Energy
The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2022
![]() Subscribe to the Elements free mailing list for more like this
Subscribe to the Elements free mailing list for more like this
The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2022
This was originally posted on Elements. Sign up to the free mailing list to get beautiful visualizations on natural resource megatrends in your email every week.
The global electric vehicle (EV) battery market is expected to grow from $17 billion to more than $95 billion between 2019 and 2028.
With increasing demand to decarbonize the transportation sector, companies producing the batteries that power EVs have seen substantial momentum.
Here we update our previous graphic of the top 10 EV battery manufacturers, bringing you the world’s biggest battery manufacturers in 2022.
Chinese Dominance
Despite efforts from the United States and Europe to increase the domestic production of batteries, the market is still dominated by Asian suppliers.
The top 10 producers are all Asian companies.
Currently, Chinese companies make up 56% of the EV battery market, followed by Korean companies (26%) and Japanese manufacturers (10%).
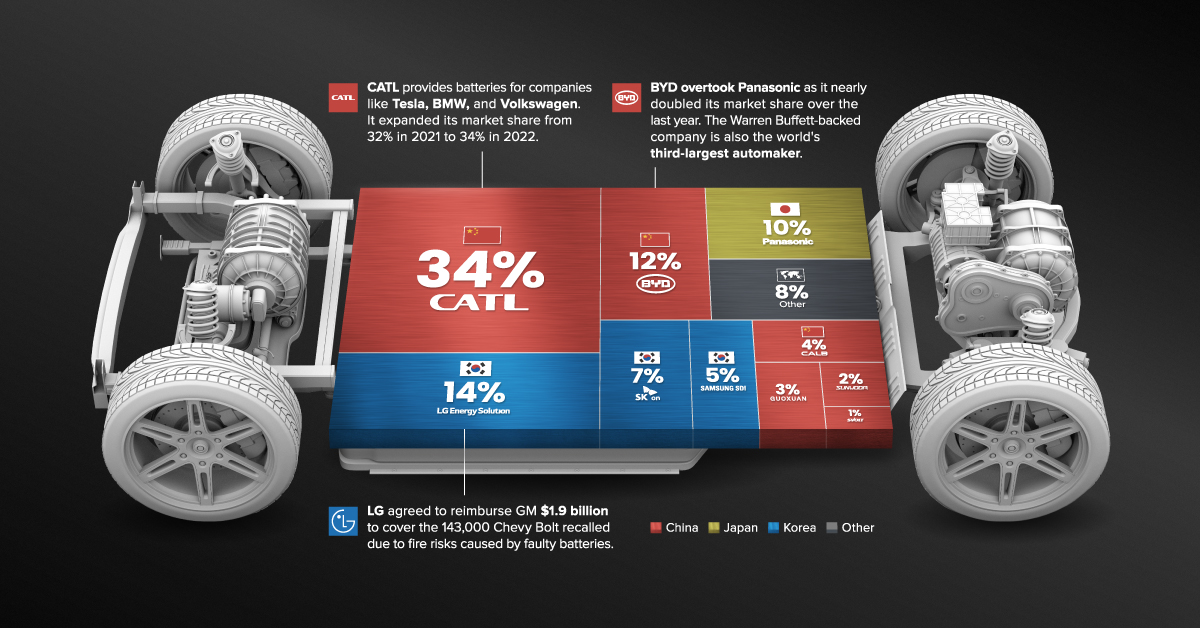
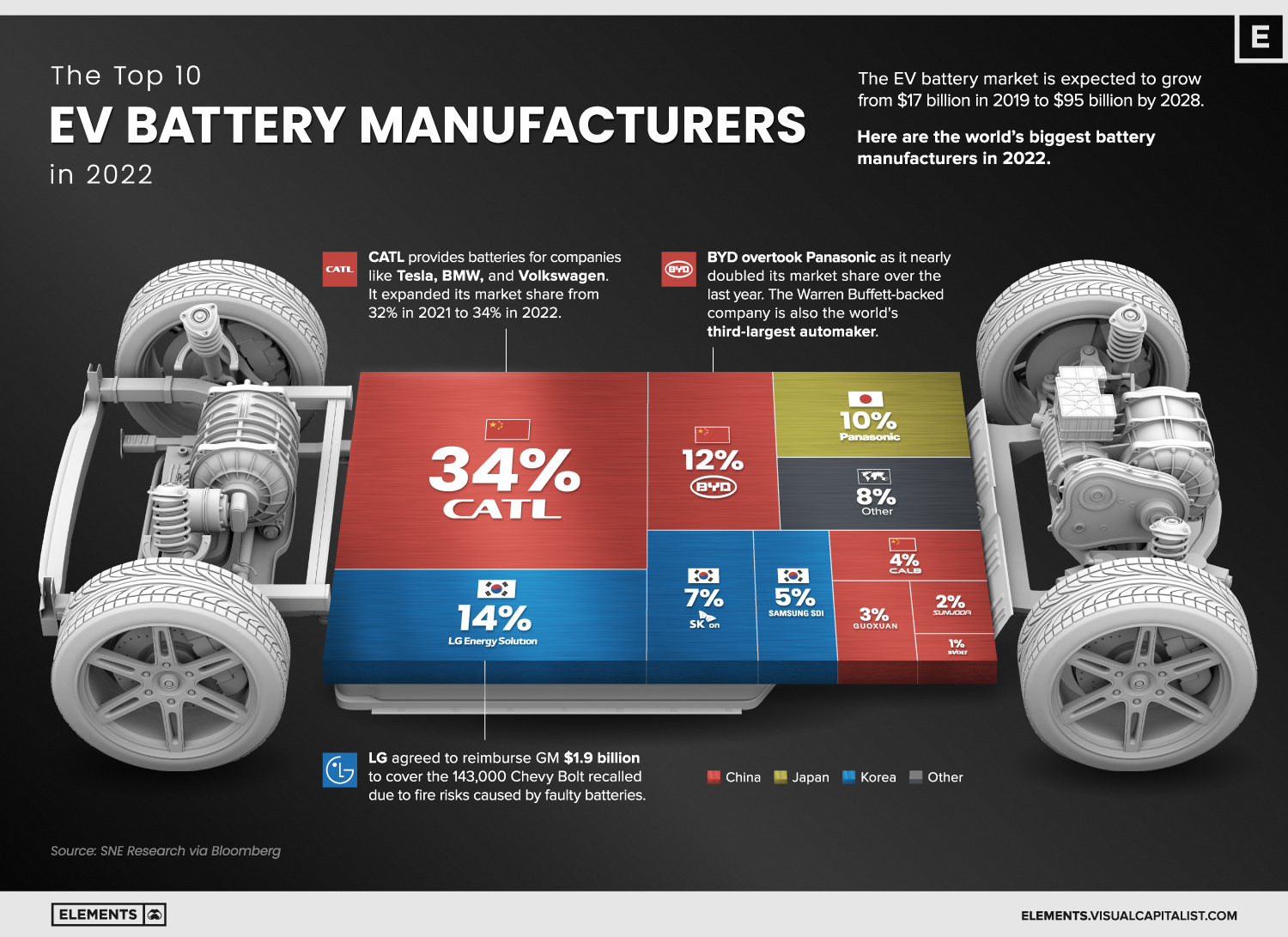
The leading battery supplier, CATL, expanded its market share from 32% in 2021 to 34% in 2022. One-third of the world’s EV batteries come from the Chinese company. CATL provides lithium-ion batteries to Tesla, Peugeot, Hyundai, Honda, BMW, Toyota, Volkswagen, and Volvo.
| Rank | Company | 2022 Market Share | Country |
|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | CATL | 34% | China 🇨🇳 |
| #2 | LG Energy Solution | 14% | Korea 🇰🇷 |
| #3 | BYD | 12% | China 🇨🇳 |
| #4 | Panasonic | 10% | Japan 🇯🇵 |
| #5 | SK On | 7% | Korea 🇰🇷 |
| #6 | Samsung SDI | 5% | Korea 🇰🇷 |
| #7 | CALB | 4% | China 🇨🇳 |
| #8 | Guoxuan | 3% | China 🇨🇳 |
| #9 | Sunwoda | 2% | China 🇨🇳 |
| #10 | SVOLT | 1% | China 🇨🇳 |
| Other | 8% | ROW 🌐 |
Despite facing strict scrutiny after EV battery-fire recalls in the United States, LG Energy Solution remains the second-biggest battery manufacturer. In 2021, the South Korean supplier agreed to reimburse General Motors $1.9 billion to cover the 143,000 Chevy Bolt EVs recalled due to fire risks from faulty batteries.
BYD took the third spot from Panasonic as it nearly doubled its market share over the last year. The Warren Buffett-backed company is the world’s third-largest automaker by market cap, but it also produces batteries sold in markets around the world. Recent sales figures point to BYD overtaking LG Energy Solution in market share the coming months or years.
The Age of Battery Power
Electric vehicles are here to stay, while internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles are set to fade away in the coming decades. Recently, General Motors announced that it aims to stop selling ICE vehicles by 2035, while Audi plans to stop producing such models by 2033.
Besides EVs, battery technology is essential for the energy transition, providing storage capacity for intermittent solar and wind generation.
As battery makers work to supply the EV transition’s increasing demand and improve energy density in their products, we can expect more interesting developments within this industry.
Energy
The World’s Biggest Nuclear Energy Producers
China has grown its nuclear capacity over the last decade, now ranking second on the list of top nuclear energy producers.

The World’s Biggest Nuclear Energy Producers
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Scientists in South Korea recently broke a record in a nuclear fusion experiment. For 48 seconds, they sustained a temperature seven times that of the sun’s core.
But generating commercially viable energy from nuclear fusion still remains more science fiction than reality. Meanwhile, its more reliable sibling, nuclear fission, has been powering our world for many decades.
In this graphic, we visualized the top producers of nuclear energy by their share of the global total, measured in terawatt hours (TWh). Data for this was sourced from the Nuclear Energy Institute, last updated in August 2022.
Which Country Generates the Most Nuclear Energy?
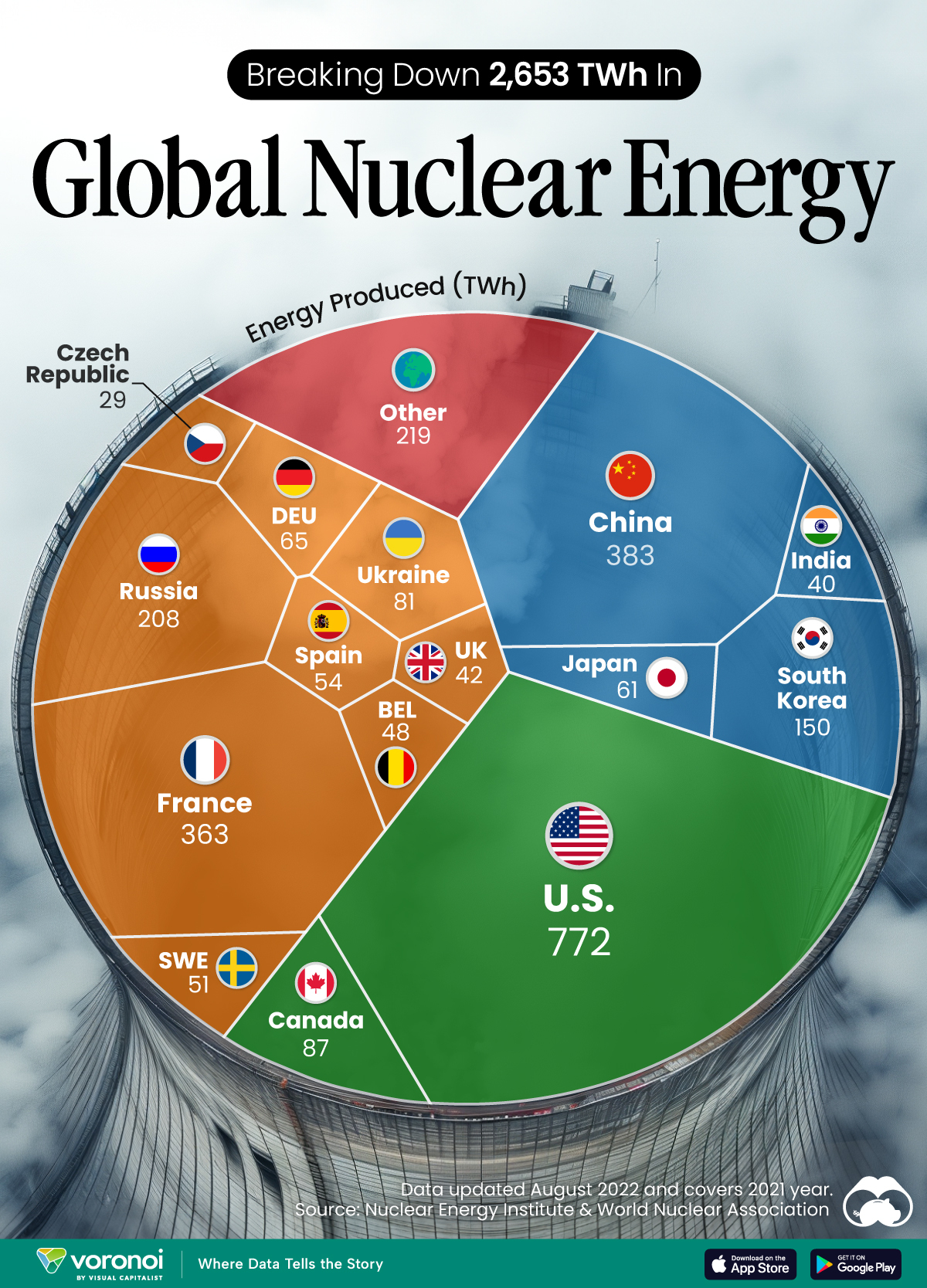
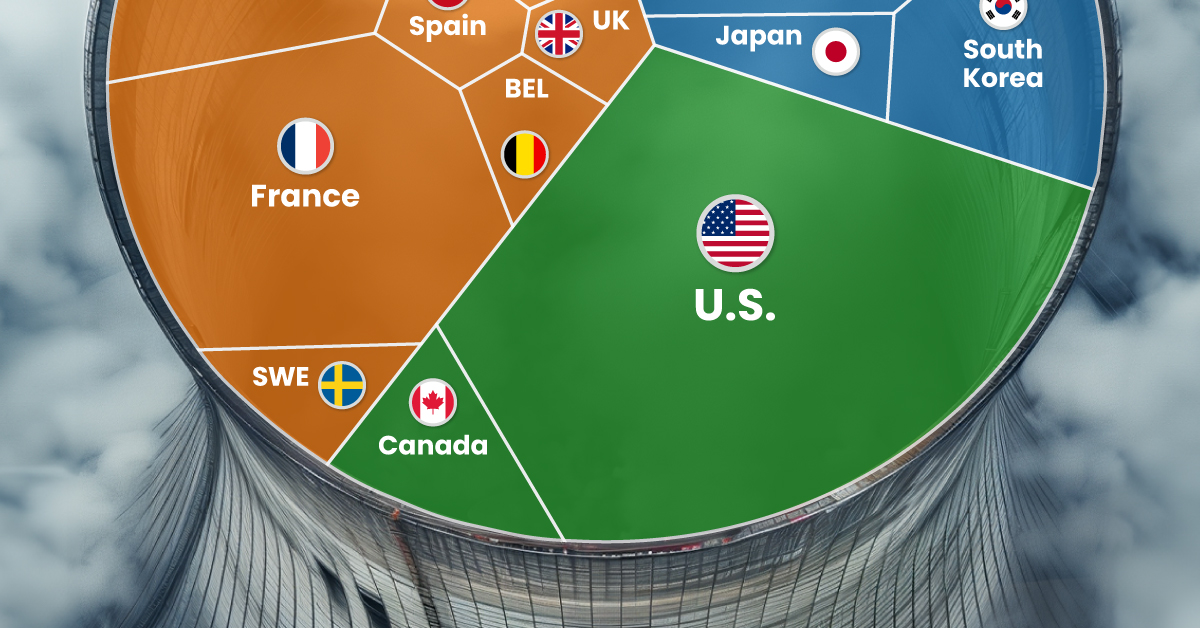
Nuclear energy production in the U.S. is more than twice the amount produced by China (ranked second) and France (ranked third) put together. In total, the U.S. accounts for nearly 30% of global nuclear energy output.
However, nuclear power only accounts for one-fifth of America’s electricity supply. This is in contrast to France, which generates 60% of its electricity from nuclear plants.
| Rank | Country | Nuclear Energy Produced (TWh) | % of Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇺🇸 U.S. | 772 | 29% |
| 2 | 🇨🇳 China | 383 | 14% |
| 3 | 🇫🇷 France | 363 | 14% |
| 4 | 🇷🇺 Russia | 208 | 8% |
| 5 | 🇰🇷 South Korea | 150 | 6% |
| 6 | 🇨🇦 Canada | 87 | 3% |
| 7 | 🇺🇦 Ukraine | 81 | 3% |
| 8 | 🇩🇪 Germany | 65 | 2% |
| 9 | 🇯🇵 Japan | 61 | 2% |
| 10 | 🇪🇸 Spain | 54 | 2% |
| 11 | 🇸🇪 Sweden | 51 | 2% |
| 12 | 🇧🇪 Belgium | 48 | 2% |
| 13 | 🇬🇧 UK | 42 | 2% |
| 14 | 🇮🇳 India | 40 | 2% |
| 15 | 🇨🇿 Czech Republic | 29 | 1% |
| N/A | 🌐 Other | 219 | 8% |
| N/A | 🌍 Total | 2,653 | 100% |
Another highlight is how China has rapidly grown its nuclear energy capabilities in the last decade. Between 2016 and 2021, for example, it increased its share of global nuclear energy output from less than 10% to more than 14%, overtaking France for second place.
On the opposite end, the UK’s share has slipped to 2% over the same time period.
Meanwhile, Ukraine has heavily relied on nuclear energy to power its grid. In March 2022, it lost access to its key Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Station after Russian forces wrested control of the facility. With six 1,000 MW reactors, the plant is one of the largest in Europe. It is currently not producing any power, and has been the site of recent drone attacks.
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoMapped: Average Wages Across Europe
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI1 week ago
AI1 week agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001