Mining
The 50 Minerals Critical to U.S. Security
![]() Subscribe to the Elements free mailing list for more like this
Subscribe to the Elements free mailing list for more like this
The 50 Minerals Critical to U.S. Security
This was originally posted on Elements. Sign up to the free mailing list to get beautiful visualizations on natural resource megatrends in your email every week.
The U.S. aims to cut its greenhouse gas emissions in half by 2030 as part of its commitment to tackling climate change, but might be lacking the critical minerals needed to achieve its goals.
The American green economy will rely on renewable sources of energy like wind and solar, along with the electrification of transportation. However, local production of the raw materials necessary to produce these technologies, including solar panels, wind turbines, and electric vehicles, is lacking. Understandably, this has raised concerns in Washington.
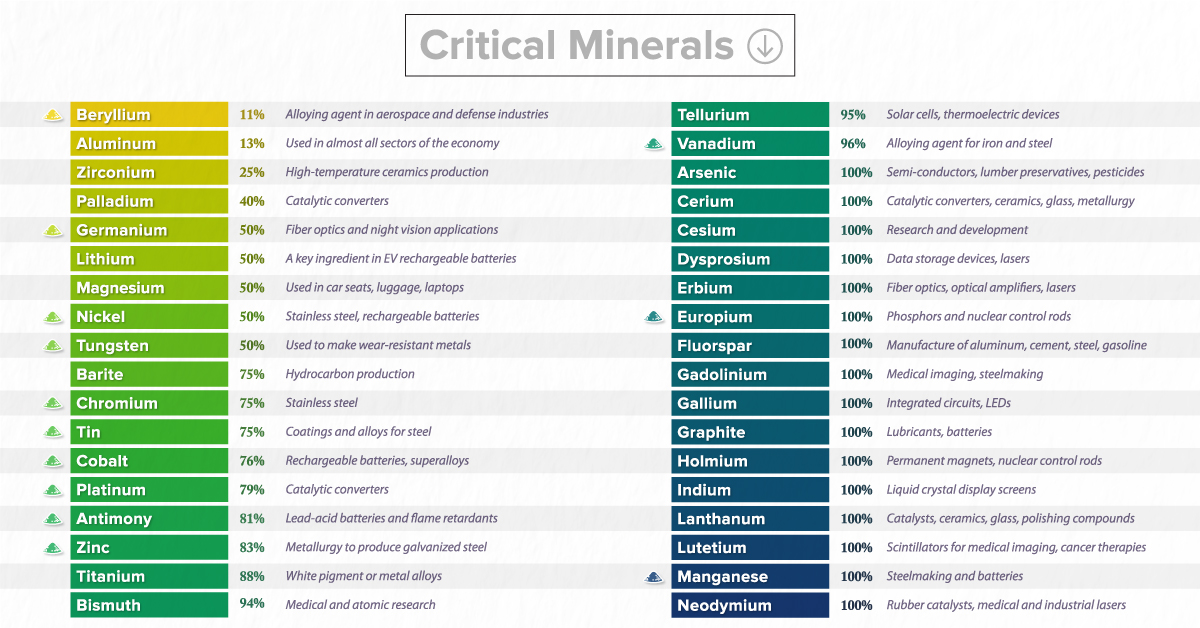
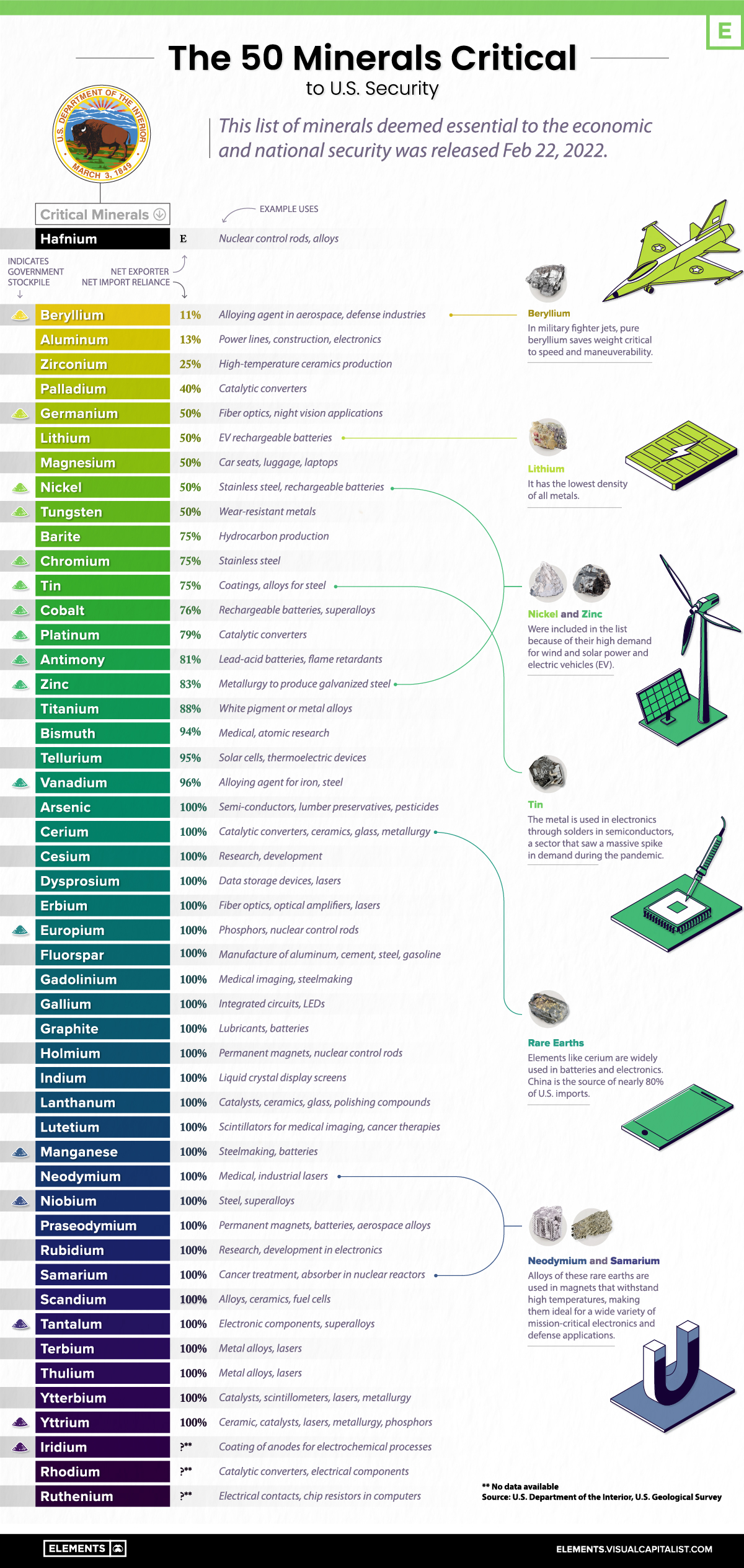
In this graphic, based on data from the U.S. Geological Survey, we list all of the minerals that the government has deemed critical to both the economic and national security of the United States.
What are Critical Minerals?
A critical mineral is defined as a non-fuel material considered vital for the economic well-being of the world’s major and emerging economies, whose supply may be at risk. This can be due to geological scarcity, geopolitical issues, trade policy, or other factors.
In 2018, the U.S. Department of the Interior released a list of 35 critical minerals. The new list, released in February 2022, contains 15 more commodities.
Much of the increase in the new list is the result of splitting the rare earth elements and platinum group elements into individual entries rather than including them as “mineral groups.” In addition, the 2022 list of critical minerals adds nickel and zinc to the list while removing helium, potash, rhenium, and strontium.
| Mineral | Example Uses | Net Import Reliance |
|---|---|---|
| Beryllium | Alloying agent in aerospace, defense industries | 11% |
| Aluminum | Power lines, construction, electronics | 13% |
| Zirconium | High-temparature ceramics production | 25% |
| Palladium | Catalytic converters | 40% |
| Germanium | Fiber optics, night vision applications | 50% |
| Lithium | Rechargeable batteries | 50% |
| Magnesium | Alloys, electronics | 50% |
| Nickel | Stainless steel, rechargeable batteries | 50% |
| Tungsten | Wear-resistant metals | 50% |
| Barite | Hydrocarbon production | 75% |
| Chromium | Stainless steel | 75% |
| Tin | Coatings, alloys for steel | 75% |
| Cobalt | Rechargeable batteries, superalloys | 76% |
| Platinum | Catalytic converters | 79% |
| Antimony | Lead-acid batteries, flame retardants | 81% |
| Zinc | Metallurgy to produce galvanized steel | 83% |
| Titanium | White pigment, metal alloys | 88% |
| Bismuth | Medical, atomic research | 94% |
| Tellurium | Solar cells, thermoelectric devices | 95% |
| Vanadium | Alloying agent for iron and steel | 96% |
| Arsenic | Semi-conductors, lumber preservatives, pesticides | 100% |
| Cerium | Catalytic converters, ceramics, glass, metallurgy | 100% |
| Cesium | Research, development | 100% |
| Dysprosium | Data storage devices, lasers | 100% |
| Erbium | Fiber optics, optical amplifiers, lasers | 100% |
| Europium | Phosphors, nuclear control rods | 100% |
| Fluorspar | Manufacture of aluminum, cement, steel, gasoline | 100% |
| Gadolinium | Medical imaging, steelmaking | 100% |
| Gallium | Integrated circuits, LEDs | 100% |
| Graphite | Lubricants, batteries | 100% |
| Holmium | Permanent magnets, nuclear control rods | 100% |
| Indium | Liquid crystal display screens | 100% |
| Lanthanum | Catalysts, ceramics, glass, polishing compounds | 100% |
| Lutetium | Scintillators for medical imaging, cancer therapies | 100% |
| Manganese | Steelmaking, batteries | 100% |
| Neodymium | Rubber catalysts, medical, industrial lasers | 100% |
| Niobium | Steel, superalloys | 100% |
| Praseodymium | Permanent magnets, batteries, aerospace alloys | 100% |
| Rubidium | Research, development in electronics | 100% |
| Samarium | Cancer treatment, absorber in nuclear reactors | 100% |
| Scandium | Alloys, ceramics, fuel cells | 100% |
| Tantalum | Electronic components, superalloys | 100% |
| Terbium | Permanent magnets, fiber optics, lasers | 100% |
| Thulium | Metal alloys, lasers | 100% |
| Ytterbium | Catalysts, scintillometers, lasers, metallurgy | 100% |
| Yttrium | Ceramic, catalysts, lasers, metallurgy, phosphors | 100% |
| Iridium | Coating of anodes for electrochemical processes | No data available |
| Rhodium | Catalytic converters, electrical components | No data available |
| Ruthenium | Electrical contacts, chip resistors in computers | No data available |
| Hafnium | Nuclear control rods, alloys | Net exporter |
The challenge for the U.S. is that the local production of these raw materials is extremely limited.
For instance, in 2021 there was only one operating nickel mine in the country, the Eagle mine in Michigan. The facility ships its concentrates abroad for refining and is scheduled to close in 2025. Likewise, the country only hosted one lithium mine, the Silver Peak Mine in Nevada.
At the same time, most of the country’s supply of critical minerals depends on countries that have historically competed with America.
China’s Dominance in Minerals
Perhaps unsurprisingly, China is the single largest supply source of mineral commodities for the United States.
Cesium, a critical metal used in a wide range of manufacturing, is one example. There are only three pegmatite mines in the world that can produce cesium, and all were controlled by Chinese companies in 2021.
Furthermore, China refines nearly 90% of the world’s rare earths. Despite the name, these elements are abundant on the Earth’s crust and make up the majority of listed critical minerals. They are essential for a variety of products like EVs, advanced ceramics, computers, smartphones, wind turbines, monitors, and fiber optics.
After China, the next largest source of mineral commodities to the United States has been Canada, which provided the United States with 16 different elements in 2021.
The Rising Demand for Critical Minerals
As the world’s clean energy transitions gather pace, demand for critical minerals is expected to grow quickly.
According to the International Energy Association, the rise of low-carbon power generation is projected to triple mineral demand from this sector by 2040.
The shift to a sustainable economy is important, and consequently, securing the critical minerals necessary for it is just as vital.
Copper
Brass Rods: The Secure Choice
This graphic shows why brass rods are the secure choice for precision-machined and forged parts.

Brass Rods: The Secure Choice
The unique combination of machinability and recyclability makes brass rods the secure choice for manufacturers seeking future-proof raw material solutions.
This infographic, from the Copper Development Association, shows three ways brass rods give manufacturers greater control and a license to grow in the competitive market for precision-machined and forged products.
Future-Proof Investments in New Machine Tools
A material’s machinability directly impacts machine throughput, which typically has the largest impact on machine shop profitability.
The high-speed machining capabilities of brass rods maximize machine tool performance, allowing manufacturers to run the material faster and longer without sacrificing tool life, chip formation, or surface quality.
The high machining efficiency of brass leads to reduced per-part costs, quicker return on investment (ROI) for new machine tools, and expanded production capacity for new projects.
Supply Security Through Closed Loop Recycling
Brass, like its parent element copper, can be infinitely recycled.
In 2022, brass- and wire-rod mills accounted for the majority of the 830,000 tonnes of copper recycled from scrap in the United States.
Given that scrap ratios for machined parts typically range from 60-70% by weight, producing mills benefit from a secure and steady supply of clean scrap returned directly from customers, which is recycled to create new brass rods.
The high residual value of brass scrap creates a strong recycling incentive. Scrap buy back programs give manufacturers greater control over raw material net costs as scrap value is often factored into supplier purchase agreements.
Next Generation Alloys for a Lead-Free Future
Increasingly stringent global regulations continue to pressure manufacturers to minimize the use of materials containing trace amounts of lead and other harmful impurities.
The latest generation of brass-rod alloys is engineered to meet the most demanding criteria for lead leaching in drinking water and other sensitive applications.
Seven brass-rod alloys passed rigorous testing to become the only ‘Acceptable Materials’ against lower lead leaching criteria recently adopted in the national U.S. drinking water quality standard, NSF 61.

Learn more about the advantages of brass rods solutions.

-

 Base Metals1 year ago
Base Metals1 year agoRanked: The World’s Largest Copper Producers
Many new technologies critical to the energy transition rely on copper. Here are the world’s largest copper producers.
-
 Silver2 years ago
Silver2 years agoMapped: Solar Power by Country in 2021
In 2020, solar power saw its largest-ever annual capacity expansion at 127 gigawatts. Here’s a snapshot of solar power capacity by country.
-

 Batteries5 years ago
Batteries5 years agoVisualizing Copper’s Role in the Transition to Clean Energy
A clean energy transition is underway as wind, solar, and batteries take center stage. Here’s how copper plays the critical role in these technologies.
-
 Science5 years ago
Science5 years agoEverything You Need to Know on VMS Deposits
Deep below the ocean’s waves, VMS deposits spew out massive amounts of minerals like copper, zinc, and gold, making them a key source of the metals…
-
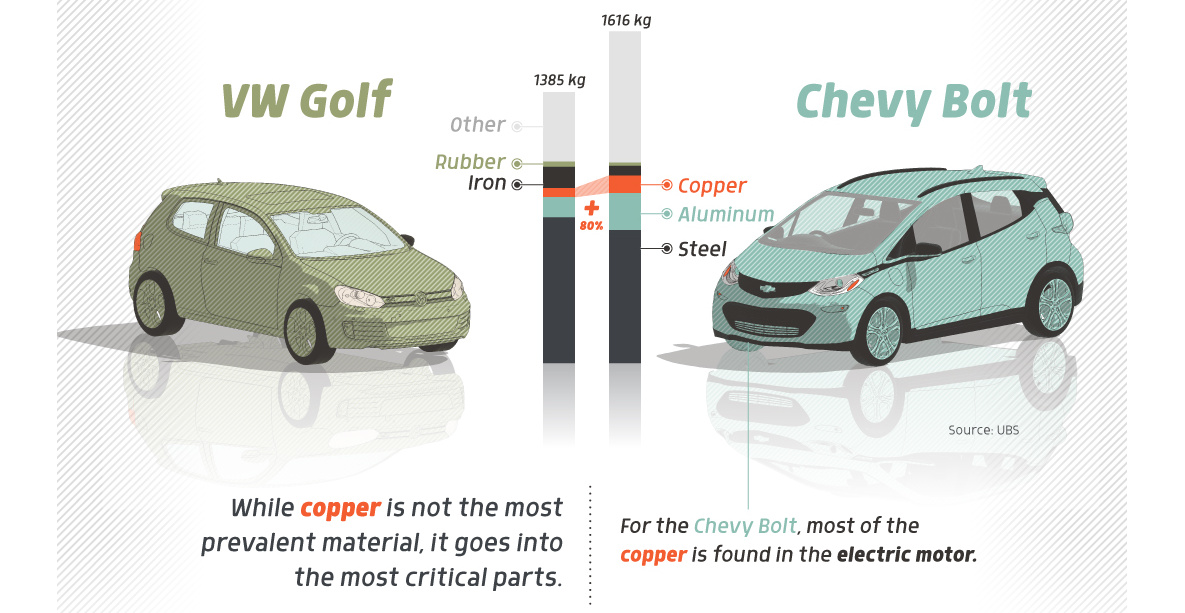
 Copper5 years ago
Copper5 years agoHow Much Copper is in an Electric Vehicle?
Have you ever wondered how much copper is in an electric vehicle? This infographic shows the metal’s properties as well as the quantity of copper used.
-
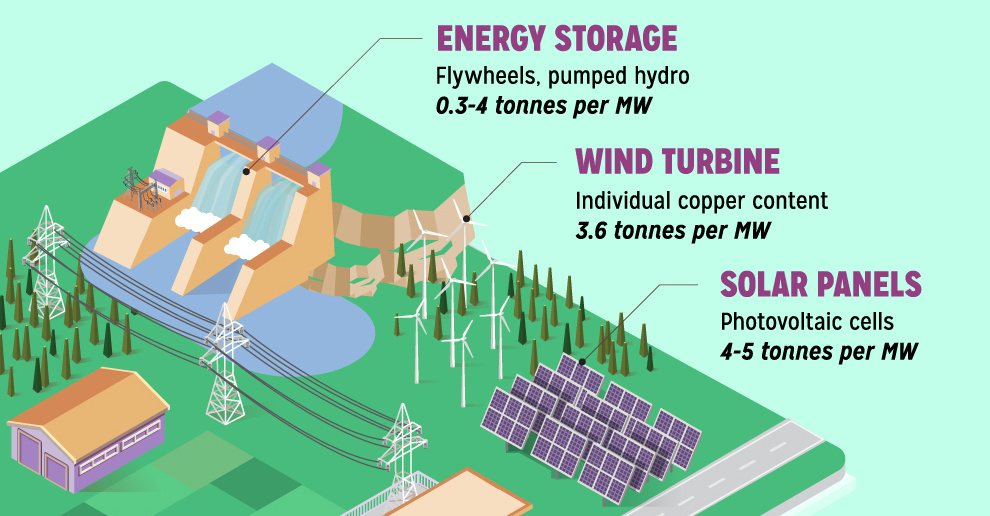
 Copper6 years ago
Copper6 years agoCopper: Driving the Green Energy Revolution
Renewable energy is set to fuel a new era of copper demand – here’s how much copper is used in green applications from EVs to photovoltaics.
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoMapped: Average Wages Across Europe
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI1 week ago
AI1 week agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001