Mining
The Looming Copper Supply Crunch

The Looming Copper Supply Crunch
This infographic is presented by Western Copper & Gold
Copper is among the three most used metals in the world, and high quantities of the red metal must be mined every year to meet global demand.
The market for copper is equal to approximately $120 billion each year, which rivals that of even iron ore, the most widely traded metal. This is because infrastructure, technology, and automobiles consume massive amounts of copper.
Behind silver, copper is the second best metal for conducting electricity. That’s why 75% of copper is used in electrical wires or for wiring in machinery. From power grids to motherboards, copper wire is indispensable to modern society.
Copper is also essential for green energy and a sustainable future. For example, each generation of car needs more copper wiring: a gasoline-powered car needs 55 lbs, while hybrids and electric vehicles need 110 lbs and 165 lbs respectively. Further, it is estimated that an average of 3.6 tonnes of copper is used for each MW of wind power.
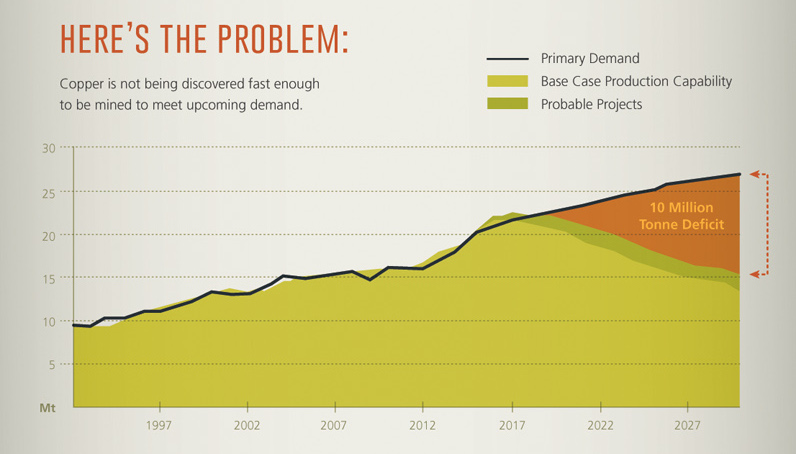
The Copper Supply Problem
The problem is: copper is not being discovered fast enough to meet upcoming demand. A study by Wood Mackenzie found that there will be a 10 million tonne supply deficit by 2028. That’s equal to the annual production of the world’s biggest copper mine (Escondida) multiplied by a factor of ten.
There are several reasons for this.
First, it now takes longer to go from discovery to production than ever before in the mining industry. Geological, environmental, and political challenges have brought the average lead time to around 20 years for new mines.
Beyond all of the challenges above, the economics also have to line up. Thomson Reuters GFMS estimates that for new copper supply to be incentivized to come online, the copper price must be $3.50 per pound.
Copper mining is all about grade or scale. The majority of global output comes from mega mines that have massive economies of scale to reduce costs. However, it has been a long-running trend that the grades for these established mines are dropping.
A good example of this is Escondida, the world’s largest copper mine which is located in Chile. It produced 6% of global copper output in 2014, but the mine is facing a similar problem to that of other large copper projects: grades are dropping. In 2007, the copper grade was 1.72%, but it is predicted to drop to half of that in upcoming years. In fact, BHP Billiton is expecting a year-over-year decline of 24% between 2015 and 2016.
Codelco is the world’s largest copper miner overall, and has recently announced a $25 billion investment plan to expand aging mines. It will spend $5 billion each year, but it expects no significant gain in production for its efforts.
The Coming Supply Gap
Add these factors together, and stocks of copper are at their lowest levels since 2008. Further, 4% of the world’s copper mining capacity falls off the table each year, which means that this must be replaced somehow.
With 10 Escondidas needed to fill a 10 million tonne supply deficit by 2028, metals investors need to stay vigilant as changes in the market will be coming.
Copper
Brass Rods: The Secure Choice
This graphic shows why brass rods are the secure choice for precision-machined and forged parts.

Brass Rods: The Secure Choice
The unique combination of machinability and recyclability makes brass rods the secure choice for manufacturers seeking future-proof raw material solutions.
This infographic, from the Copper Development Association, shows three ways brass rods give manufacturers greater control and a license to grow in the competitive market for precision-machined and forged products.
Future-Proof Investments in New Machine Tools
A material’s machinability directly impacts machine throughput, which typically has the largest impact on machine shop profitability.
The high-speed machining capabilities of brass rods maximize machine tool performance, allowing manufacturers to run the material faster and longer without sacrificing tool life, chip formation, or surface quality.
The high machining efficiency of brass leads to reduced per-part costs, quicker return on investment (ROI) for new machine tools, and expanded production capacity for new projects.
Supply Security Through Closed Loop Recycling
Brass, like its parent element copper, can be infinitely recycled.
In 2022, brass- and wire-rod mills accounted for the majority of the 830,000 tonnes of copper recycled from scrap in the United States.
Given that scrap ratios for machined parts typically range from 60-70% by weight, producing mills benefit from a secure and steady supply of clean scrap returned directly from customers, which is recycled to create new brass rods.
The high residual value of brass scrap creates a strong recycling incentive. Scrap buy back programs give manufacturers greater control over raw material net costs as scrap value is often factored into supplier purchase agreements.
Next Generation Alloys for a Lead-Free Future
Increasingly stringent global regulations continue to pressure manufacturers to minimize the use of materials containing trace amounts of lead and other harmful impurities.
The latest generation of brass-rod alloys is engineered to meet the most demanding criteria for lead leaching in drinking water and other sensitive applications.
Seven brass-rod alloys passed rigorous testing to become the only ‘Acceptable Materials’ against lower lead leaching criteria recently adopted in the national U.S. drinking water quality standard, NSF 61.

Learn more about the advantages of brass rods solutions.

-

 Copper1 year ago
Copper1 year agoRanked: The World’s Largest Copper Producers
Many new technologies critical to the energy transition rely on copper. Here are the world’s largest copper producers.
-
 Mining2 years ago
Mining2 years agoMapped: Solar Power by Country in 2021
In 2020, solar power saw its largest-ever annual capacity expansion at 127 gigawatts. Here’s a snapshot of solar power capacity by country.
-

 Energy5 years ago
Energy5 years agoVisualizing Copper’s Role in the Transition to Clean Energy
A clean energy transition is underway as wind, solar, and batteries take center stage. Here’s how copper plays the critical role in these technologies.
-
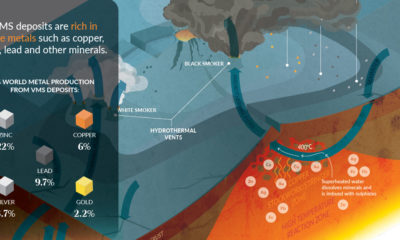
 Mining5 years ago
Mining5 years agoEverything You Need to Know on VMS Deposits
Deep below the ocean’s waves, VMS deposits spew out massive amounts of minerals like copper, zinc, and gold, making them a key source of the metals…
-
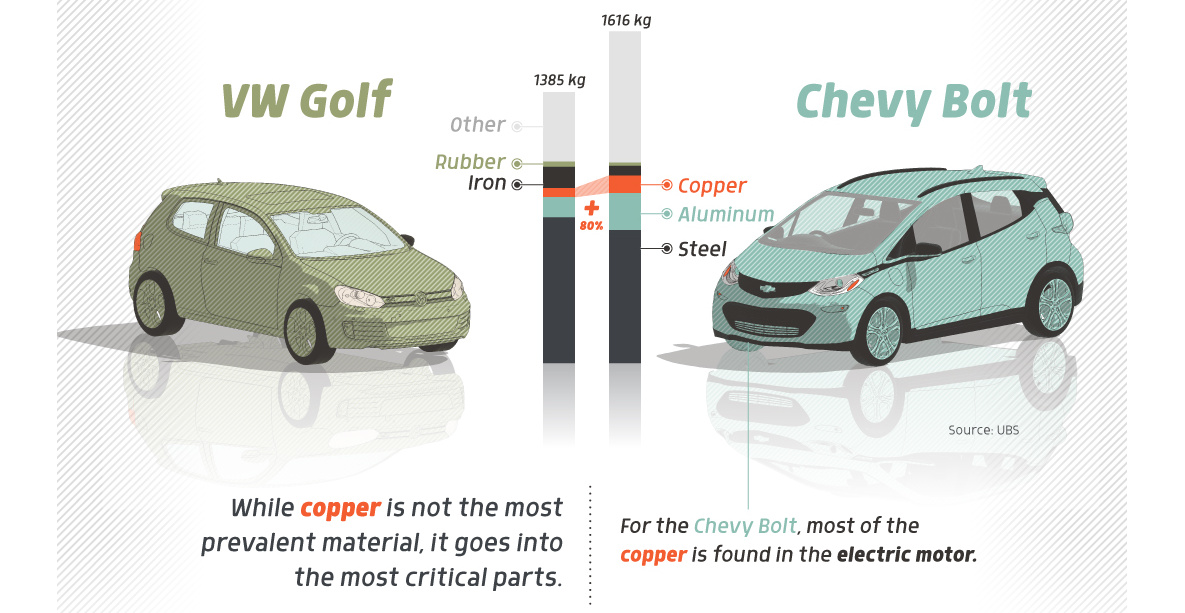
 Copper5 years ago
Copper5 years agoHow Much Copper is in an Electric Vehicle?
Have you ever wondered how much copper is in an electric vehicle? This infographic shows the metal’s properties as well as the quantity of copper used.
-
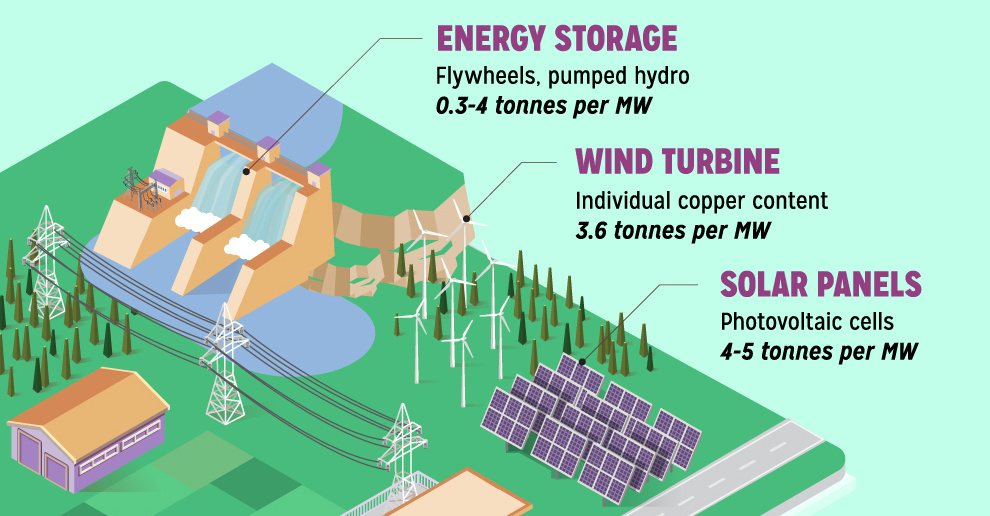
 Mining6 years ago
Mining6 years agoCopper: Driving the Green Energy Revolution
Renewable energy is set to fuel a new era of copper demand – here’s how much copper is used in green applications from EVs to photovoltaics.
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
-

 Travel2 weeks ago
Travel2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024