Mining
The History of Jade: The Emperor’s Stone







The History of Jade: The Emperor’s Stone
Infographic presented by Electra Stone
In Chinese writing, it is no accident that the character for “emperor” looks almost identical to the character for “jade”.
In the West, precious gems such as diamonds or rubies were worn by high-ranking people as status symbols. However, in China, it is jade that has been a symbol of status, spirituality, purity, and health for over 9,000 years.
The Origins of Jade
Jade has been mined and worked in China since the Stone Age. In prehistoric sites, jade artifacts include simple ornaments with bead, button, and tubular shapes. It was also used for tools and weapons. Jade later became revered with special significance. Beautiful designs were used for carvings, decorations, ceremonies, furnishings, and jewelry for the Imperial families.
By 3,000 BC, jade became known as “yu” or the “royal gem”.
Xu Shen, from the Han Dynasty (206 BC to 221 AD), details the five virtues of jade in his work Shuowen Jiezi:
Benevolence for its lustre and brilliance.
Honesty for its translucent texture.
Wisdom for its tranquil and far-reaching tone.
Integrity and Bravery for it may be broken but cannot be twisted.
The most wealthy and influential members of society would be buried in jade suits. Extremely costly and taking years to assemble, the thread used to join the pieces of jade would be gold, silver, copper, silk, or other materials depending on the status of the person buried.
The first archaeological discoveries of these suits, of Prince Liu Sheng and Dou Wan of the Western Han dynasty, consisted of: 2498 pieces of jade and 2.5 lbs of gold wire.
The gemstone’s significance to Chinese culture cannot be understated. Entire kingdoms in China have started wars over particularly precious stones.
What is Jade?
Jade is different than other types of valuable gems or precious metals. In fact, the cultural term “jade” refers to two different and similar types of ornamental rocks, both made of different silicate minerals.
Nephrite jade was the very first of these materials discovered in China, and was the traditional jade used and carved since ancient times. Nephrite was so important that the traditional deposits in China are now all but depleted.
There is evidence that jadeite jade, coming primarily from Burma, began to be traded in China on a wider scale in the 14th century. It was harder, denser, and worked easier – it eventually became the form of the gemstone preferred by Chinese artisans and prized by the Chinese people.
Today, most jade traded in China is of the jadeite variety.
However, the country’s traditional nephrite jade is not forgotten. Every athlete’s medal, at the 2008 Beijing Olympics, was embedded with a piece of pure, natural-carved jade. The gold medal featured a rare form of white nephrite known as “mutton fat” jade.
The Value of Jade
Gold has a price; jade is priceless (Chinese proverb)
Jade is valued differently than other comparable gemstones or precious metals. Jade is not fungible like gold, and jade is not a single polished and cut crystal, such as in the case of diamonds or rubies.
Both jadeite and nephrite jade are stones formed of interlocking microcrystals. Jade comes in different shapes and sizes, and can have impurities or grains in the stone that define its character. This means each piece of jade is unique.
Professional craftsmen look at raw jade’s beauty, flaws, and spirit to determine what shall be carved from it. This potential ties into the price that people are willing to pay for it.
Jade jewelry and artwork are extremely important to China’s culture and history.
This is why buyers are willing to pay a steep price for the finest jade. What does the best jade sell for in China? It sells for the same price per carat as diamonds in the United States.
Copper
Brass Rods: The Secure Choice
This graphic shows why brass rods are the secure choice for precision-machined and forged parts.

Brass Rods: The Secure Choice
The unique combination of machinability and recyclability makes brass rods the secure choice for manufacturers seeking future-proof raw material solutions.
This infographic, from the Copper Development Association, shows three ways brass rods give manufacturers greater control and a license to grow in the competitive market for precision-machined and forged products.
Future-Proof Investments in New Machine Tools
A material’s machinability directly impacts machine throughput, which typically has the largest impact on machine shop profitability.
The high-speed machining capabilities of brass rods maximize machine tool performance, allowing manufacturers to run the material faster and longer without sacrificing tool life, chip formation, or surface quality.
The high machining efficiency of brass leads to reduced per-part costs, quicker return on investment (ROI) for new machine tools, and expanded production capacity for new projects.
Supply Security Through Closed Loop Recycling
Brass, like its parent element copper, can be infinitely recycled.
In 2022, brass- and wire-rod mills accounted for the majority of the 830,000 tonnes of copper recycled from scrap in the United States.
Given that scrap ratios for machined parts typically range from 60-70% by weight, producing mills benefit from a secure and steady supply of clean scrap returned directly from customers, which is recycled to create new brass rods.
The high residual value of brass scrap creates a strong recycling incentive. Scrap buy back programs give manufacturers greater control over raw material net costs as scrap value is often factored into supplier purchase agreements.
Next Generation Alloys for a Lead-Free Future
Increasingly stringent global regulations continue to pressure manufacturers to minimize the use of materials containing trace amounts of lead and other harmful impurities.
The latest generation of brass-rod alloys is engineered to meet the most demanding criteria for lead leaching in drinking water and other sensitive applications.
Seven brass-rod alloys passed rigorous testing to become the only ‘Acceptable Materials’ against lower lead leaching criteria recently adopted in the national U.S. drinking water quality standard, NSF 61.

Learn more about the advantages of brass rods solutions.

-

 Base Metals1 year ago
Base Metals1 year agoRanked: The World’s Largest Copper Producers
Many new technologies critical to the energy transition rely on copper. Here are the world’s largest copper producers.
-
 Silver2 years ago
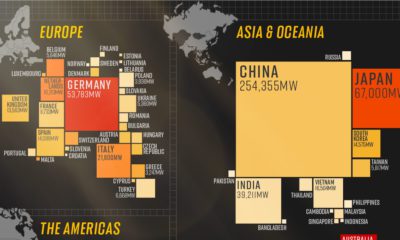
Silver2 years agoMapped: Solar Power by Country in 2021
In 2020, solar power saw its largest-ever annual capacity expansion at 127 gigawatts. Here’s a snapshot of solar power capacity by country.
-

 Batteries5 years ago
Batteries5 years agoVisualizing Copper’s Role in the Transition to Clean Energy
A clean energy transition is underway as wind, solar, and batteries take center stage. Here’s how copper plays the critical role in these technologies.
-
 Science5 years ago
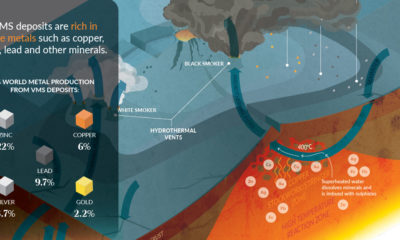
Science5 years agoEverything You Need to Know on VMS Deposits
Deep below the ocean’s waves, VMS deposits spew out massive amounts of minerals like copper, zinc, and gold, making them a key source of the metals…
-
 Copper5 years ago
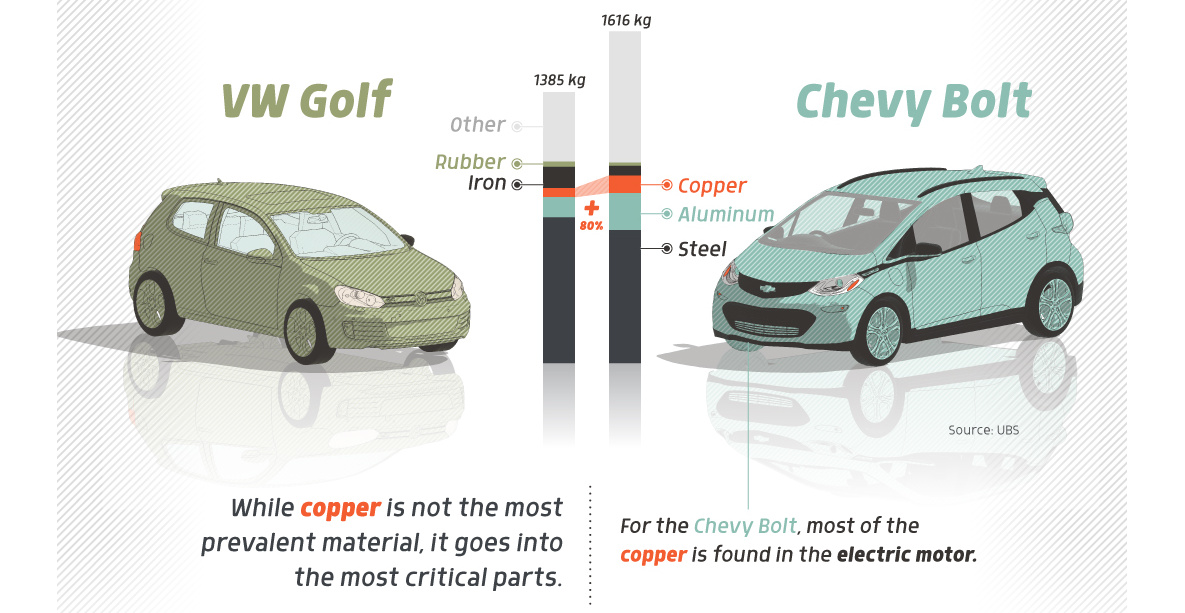
Copper5 years agoHow Much Copper is in an Electric Vehicle?
Have you ever wondered how much copper is in an electric vehicle? This infographic shows the metal’s properties as well as the quantity of copper used.
-
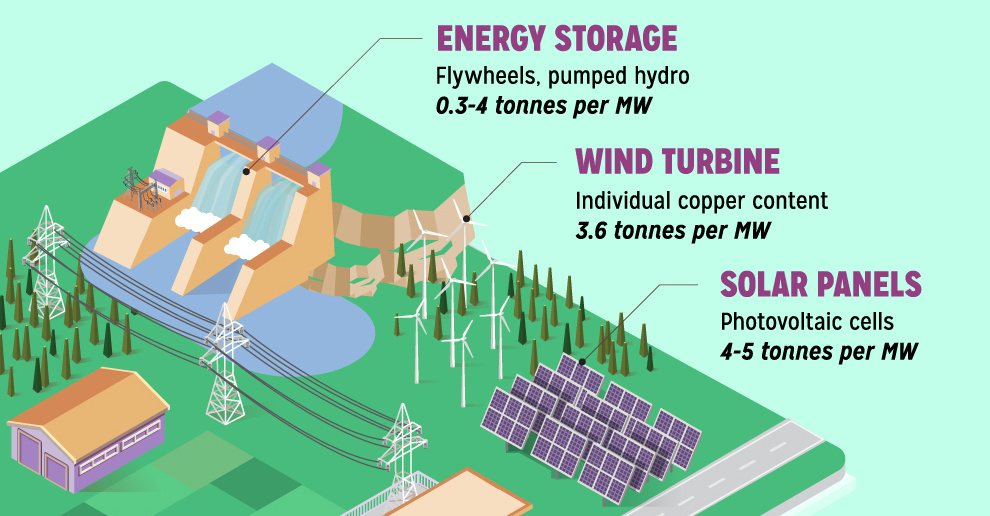
 Copper6 years ago
Copper6 years agoCopper: Driving the Green Energy Revolution
Renewable energy is set to fuel a new era of copper demand – here’s how much copper is used in green applications from EVs to photovoltaics.
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Misc2 weeks ago
Misc2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?