The High Cost of Chronic Diseases Worldwide
The following content is sponsored by NuGen Medical Devices.
The High Cost of Chronic Diseases Worldwide
Are humans healthier than we ever were in the course of history?
While the state of healthcare systems has drastically improved and we’re living longer lives, there are some diseases that are proving difficult to beat completely—specifically, they are called chronic diseases.
This infographic from NuGen Medical Devices highlights the true cost of chronic diseases, and the pressing challenges we face in treating them.
The Impacts of Chronic Diseases on Healthcare
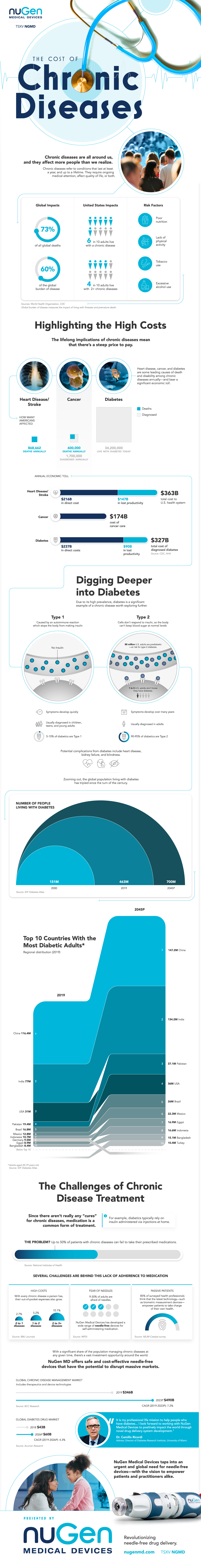
Chronic diseases refer to conditions that last at least a year, and up to a lifetime. They typically require ongoing medical attention, affect quality of life, or both.
According to the World Health Organization, chronic diseases make up 73% of all global deaths, and an additional 60% of the global burden of disease. This latter measure is an indicator of the impact of living with illnesses and premature deaths.
Here are some contributing risk factors for contracting a chronic disease:
- Poor nutrition
- Lack of physical activity
- Tobacco use
- Excessive alcohol use
Chronic diseases affect more people than we realize. In the U.S. alone, 6 in 10 adults have at least one chronic disease. They can also compound significantly: it’s estimated that 4 in 10 adults suffer from at least two or more.
So what are the major types of chronic diseases, and their implications?
Highlighting the High Costs of Chronic Diseases
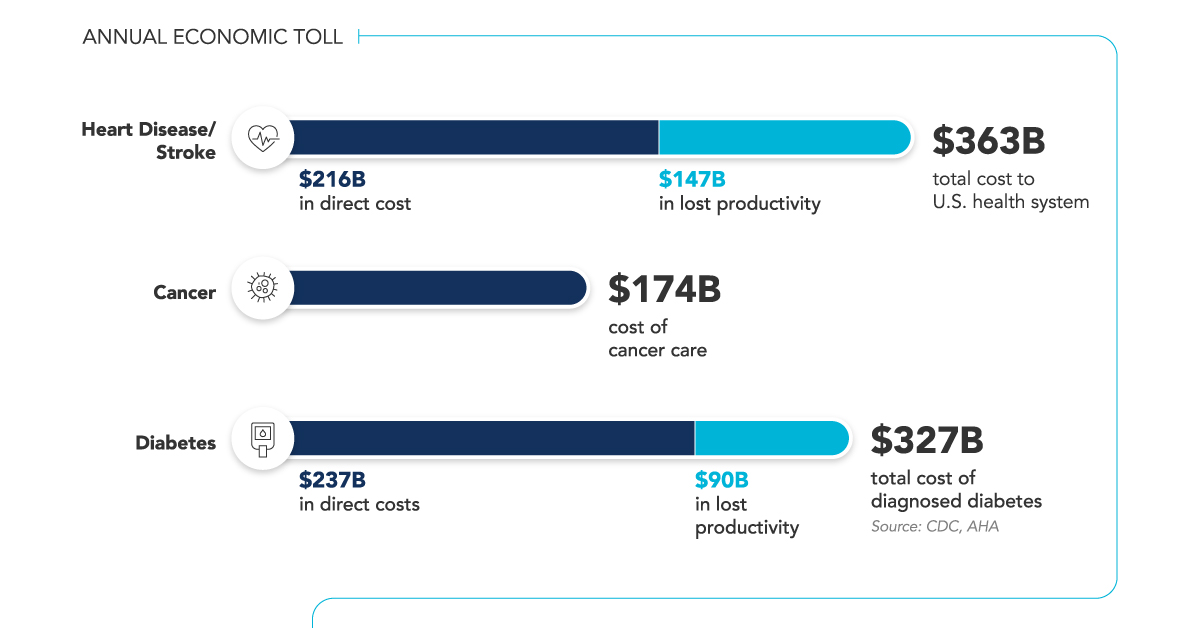
Heart disease, cancer, and diabetes are some leading causes of death and disability among chronic diseases annually. In addition, the lifelong implications of chronic diseases mean that there’s not only a steep human cost, but a significant economic one too.
| Disease type | How many Americans affected | Annual economic toll |
|---|---|---|
| Heart disease/stroke | 868,662 annual deaths | $363B total cost to U.S. health system • $216B in direct cost • $147B in lost productivity |
| Cancer | 600,000 annual deaths 1.7 million diagnosed annually | $174B cost of cancer care |
| Diabetes | >34.2 million live with diabetes today | $327B total cost of diagnosed diabetes • $237B in direct costs • $90B in lost productivity |
Sources: CDC, AHA
It’s not a surprise then that these three chronic diseases also account for some of the most prescribed drugs in America to try and combat or mitigate their effects on everyday lives.
Due to its high prevalence, diabetes is a significant example of a chronic disease worth exploring further.
Digging Deeper into Diabetes
Did you know that 1 in 5 U.S. adults don’t know they have diabetes? Here is a breakdown of the two major types of diabetes, including their different causes, symptoms, and proportion in the population.
| Type 1 | Type 2 |
|---|---|
| Caused by an autoimmune reaction which stops the body from making insulin | Cells don’t respond to insulin, so the body can’t keep blood sugar at normal levels |
| Symptoms develop quickly | Symptoms develop over many years |
| Usually diagnosed in children, teens, and young adults | Usually diagnosed in adults |
| 5-10% of diabetics are Type 1 | 90-95% of diabetics are Type 2 |
About 88 million U.S. adults are prediabetic, namely, at risk for type 2 diabetes. Potential additional complications from diabetes include heart disease, kidney failure, and blindness.
The Top 10 Countries With Highest Diabetic Population (2019-2045P)
Zooming out, the global population living with diabetes has tripled since the turn of the century, from 151 million in 2000 to 463 million in 2019. It’s also estimated that 700 million people may have to live with diabetes by the year 2045.
Which countries are at highest risk of having the most diabetic adults (aged 20-79 years old) now and in the future?
| Rank | Country | Millions, 2019 | Country | Millions, 2045P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | 🇨🇳 China | 116.4 | 🇨🇳 China | 147.2 |
| #2 | 🇮🇳 India | 77 | 🇮🇳 India | 134.2 |
| #3 | 🇺🇸 U.S. | 31 | 🇵🇰 Pakistan | 37.1 |
| #4 | 🇵🇰 Pakistan | 19.4 | 🇺🇸 U.S. | 36 |
| #5 | 🇧🇷 Brazil | 16.8 | 🇧🇷 Brazil | 26 |
| #6 | 🇲🇽 Mexico | 12.8 | 🇲🇽 Mexico | 22.3 |
| #7 | 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 10.7 | 🇪🇬 Egypt | 16.9 |
| #8 | 🇩🇪 Germany | 9.5 | 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 16.6 |
| #9 | 🇪🇬 Egypt | 8.9 | 🇧🇩 Bangladesh | 15.1 |
| #10 | 🇧🇩 Bangladesh | 8.4 | 🇹🇷 Turkey | 10.4 |
A significant share of diabetic adults worldwide will be found across Asia. Notably, China and India are demographically at the highest risk.
The Challenges of Chronic Disease Treatment
Since there aren’t really any “cures” for chronic diseases, medication is a common form of treatment. For example, many diabetics typically rely on insulin administered via injections at home.
However, this can run into issues of a lack of adherence. In fact, up to 50% of patients with chronic diseases can fail to take their prescribed medications. What’s behind this trend?
- High costs
The more chronic diseases a person has, their out-of-pocket expenses increase as well.
For example, for someone with 3+ chronic diseases, their typical costs can shoot up to 10.1x the baseline, namely those not living with any chronic diseases. - Passive patients
In a survey of health professionals, 85% think that the latest technology—such as biometric measurement devices—empower patients to take charge of their own health.
This means that patients who aren’t using such devices may not feel the urgency to take their medications. - Fear of needles
A significant share of the adult population is afraid of needles, ranging from 9-30%.
With a significant share of the population managing chronic diseases at any given time, there’s a vast investment opportunity around the world.
That’s where NuGen Medical Devices comes in. The company has developed a wide range of safe, cost-effective, and needle-free devices for self-administering medication.
This has the potential to disrupt massive industries, such as the global chronic disease management market. In 2019 alone, this market was worth $326 billion. At a compound annual growth rate of 7.2%, it could reach $490 billion by 2023.
NuGen Medical Devices taps into an urgent and global need for needle-free devices—with the vision to empower patients and practitioners alike.
-

 Sponsored3 years ago
Sponsored3 years agoMore Than Precious: Silver’s Role in the New Energy Era (Part 3 of 3)
Long known as a precious metal, silver in solar and EV technologies will redefine its role and importance to a greener economy.
-

 Sponsored7 years ago
Sponsored7 years agoThe History and Evolution of the Video Games Market
Everything from Pong to the rise of mobile gaming and AR/VR. Learn about the $100 billion video games market in this giant infographic.
-

 Sponsored8 years ago
Sponsored8 years agoThe Extraordinary Raw Materials in an iPhone 6s
Over 700 million iPhones have now been sold, but the iPhone would not exist if it were not for the raw materials that make the technology...
-

 Sponsored8 years ago
Sponsored8 years agoThe Industrial Internet, and How It’s Revolutionizing Mining
The convergence of the global industrial sector with big data and the internet of things, or the Industrial Internet, will revolutionize how mining works.