Markets
Chart: Is U.S. or China the World’s Economic Superpower?
Is U.S. or China the World’s Economic Superpower?
Popular opinion changes depending on where you live
The Chart of the Week is a weekly Visual Capitalist feature on Fridays.
Since the collapse of the Berlin Wall in 1989, the world has had one undisputed economic superpower: the United States.
But while the U.S. has enjoyed its moment in the sun, the balance of power has been slowly shifting towards the inevitable rise of China. It’s been a long time coming, but China now has the manpower, influence, and economic might to compete at a similar level – and if you ask people around the world, they’ve certainly taken notice.
Economic Superpowers
The United States and China combine for 39% of global GDP, 53% of estimated economic growth in the coming years, and 23% of the world’s population.
But which one is perceived as the more dominant economic power?
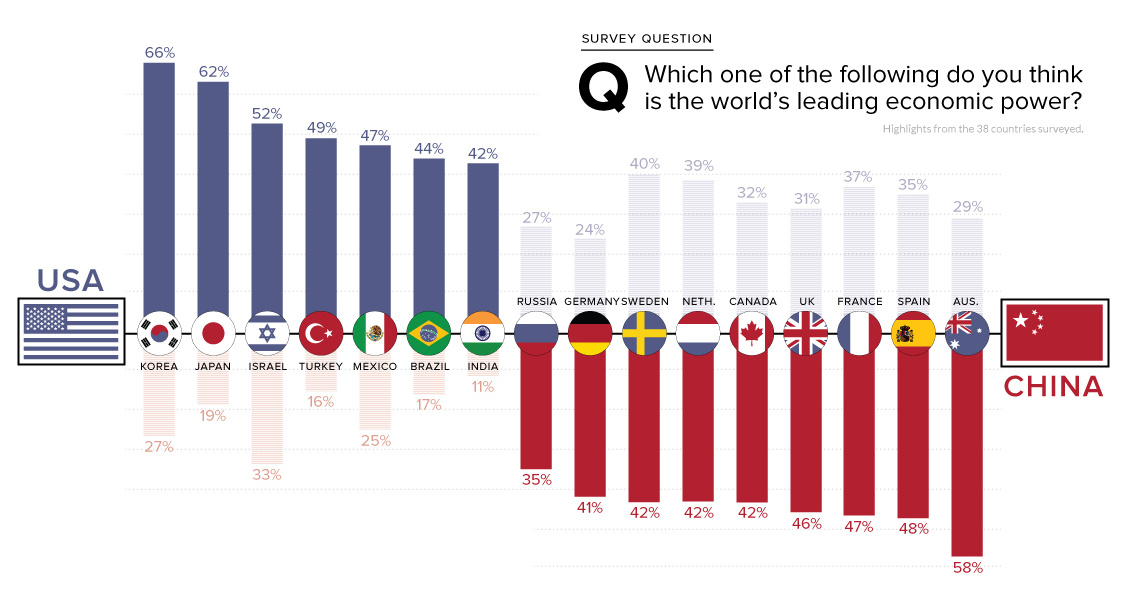
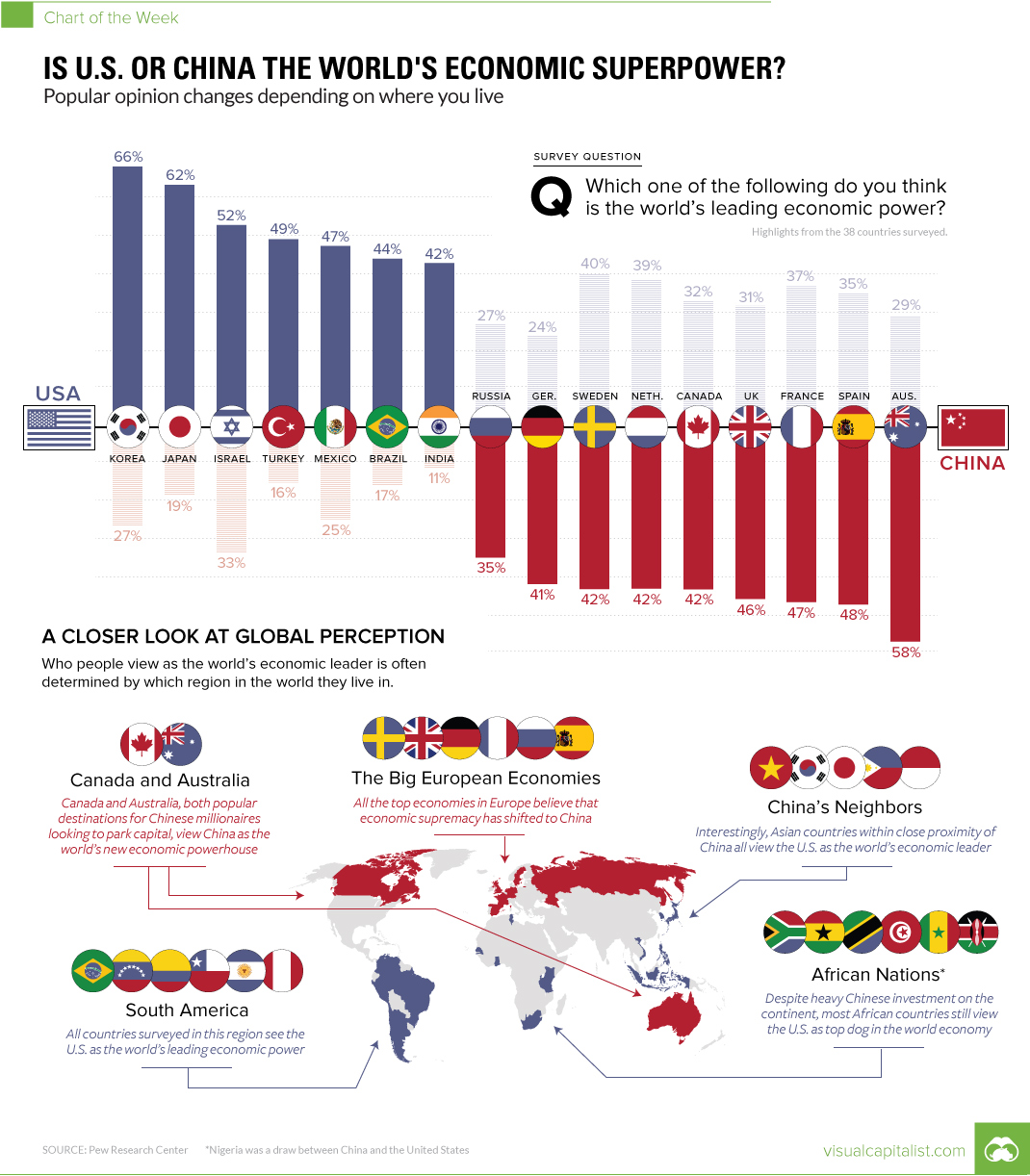
According to a recent survey by Pew Research Center, the vary wildly depending on the people and country surveyed. However, on an aggregate level that uses the results from the people in 38 countries surveyed, Pew determined that a median of 42% of people list the United States as the world’s leading economic power, while 32% name China as top dog.
Which one of the following do you think is the world’s leading economic power?
| Rank | Country | Global median (%) |
|---|---|---|
| #1 | United States | 42% |
| #2 | China | 32% |
| #3 | Countries of the EU | 9% |
| #4 | Japan | 7% |
| #5 | Other / None | 10% |
While the U.S. maintains a narrow lead in aggregate, things get much more interesting when we look at individual countries.
Different Perspectives
Do America’s closest allies view it as the clear global superpower? What about the countries that neighbor China – surely, they must witness China’s economic might firsthand.
Weirdly, the dominant perspectives in these places are not as obvious as one would think.
More people living in Canada, Australia, and major European countries like France, Germany, Sweden, Spain, and the United Kingdom tend to view China as the global economic superpower.
Meanwhile, the majority of people in South American and African countries see the United States as the world’s major economic power – and people in countries near China (such as South Korea, Japan, Philippines, Indonesia, and Vietnam) all tend to agree with that sentiment as well.
Markets
U.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
U.S. debt interest payments have surged past the $1 trillion dollar mark, amid high interest rates and an ever-expanding debt burden.

U.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
The cost of paying for America’s national debt crossed the $1 trillion dollar mark in 2023, driven by high interest rates and a record $34 trillion mountain of debt.
Over the last decade, U.S. debt interest payments have more than doubled amid vast government spending during the pandemic crisis. As debt payments continue to soar, the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) reported that debt servicing costs surpassed defense spending for the first time ever this year.
This graphic shows the sharp rise in U.S. debt payments, based on data from the Federal Reserve.
A $1 Trillion Interest Bill, and Growing
Below, we show how U.S. debt interest payments have risen at a faster pace than at another time in modern history:
| Date | Interest Payments | U.S. National Debt |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | $1.0T | $34.0T |
| 2022 | $830B | $31.4T |
| 2021 | $612B | $29.6T |
| 2020 | $518B | $27.7T |
| 2019 | $564B | $23.2T |
| 2018 | $571B | $22.0T |
| 2017 | $493B | $20.5T |
| 2016 | $460B | $20.0T |
| 2015 | $435B | $18.9T |
| 2014 | $442B | $18.1T |
| 2013 | $425B | $17.2T |
| 2012 | $417B | $16.4T |
| 2011 | $433B | $15.2T |
| 2010 | $400B | $14.0T |
| 2009 | $354B | $12.3T |
| 2008 | $380B | $10.7T |
| 2007 | $414B | $9.2T |
| 2006 | $387B | $8.7T |
| 2005 | $355B | $8.2T |
| 2004 | $318B | $7.6T |
| 2003 | $294B | $7.0T |
| 2002 | $298B | $6.4T |
| 2001 | $318B | $5.9T |
| 2000 | $353B | $5.7T |
| 1999 | $353B | $5.8T |
| 1998 | $360B | $5.6T |
| 1997 | $368B | $5.5T |
| 1996 | $362B | $5.3T |
| 1995 | $357B | $5.0T |
| 1994 | $334B | $4.8T |
| 1993 | $311B | $4.5T |
| 1992 | $306B | $4.2T |
| 1991 | $308B | $3.8T |
| 1990 | $298B | $3.4T |
| 1989 | $275B | $3.0T |
| 1988 | $254B | $2.7T |
| 1987 | $240B | $2.4T |
| 1986 | $225B | $2.2T |
| 1985 | $219B | $1.9T |
| 1984 | $205B | $1.7T |
| 1983 | $176B | $1.4T |
| 1982 | $157B | $1.2T |
| 1981 | $142B | $1.0T |
| 1980 | $113B | $930.2B |
| 1979 | $96B | $845.1B |
| 1978 | $84B | $789.2B |
| 1977 | $69B | $718.9B |
| 1976 | $61B | $653.5B |
| 1975 | $55B | $576.6B |
| 1974 | $50B | $492.7B |
| 1973 | $45B | $469.1B |
| 1972 | $39B | $448.5B |
| 1971 | $36B | $424.1B |
| 1970 | $35B | $389.2B |
| 1969 | $30B | $368.2B |
| 1968 | $25B | $358.0B |
| 1967 | $23B | $344.7B |
| 1966 | $21B | $329.3B |
Interest payments represent seasonally adjusted annual rate at the end of Q4.
At current rates, the U.S. national debt is growing by a remarkable $1 trillion about every 100 days, equal to roughly $3.6 trillion per year.
As the national debt has ballooned, debt payments even exceeded Medicaid outlays in 2023—one of the government’s largest expenditures. On average, the U.S. spent more than $2 billion per day on interest costs last year. Going further, the U.S. government is projected to spend a historic $12.4 trillion on interest payments over the next decade, averaging about $37,100 per American.
Exacerbating matters is that the U.S. is running a steep deficit, which stood at $1.1 trillion for the first six months of fiscal 2024. This has accelerated due to the 43% increase in debt servicing costs along with a $31 billion dollar increase in defense spending from a year earlier. Additionally, a $30 billion increase in funding for the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation in light of the regional banking crisis last year was a major contributor to the deficit increase.
Overall, the CBO forecasts that roughly 75% of the federal deficit’s increase will be due to interest costs by 2034.
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
-

 Travel1 week ago
Travel1 week agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024