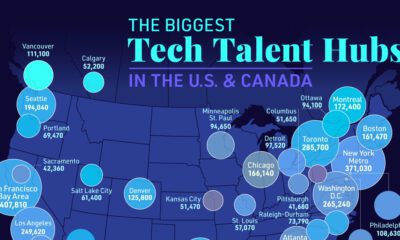
Technology
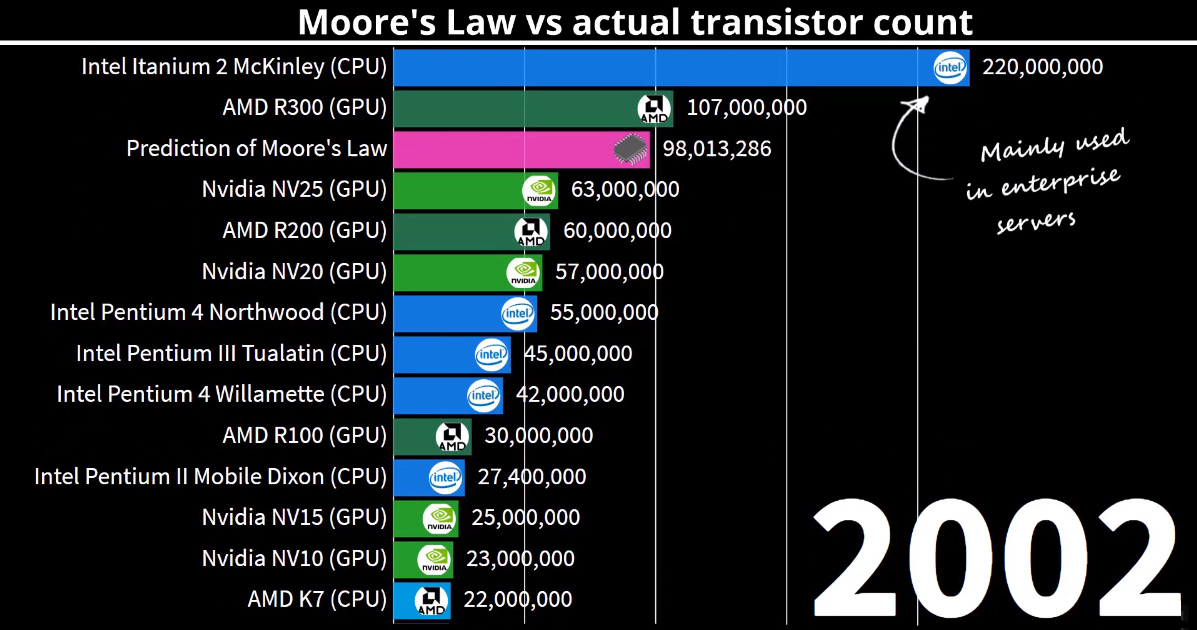
Visualizing Moore’s Law in Action (1971-2019)
Animation: Visualizing Moore’s Law in Action (1971-2019)
The pace of technological progress keeps accelerating.
There are many ways to show this, but perhaps the simplest way is to create a visual representation of Moore’s Law in action.
Today’s animation comes to us from DataGrapha, and it compares the predictions of Moore’s Law with data from actual computer chip innovations occurring between 1971 to 2019.
Defining Moore’s Law
Moore’s Law was originally derived from an observation by Gordon Moore, the co-founder of Fairchild Semiconductor and later the co-founder and CEO of Intel.
In 1965, Moore wrote that the number of components in a dense integrated circuit (i.e., transistors, resistors, diodes, or capacitors) had been doubling with every year of research, and he predicted that this would continue for another decade.
Later on in 1975, he revised his prediction to the doubling occurring every two years.
Like the animation, the following chart from Our World in Data helps plot out the predictions of Moore’s Law versus real world data — note that the Y Axis is logarithmic:
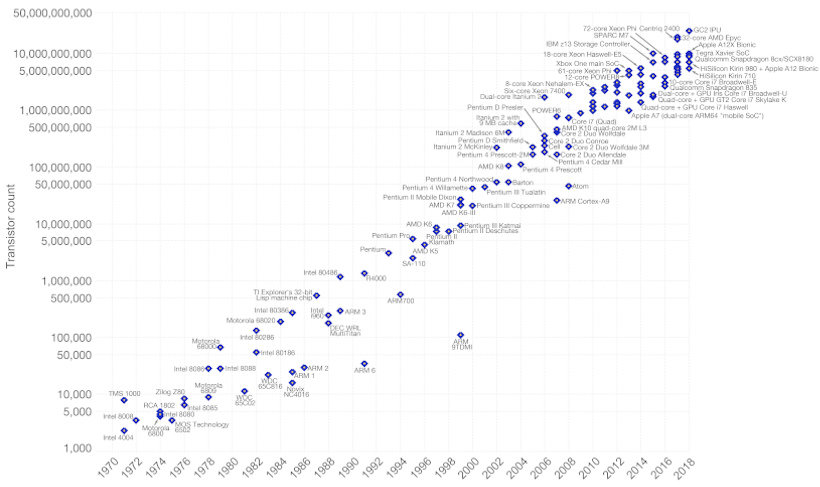
The prophetic prediction of Moore’s Law has led to exponential progress in computing — as well as for everything else touched by computers.
It’s no surprise then, especially given that the modern information age is largely driven by increasingly efficient computing, that this law has had a trickle down effect on nearly every significant aspect of global innovation.
An Accelerated Pace of Change
Moore’s Law has translated into a faster rate of change for society as a whole.
A new idea, like the smartphone, can get immediate traction because of instantaneous communication, increased global connectivity, and the ubiquity of information. New tech advancements can now change business or culture in a heartbeat:
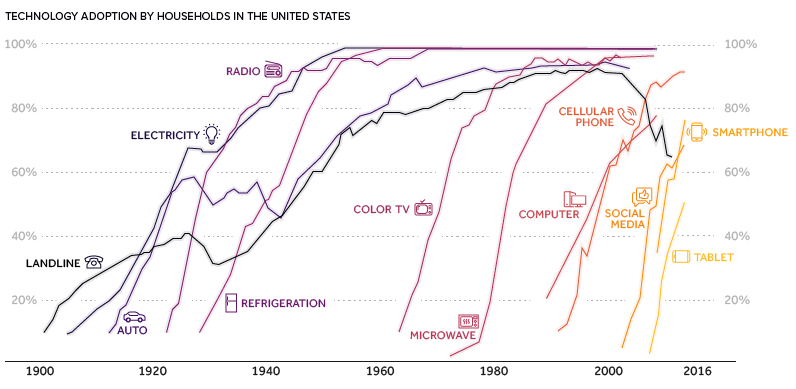
Further, since software is a “layer” built upon the foundation of computing, it means that digital products can be replicated at almost no marginal cost. This is why a phenomenon like Pokémon Go was able to captivate 50 million users in just 19 days.
Imagine this kind of scalability, when applied to things like artificial intelligence or virtual reality.
Is Moore’s Law Dead or Alive?
As with any enduring prediction, there are always naysayers out there that will boldly forecast an imminent end to the trend.
Since the 2000s, there has been an ongoing debate within the semiconductor community on whether Moore’s Law will continue its reign, or if progress will ultimately sputter out as certain physical limitations catch up with the process of miniaturization.
Earlier in 2019, Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang declared that Moore’s Law is no longer possible. For what it’s worth, Intel still says technology in chipmaking always finds a way to advance — while TSMC has recently said the law is actually alive and well.
Regardless of who is right, Moore’s Law has held true for close to 50 years, and its repercussions will continue to be felt in almost every aspect of life and society going forward.
Technology
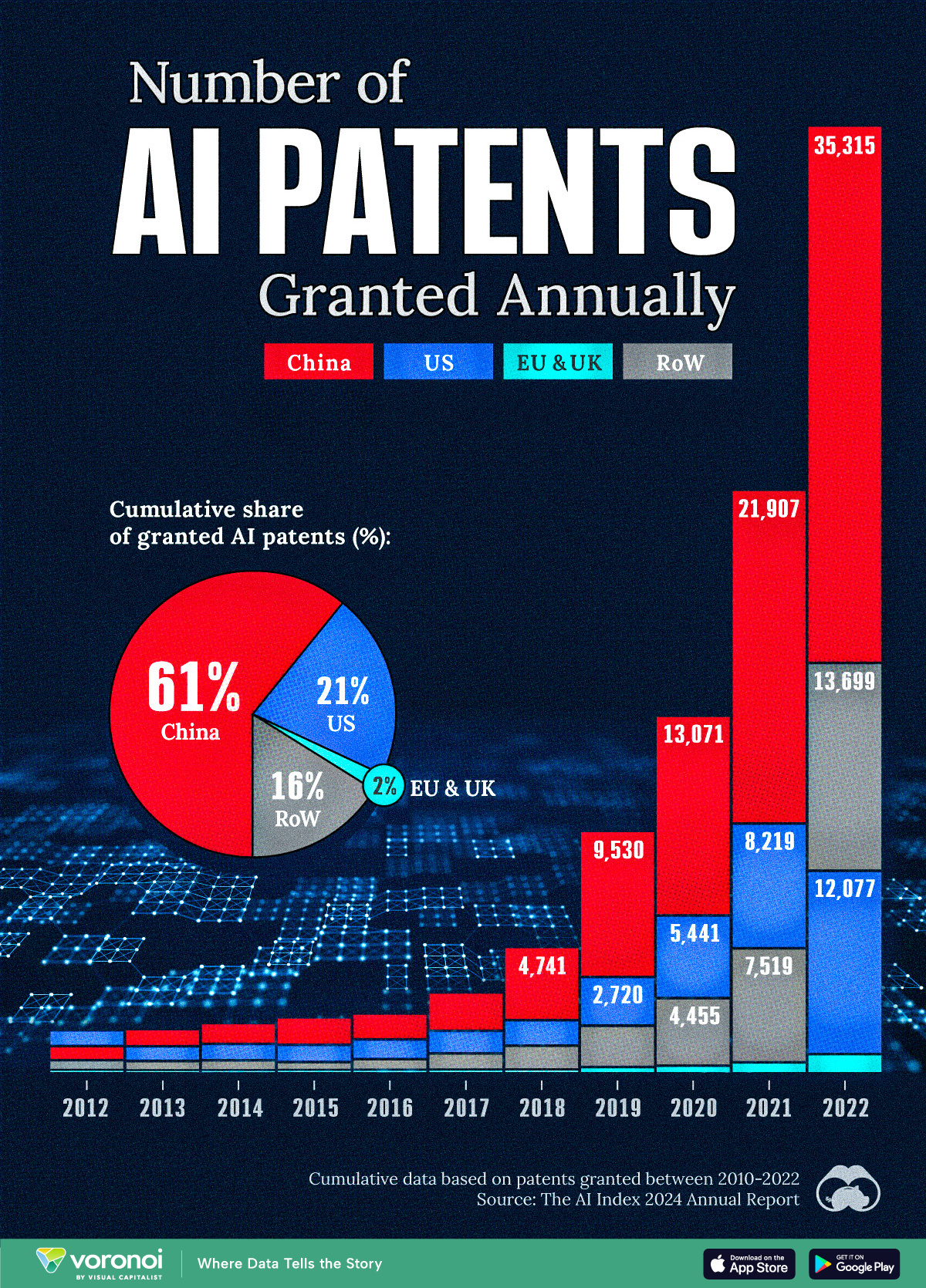
Visualizing AI Patents by Country
See which countries have been granted the most AI patents each year, from 2012 to 2022.
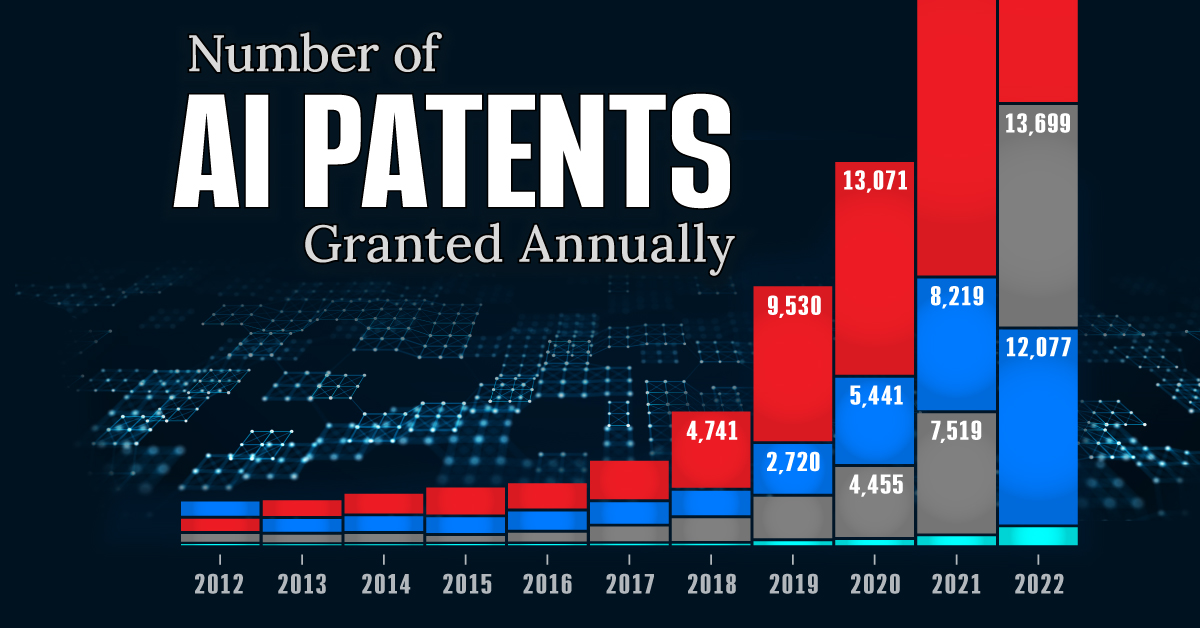
Visualizing AI Patents by Country
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This infographic shows the number of AI-related patents granted each year from 2010 to 2022 (latest data available). These figures come from the Center for Security and Emerging Technology (CSET), accessed via Stanford University’s 2024 AI Index Report.
From this data, we can see that China first overtook the U.S. in 2013. Since then, the country has seen enormous growth in the number of AI patents granted each year.
| Year | China | EU and UK | U.S. | RoW | Global Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 307 | 137 | 984 | 571 | 1,999 |
| 2011 | 516 | 129 | 980 | 581 | 2,206 |
| 2012 | 926 | 112 | 950 | 660 | 2,648 |
| 2013 | 1,035 | 91 | 970 | 627 | 2,723 |
| 2014 | 1,278 | 97 | 1,078 | 667 | 3,120 |
| 2015 | 1,721 | 110 | 1,135 | 539 | 3,505 |
| 2016 | 1,621 | 128 | 1,298 | 714 | 3,761 |
| 2017 | 2,428 | 144 | 1,489 | 1,075 | 5,136 |
| 2018 | 4,741 | 155 | 1,674 | 1,574 | 8,144 |
| 2019 | 9,530 | 322 | 3,211 | 2,720 | 15,783 |
| 2020 | 13,071 | 406 | 5,441 | 4,455 | 23,373 |
| 2021 | 21,907 | 623 | 8,219 | 7,519 | 38,268 |
| 2022 | 35,315 | 1,173 | 12,077 | 13,699 | 62,264 |
In 2022, China was granted more patents than every other country combined.
While this suggests that the country is very active in researching the field of artificial intelligence, it doesn’t necessarily mean that China is the farthest in terms of capability.
Key Facts About AI Patents
According to CSET, AI patents relate to mathematical relationships and algorithms, which are considered abstract ideas under patent law. They can also have different meaning, depending on where they are filed.
In the U.S., AI patenting is concentrated amongst large companies including IBM, Microsoft, and Google. On the other hand, AI patenting in China is more distributed across government organizations, universities, and tech firms (e.g. Tencent).
In terms of focus area, China’s patents are typically related to computer vision, a field of AI that enables computers and systems to interpret visual data and inputs. Meanwhile America’s efforts are more evenly distributed across research fields.
Learn More About AI From Visual Capitalist
If you want to see more data visualizations on artificial intelligence, check out this graphic that shows which job departments will be impacted by AI the most.
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries