Green
UN Sustainable Development Goals: How Companies Stack Up
The UN SDGs: How Companies Stack Up
Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) investing witnessed a breakthrough year in 2020 with the most fund inflows on record.
Importantly, for companies that are judged according to ESG metrics, one way to track their progress is through their alignment to the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Established in 2012, the UN SDGs are a blueprint for creating a more sustainable future by 2030 that have been adopted by 193 countries worldwide.
As investors and stakeholders pay closer attention to sustainability concerns, this graphic from MSCI breaks down how companies stack up according to their alignment to the UN SDGs.
How Were Companies Measured?
To track companies net contribution to the UN SDGs, companies were scored by their positive or negative contribution to each of the 17 goals.
The 17 UN SDGs are designed to achieve three primary objectives by 2030:
- Protect the planet
- End poverty
- Create prosperity and peace for all
Specifically, the framework centers on a discussion paper that was developed in partnership with the OECD in 2018. Company policies, operations, products and services, and practices are analyzed according to reported and publicly available information.
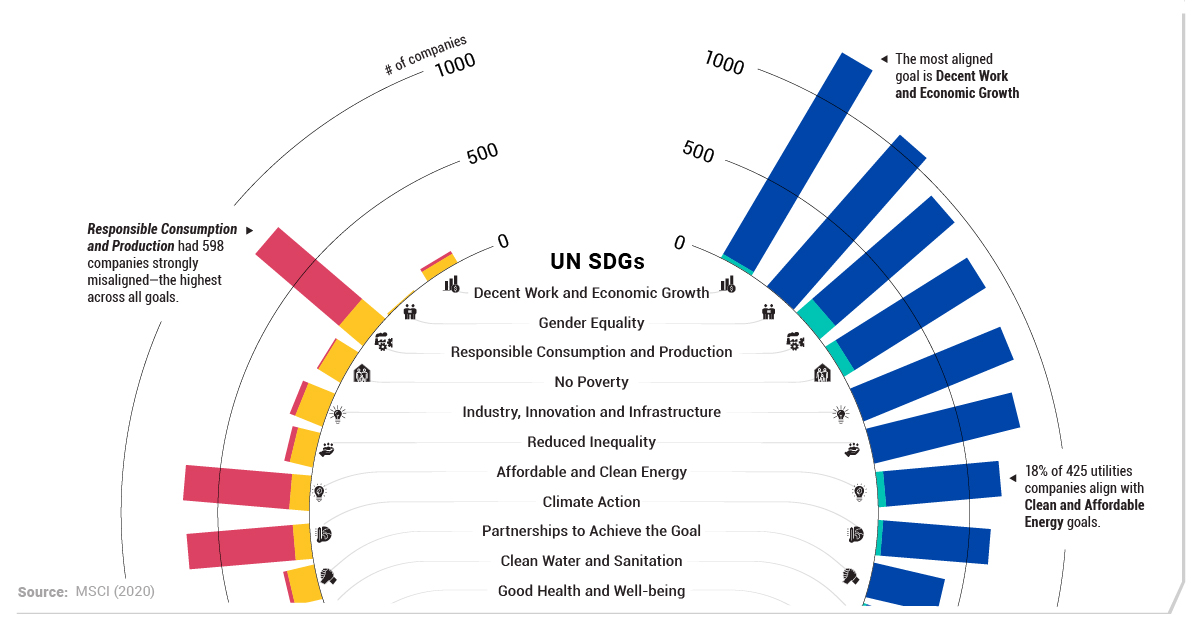
Tracking the Alignment of Companies
Across a universe of 8,550 companies in the MSCI All Country World Index, constituents were measured from strongly aligned to strongly misaligned to the UN SDGs.
| Sustainable Development Goal | Strongly Aligned | Aligned | Misaligned | Strongly Misaligned |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | No Poverty | 0 | 892 | 155 | 32 |
| 2 | Zero Hunger | 24 | 234 | 30 | 0 |
| 3 | Good Health and Well-being | 0 | 315 | 141 | 29 |
| 4 | Quality Education | 8 | 31 | 52 | 0 |
| 5 | Gender Equality | 0 | 1092 | 9 | 0 |
| 6 | Clean Water and Sanitation | 17 | 325 | 36 | 10 |
| 7 | Affordable and Clean Energy | 43 | 639 | 109 | 587 |
| 8 | Decent Work and Economic Growth | 25 | 1269 | 52 | 17 |
| 9 | Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 68 | 844 | 137 | 9 |
| 10 | Reduced Inequality | 0 | 828 | 127 | 31 |
| 11 | Sustainable Cities and Communities | 0 | 0 | 167 | 19 |
| 12 | Responsible Consumption and Production | 115 | 855 | 150 | 598 |
| 13 | Climate Action | 27 | 594 | 95 | 587 |
| 14 | Life Below Water | 0 | 36 | 151 | 92 |
| 15 | Life on Land | 0 | 0 | 128 | 17 |
| 16 | Peace and Justice Strong Institutions | 0 | 135 | 241 | 27 |
| 17 | Partnerships to Achieve the Goal | 0 | 401 | 152 | 22 |
Source: MSCI ESG Research LLC as of August 11, 2020
Broadly speaking, companies fell mostly in the middle—roughly 38% were aligned while almost 55% were misaligned or neutral. Meanwhile, just 0.2% of companies were strongly aligned to the UN SDGs.
Overall, one of the most strongly aligned goals was Responsible Production and Consumption, with 115 companies meeting this criteria. Specifically, these include companies that are building sustainable infrastructure, energy efficiency, or creating green jobs.
Interestingly, the worst performing goal was also Responsible Production and Consumption, with over five times as many companies (598) strongly misaligned. Along with this goal, both Climate Action and Affordable and Clean Energy each had over 500 companies strongly misaligned.
UN SDGs: A Sector Focus
Unsurprisingly, SDG-alignment varied widely according to company sectors.
Educational companies, for instance, represented the highest level of alignment to Gender Equality. Meanwhile, 18% of 425 utilities companies assessed ended up aligning with Clean and Affordable Energy goals.
As one would expect, the energy sector lagged behind. In 2020, fossil fuels were a key source of revenue for 91% of the companies in the energy business. In fact, just three companies derived over 50% of their revenues from green alternatives: REX American Resources, Renewable Energy Group, and Verbio.
A Call to Action?
Despite the growing wave of interest in ESG investing, the reality is that progress to meet the UN SDGs has been slower going than expected.
However, a greater number of individuals, stakeholders, and activists are sounding the alarm. Today, over 3,000 signatories representing trillions in assets under management have committed to the UN Principles of Responsible Investment, which has established six key actions for ESG investing. Now, many companies are required to report their ESG disclosures in Europe.
Along with these key markers of progress, investors can move the dial by tracking a company’s alignment to sustainable development goals.
Green
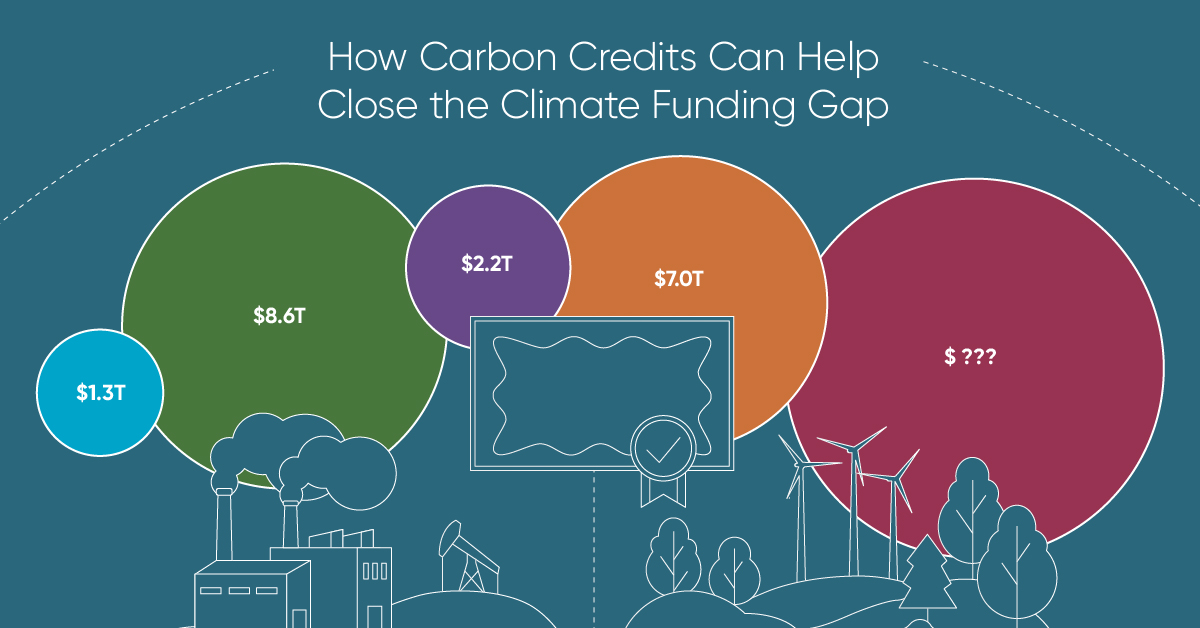
How Carbon Credits Can Help Close the Climate Funding Gap
To keep a 1.5℃ world within reach, global emissions need to fall by as much as 45% by 2030, and carbon credits could help close the gap.
How Carbon Credits Can Help Close the Climate Funding Gap
Governments around the world have committed to the goals of the Paris Agreement, but their climate pledges are insufficient. To keep a 1.5℃ world within reach, global emissions need to fall by as much as 45% by 2030.
Bold and immediate action is essential, but so are resources that will make it happen.
In this graphic, we have partnered with Carbon Streaming to look at the role that the voluntary carbon market and carbon credits can play in closing that gap.
More Funds are Needed for Climate Finance
According to data from the Climate Policy Initiative, climate finance, which includes funds for both adaptation and mitigation, needs to increase at least five-fold, from $1.3T in 2021/2022, to an average $8.6T annually until 2030, and then to just over $10T in the two decades leading up to 2050.
That adds up to a very large number, but consider that in 2022, $7.0T went to fossil fuel subsidies, which almost covers the annual estimated outlay. And the world has shown that when pressed, governments can come up with the money, if the global pandemic is any indication.
Mobilizing Carbon Finance to the Developing World
But the same cannot be said of the developing world, where debt, inequality, and poverty reduce the ability of governments to act. And this is where carbon credits can play an important role. According to analyses from Ecosystem Marketplace, carbon credits help move capital from developed countries, to where funds are needed in the developing world.
For example, in 2019, 69.2% of the carbon credits by volume in the voluntary carbon market were purchased by buyers in Europe, and nearly a third from North America. Compare that to over 90% of the volume of carbon credits sold in the voluntary carbon market in 2022 came from projects that were located outside of those two regions.
Carbon Credits Can Complement Decarbonization Efforts
Carbon credits can also complement decarbonization efforts in the corporate world, where more and more companies have been signing up to reduce emissions. According to the 2022 monitoring report from the Science Based Targets initiative, 4,230 companies around the world had approved targets and commitments, which represented an 88% increase from the prior year. However, as of year end 2022, combined scope 1 and 2 emissions covered by science-based targets totaled approximately 2 GtCO2e, which represents just a fraction of global emissions.
The fine print is that this is just scope 1 and 2 emissions, and doesn’t include scope 3 emissions, which can account for more than 70% of a company’s total emissions. And as these emissions come under greater and greater scrutiny the closer we get to 2030 and beyond, the voluntary carbon credit market could expand exponentially to help meet the need to compensate for these emissions.
Potential Carbon Credit Market Size in 2030
OK, but how big? In 2022, the voluntary carbon credit market was around $2B, but some analysts predict that it could grow to between $5–250 billion by 2030.
| Firm | Low Estimate | High Estimate |
|---|---|---|
| Bain & Company | $15B | $30B |
| Barclays | N/A | $250B |
| Citigroup | $5B | $50B |
| McKinsey & Company | $5B | $50B |
| Morgan Stanley | N/A | $100B |
| Shell / Boston Consulting Group | $10B | $40B |
Morgan Stanley and Barclays were the most bullish on the size of the voluntary carbon credit market in 2030, but the latter firm was even more optimistic about 2050, and predicted that the voluntary carbon credit market could grow to a colossal $1.5 trillion.
Carbon Streaming is Focused on Carbon Credit Integrity
Ultimately, carbon credits could have an important role to play in marshaling the resources needed to keep the world on track to net zero by 2050, and avoiding the worst consequences of a warming world.
Carbon Streaming uses streaming transactions, a proven and flexible funding model, to scale high-integrity carbon credit projects to advance global climate action and UN Sustainable Development Goals.

Learn more at www.carbonstreaming.com.

-

 Green1 week ago
Green1 week agoRanking the Top 15 Countries by Carbon Tax Revenue
This graphic highlights France and Canada as the global leaders when it comes to generating carbon tax revenue.
-

 Green1 week ago
Green1 week agoRanked: The Countries With the Most Air Pollution in 2023
South Asian nations are the global hotspot for pollution. In this graphic, we rank the world’s most polluted countries according to IQAir.
-

 Environment2 weeks ago
Environment2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
One country is taking reforestation very seriously, registering more than 400,000 square km of forest growth in two decades.
-

 Green3 weeks ago
Green3 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
The country with the most forest loss since 2001 lost as much forest cover as the next four countries combined.
-

 Markets2 months ago
Markets2 months agoThe World’s Top Cocoa Producing Countries
Here are the largest cocoa producing countries globally—from Côte d’Ivoire to Brazil—as cocoa prices hit record highs.
-

 Environment2 months ago
Environment2 months agoCharted: Share of World Forests by Country
We visualize which countries have the biggest share of world forests by area—and while country size plays a factor, so too, does the environment.
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023