Markets
The Controversy Around Stock Buybacks Explained
The Controversy Around Stock Buybacks Explained
At face value, the notion of companies buying back shares in their own stock may seem pretty benign.
But as soon as trillions of dollars are being poured into any single cause – regardless of how innocuous it may sound – there is always the potential to make a lightning rod for controversy.
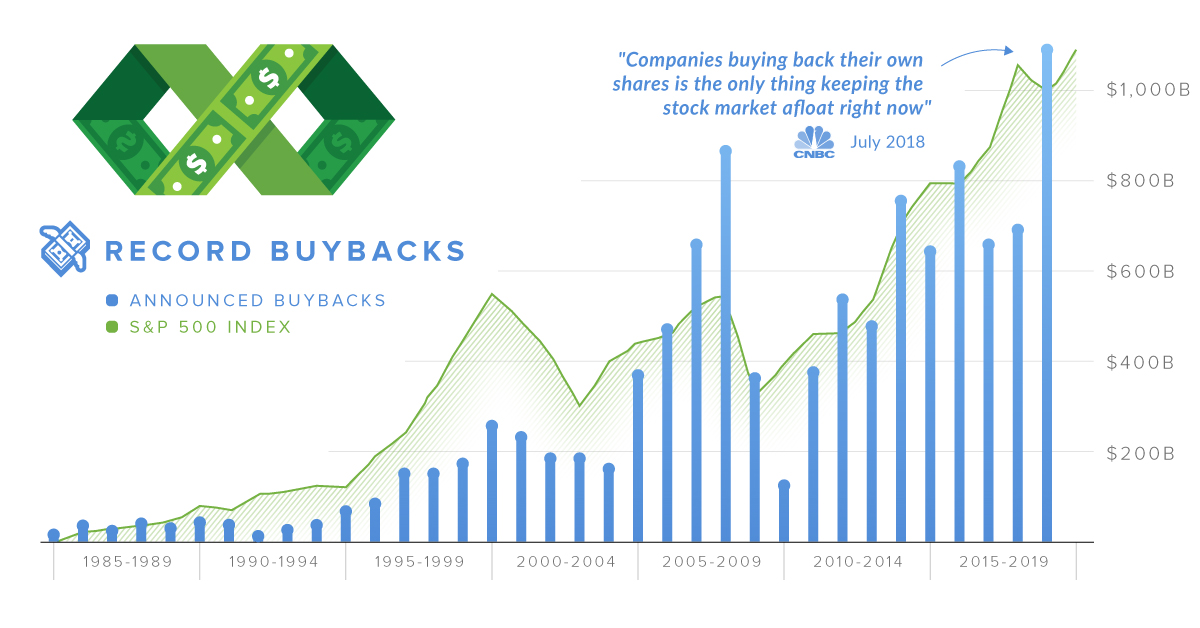
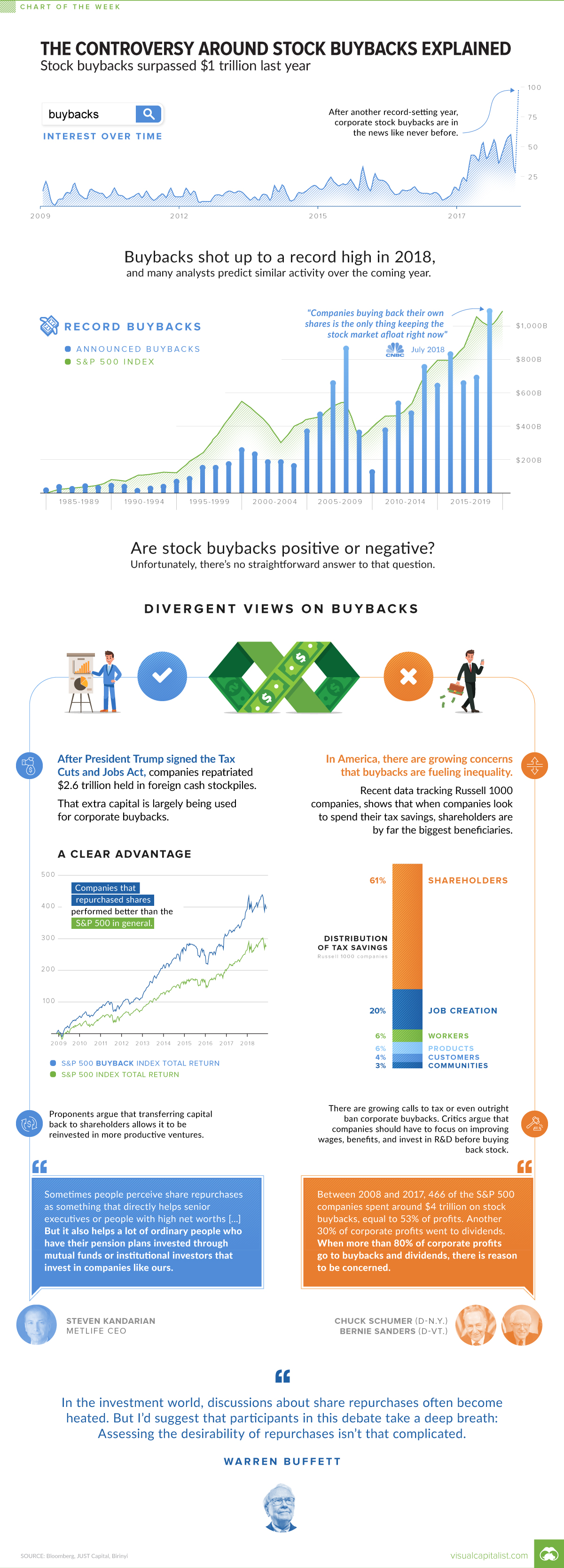
With stock buybacks totaling $1.1 trillion in 2018, they’re at the center of discussion more than ever before.
What are Stock Buybacks?
When publicly-traded companies want to return money to shareholders, they generally have two options.
The first is to declare a dividend, but the other is to repurchase its own shares on the open market.
Although it seems meta, stock buybacks are a way for companies to re-invest in themselves. Each buyback decreases the amount of shares outstanding, with the company re-absorbing the portion of ownership that was previously distributed among investors.
In other words, buybacks are somewhat analogous to buying out a business partner – they allow the remaining partners to own a higher share of the company.
Pro vs. Con
With the amount of stock buybacks rising to historic highs, they have been front and center in 2019. Here are what proponents and opponents are arguing about.
Pro Case:
Proponents of buybacks say that if they are done rationally, buybacks (like dividends) are just another way to return cash to shareholders. Stock prices for companies that have bought back shares are also higher, in general, than other companies on major indices like the S&P 500.
Con Case:
Opponents of stock buybacks say that they increase inequality, and that executives make short-term oriented decisions around buybacks that allow them to maximize personal gain. In other words, when a company probably should be investing in its people or its business, the company is instead giving money back to the wealthy owners – and only they benefit.
The Bottom Line
While both sides make a compelling argument for different reasons, the only real way to evaluate stock buybacks is based on the merits of individual companies.
If the company is returning money to shareholders because it is the best allocation of capital, then it can make perfect sense. If the company is doing it at the expense of growing its business and the wages of employees, one can see why stock buybacks may rub people the wrong way.
Economy
Economic Growth Forecasts for G7 and BRICS Countries in 2024
The IMF has released its economic growth forecasts for 2024. How do the G7 and BRICS countries compare?

G7 & BRICS Real GDP Growth Forecasts for 2024
The International Monetary Fund’s (IMF) has released its real gross domestic product (GDP) growth forecasts for 2024, and while global growth is projected to stay steady at 3.2%, various major nations are seeing declining forecasts.
This chart visualizes the 2024 real GDP growth forecasts using data from the IMF’s 2024 World Economic Outlook for G7 and BRICS member nations along with Saudi Arabia, which is still considering an invitation to join the bloc.
Get the Key Insights of the IMF’s World Economic Outlook
Want a visual breakdown of the insights from the IMF’s 2024 World Economic Outlook report?
This visual is part of a special dispatch of the key takeaways exclusively for VC+ members.
Get the full dispatch of charts by signing up to VC+.
Mixed Economic Growth Prospects for Major Nations in 2024
Economic growth projections by the IMF for major nations are mixed, with the majority of G7 and BRICS countries forecasted to have slower growth in 2024 compared to 2023.
Only three BRICS-invited or member countries, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and South Africa, have higher projected real GDP growth rates in 2024 than last year.
| Group | Country | Real GDP Growth (2023) | Real GDP Growth (2024P) |
|---|---|---|---|
| G7 | 🇺🇸 U.S. | 2.5% | 2.7% |
| G7 | 🇨🇦 Canada | 1.1% | 1.2% |
| G7 | 🇯🇵 Japan | 1.9% | 0.9% |
| G7 | 🇫🇷 France | 0.9% | 0.7% |
| G7 | 🇮🇹 Italy | 0.9% | 0.7% |
| G7 | 🇬🇧 UK | 0.1% | 0.5% |
| G7 | 🇩🇪 Germany | -0.3% | 0.2% |
| BRICS | 🇮🇳 India | 7.8% | 6.8% |
| BRICS | 🇨🇳 China | 5.2% | 4.6% |
| BRICS | 🇦🇪 UAE | 3.4% | 3.5% |
| BRICS | 🇮🇷 Iran | 4.7% | 3.3% |
| BRICS | 🇷🇺 Russia | 3.6% | 3.2% |
| BRICS | 🇪🇬 Egypt | 3.8% | 3.0% |
| BRICS-invited | 🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia | -0.8% | 2.6% |
| BRICS | 🇧🇷 Brazil | 2.9% | 2.2% |
| BRICS | 🇿🇦 South Africa | 0.6% | 0.9% |
| BRICS | 🇪🇹 Ethiopia | 7.2% | 6.2% |
| 🌍 World | 3.2% | 3.2% |
China and India are forecasted to maintain relatively high growth rates in 2024 at 4.6% and 6.8% respectively, but compared to the previous year, China is growing 0.6 percentage points slower while India is an entire percentage point slower.
On the other hand, four G7 nations are set to grow faster than last year, which includes Germany making its comeback from its negative real GDP growth of -0.3% in 2023.
Faster Growth for BRICS than G7 Nations
Despite mostly lower growth forecasts in 2024 compared to 2023, BRICS nations still have a significantly higher average growth forecast at 3.6% compared to the G7 average of 1%.
While the G7 countries’ combined GDP is around $15 trillion greater than the BRICS nations, with continued higher growth rates and the potential to add more members, BRICS looks likely to overtake the G7 in economic size within two decades.
BRICS Expansion Stutters Before October 2024 Summit
BRICS’ recent expansion has stuttered slightly, as Argentina’s newly-elected president Javier Milei declined its invitation and Saudi Arabia clarified that the country is still considering its invitation and has not joined BRICS yet.
Even with these initial growing pains, South Africa’s Foreign Minister Naledi Pandor told reporters in February that 34 different countries have submitted applications to join the growing BRICS bloc.
Any changes to the group are likely to be announced leading up to or at the 2024 BRICS summit which takes place October 22-24 in Kazan, Russia.
Get the Full Analysis of the IMF’s Outlook on VC+
This visual is part of an exclusive special dispatch for VC+ members which breaks down the key takeaways from the IMF’s 2024 World Economic Outlook.
For the full set of charts and analysis, sign up for VC+.
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries