from Omdia research.
Which Chip Company Made the Most Money in 2023?
Market leader and industry-defining veteran Intel still holds the crown for the most revenue in the sector, crossing $50 billion in 2023, or 10% of the broader industry’s topline.
All is not well at Intel, however, with the company’s stock price down over 20% year-to-date after it revealed billion-dollar losses in its foundry business.
| Rank | Company | 2023 Revenue | % of Industry Revenue |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Intel | $51B | 9.4% |
| 2 | NVIDIA | $49B | 9.0% |
| 3 | Samsung Electronics | $44B | 8.1% |
| 4 | Qualcomm | $31B | 5.7% |
| 5 | Broadcom | $28B | 5.2% |
| 6 | SK Hynix | $24B | 4.4% |
| 7 | AMD | $22B | 4.1% |
| 8 | Apple | $19B | 3.4% |
| 9 | Infineon Tech | $17B | 3.2% |
| 10 | STMicroelectronics | $17B | 3.2% |
| 11 | Texas Instruments | $17B | 3.1% |
| 12 | Micron Technology | $16B | 2.9% |
| 13 | MediaTek | $14B | 2.6% |
| 14 | NXP | $13B | 2.4% |
| 15 | Analog Devices | $12B | 2.2% |
| 16 | Renesas Electronics Corporation | $11B | 1.9% |
| 17 | Sony Semiconductor Solutions Corporation | $10B | 1.9% |
| 18 | Microchip Technology | $8B | 1.5% |
| 19 | Onsemi | $8B | 1.4% |
| 20 | KIOXIA Corporation | $7B | 1.3% |
| N/A | Others | $126B | 23.2% |
| N/A | Total | $545B | 100% |
Note: Figures are rounded. Totals and percentages may not sum to 100.
Meanwhile, Nvidia is very close to overtaking Intel, after declaring $49 billion of topline revenue for 2023. This is more than double its 2022 revenue ($21 billion), increasing its share of industry revenues to 9%.
Nvidia’s meteoric rise has gotten a huge thumbs-up from investors. It became a trillion dollar stock last year, and broke the single-day gain record for market capitalization this year.
Other chipmakers haven’t been as successful. Out of the top 20 semiconductor companies by revenue, 12 did not match their 2022 revenues, including big names like Intel, Samsung, and AMD.
The Many Different Types of Chipmakers
All of these companies may belong to the same industry, but they don’t focus on the same niche.
According to Investopedia, there are four major types of chips, depending on their functionality: microprocessors, memory chips, standard chips, and complex systems on a chip.
Nvidia’s core business was once GPUs for computers (graphics processing units), but in recent years this has drastically shifted towards microprocessors for analytics and AI.
These specialized chips seem to be where the majority of growth is occurring within the sector. For example, companies that are largely in the memory segment—Samsung, SK Hynix, and Micron Technology—saw peak revenues in the mid-2010s.
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
-

 Travel1 week ago
Travel1 week agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024