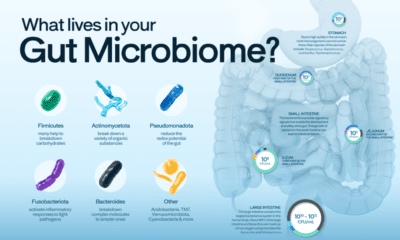
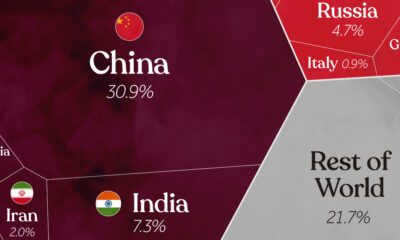
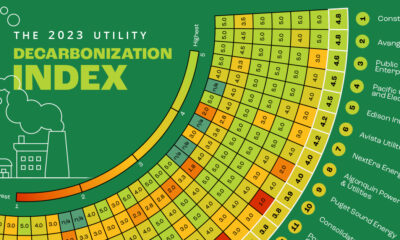
Science
The Elemental Composition of the Human Body
![]() Subscribe to the Elements free mailing list for more like this
Subscribe to the Elements free mailing list for more like this
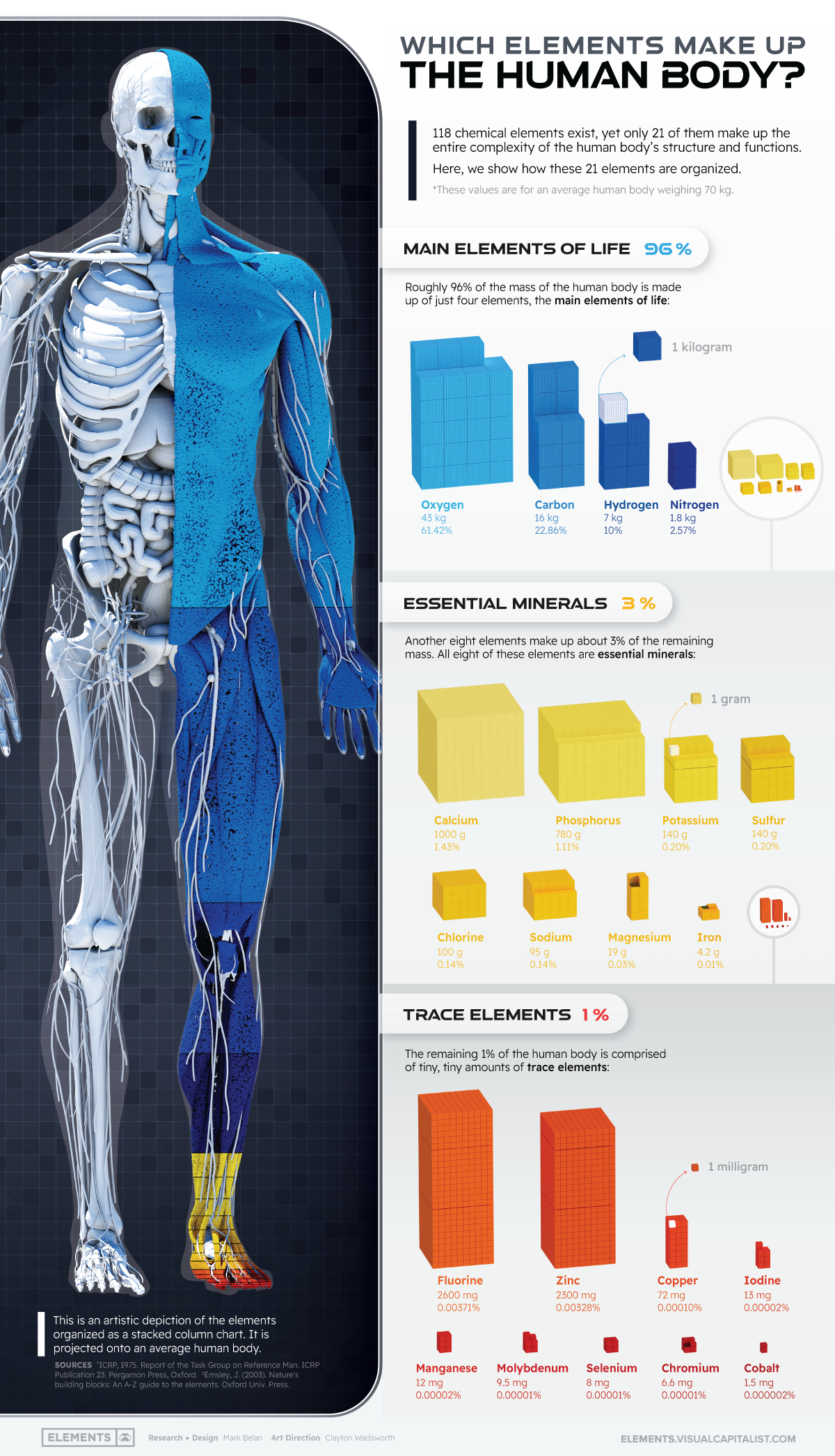
The Elemental Composition of a Human Body
This was originally posted on Elements. Sign up to the free mailing list to get beautiful visualizations on natural resource megatrends in your email every week.
The human body is a miraculous, well-oiled, and exceptionally complex machine. It requires a multitude of functioning parts to come together for a person to live a healthy life—and every biological detail in our bodies, from the mundane to the most magical, is driven by just 21 chemical elements.
Of the 118 elements on Earth, just 21 of them are found in the human body. Together, they make up the medley of divergent molecules that combine to form our DNA, cells, tissues, and organs.
Based on data presented by the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP), in the above infographic, we have broken down a human body to its elemental composition and the percentages in which they exist.
These 21 elements can be categorized into three major blocks depending on the amount found in a human body, the main building block (4 elements), essential minerals (8 elements), and trace elements (9 elements).
The Elemental Four: Ingredients for Life
Four elements, namely, oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen, are considered the most essential elements found in our body.
Oxygen is the most abundant element in the human body, accounting for approximately 61% of a person’s mass. Given that around 60-70% of the body is water, it is no surprise that oxygen and hydrogen are two of the body’s most abundantly found chemical elements. Along with carbon and nitrogen, these elements combine for 96% of the body’s mass.
Here is a look at the composition of the four elements of life:
| Element | Weight of Body Mass (kg) | Percentage of Body Mass (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen | 43 kg | 61.4% |
| Carbon | 16 kg | 22.9% |
| Hydrogen | 7.0 kg | 10.0% |
| Nitrogen | 1.8 kg | 2.6% |
Values are for an average human body weighing 70 kg.
Let’s take a look at how each of these four chemical elements contributes to the thriving functionality of our body:
Oxygen
Oxygen plays a critical role in the body’s metabolism, respiration, and cellular oxygenation. Oxygen is also found in every significant organic molecule in the body, including proteins, carbohydrates, fats, and nucleic acids. It is a substantial component of everything from our cells and blood to our cerebral and spinal fluid.
Carbon
Carbon is the most crucial structural element and the reason we are known as carbon-based life forms. It is the basic building block required to form proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. Breaking carbon bonds in carbohydrates and proteins is our primary energy source.
Hydrogen
Hydrogen, the most abundantly found chemical element in the universe, is present in all bodily fluids, allowing the toxins and waste to be transported and eliminated. With the help of hydrogen, joints in our body remain lubricated and able to perform their functions. Hydrogen is also said to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, helping improve muscle function.
Nitrogen
An essential component of amino acids used to build peptides and proteins is nitrogen. It is also an integral component of the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the chemical backbone of our genetic information and genealogy.
Essential and Supplemental Minerals
Essential minerals are important for your body to stay healthy. Your body uses minerals for several processes, including keeping your bones, muscles, heart, and brain working properly. Minerals also control beneficial enzyme and hormone production.
Minerals like calcium are a significant component of our bones and are required for bone growth and development, along with muscle contractions. Phosphorus contributes to bone and tooth strength and is vital to metabolizing energy.
Here is a look at the elemental composition of essential minerals:
| Element | Weight of Body Mass (g) | Percentage of Body Mass (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium | 1000 g | 1.43% |
| Phosphorus | 780 g | 1.11% |
| Potassium | 140 g | 0.20% |
| Sulphur | 140 g | 0.20% |
| Chlorine | 100 g | 0.14% |
| Sodium | 95 g | 0.14% |
| Magnesium | 19 g | 0.03% |
| Iron | 4.2 g | 0.01% |
Values are for an average human body weighing 70 kg.
Other macro-minerals like magnesium, potassium, iron, and sodium are essential for cell-to-cell communications, like electric transmissions that generate nerve impulses or heart rhythms, and are necessary for maintaining thyroid and bone health.
Excessive deficiency of any of these minerals can cause various disorders in your body. Most humans receive these minerals as a part of their daily diet, including vegetables, meat, legumes, and fruits. In case of deficiencies, though, these minerals are also prescribed as supplements.
Biological Composition of Trace Elements
Trace elements or trace metals are small amounts of minerals found in living tissues. Some of them are known to be nutritionally essential, while others may be considered to be nonessential. They are usually in minimal quantities in our body and make up only 1% of our mass.
Paramount among these are trace elements such as zinc, copper, manganese, and fluorine. Zinc works as a first responder against infections and thereby improves infection resistance, while balancing the immune response.
Here is the distribution of trace elements in our body:
| Element | Weight of Body Mass (mg) | Percentage of Body Mass (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Fluorine | 2600 mg | 0.00371% |
| Zinc | 2300 mg | 0.00328% |
| Copper | 72 mg | 0.00010% |
| Iodine | 13 mg | 0.00002% |
| Manganese | 12 mg | 0.00002% |
| Molybdenum | 9.5 mg | 0.00001% |
| Selenium | 8 mg | 0.00001% |
| Chromium | 6.6 mg | 0.00001% |
| Cobalt | 1.5 mg | 0.000002% |
Values are for an average human body weighing 70 kg.
Even though only it’s found in trace quantities, copper is instrumental in forming red blood cells and keeping nerve cells healthy. It also helps form collagen, a crucial part of bones and connective tissue.
Even with constant research and studies performed to thoroughly understand these trace elements’ uses and benefits, scientists and researchers are constantly making new discoveries.
For example, recent research shows that some of these trace elements could be used to cure and fight chronic and debilitating diseases ranging from ischemia to cancer, cardiovascular disease, and hypertension.
Science
What Are the 10 Most Common Primates in the World?
This list excludes humans, who would otherwise lead the ranks of most common primates by a significant margin.

What Are the 10 Most Common Primates in the World?
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
The word ‘primate’ traces its roots back to the Latin word ‘primas,’ meaning ‘of first rank’ or the highest order in the animal kingdom. This classification intuitively reflects humans’ fascination with the many species who are our closest cousins.
In this graphic, we visualize the top 10 species of primates, ranked by their estimated global population. This data comes from WorldAtlas, and was last updated in 2017.
Given the difficult nature of tracking wild animals, these numbers should be treated as approximations rather than exact figures.
Ranked: Top 10 Primates, by Population
At the top of the list, there are more than 300,000 Müller’s Bornean Gibbons in the world, found on the island of Borneo in Indonesia and Malaysia.
The larger gibbon family consists of around 20 species of small apes found swinging through Southeast Asian rainforests. These acrobatic primates are known for their loud calls, impressive agility, and monogamous family structures.
Despite their ape status, they differ from great apes by being smaller and lacking nests.
| Rank | Monkey | Region of Origin | Estimated Population (as of 2017) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Muller's Bornean Gibbon | 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 312,500 |
| 2 | Common Chimpanzee | 🌍 Sub-Saharan Africa | 236,200 |
| 3 | Gelada | 🇪🇹 Ethiopia | 200,000 |
| 4 | Western Gorilla | 🌍 Western Africa | 175,000 |
| 5 | Bornean Orangutan | 🇮🇩 Indonesia / 🇲🇾 Malaysia | 57,000 |
| 6 | Mentawai Langur | 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 36,000 |
| 7 | Bonobo | 🇨🇩 DRC | 39,750 |
| 8 | Kloss's Gibbon | 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 35,000 |
| 9 | Red-eared Guenon | 🌍 West & Central Africa | 20,000 |
| 10 | Nilgiri Langur | 🇮🇳 India | 20,000 |
Ranked second, the Common Chimpanzee can be found in the savannas and forests of sub-Saharan Africa. A subspecies—the Eastern Chimpanzees in Tanzania’s Gombe National Park—were the primary focus of noted biologist Jane Goodall’s pioneering research in the 1960s.
Despite their apparent numbers, chimpanzees are now classified as an endangered species by the UN, their survival threatened by habitat loss, poaching, and disease.
All the way across, in Ethiopia, the Gelada species is the third most populous primate on the planet. Their short, stump fingers make them adept rock climbers—useful for navigating the Semien mountains they call home.
At fourth place, the Western Gorilla, also found in Africa, is the last primate species with a population above 100,000. The Western Gorillas are a little smaller than their Eastern counterparts, who are the largest living primates.
See More Animal Graphics From Visual Capitalist
If you’re curious to learn more about animals, check out this graphic that ranks the top speeds of the world’s fastest animals.
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoMapped: Average Wages Across Europe
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI1 week ago
AI1 week agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001