Investing in Core Cybersecurity Technology
The following content is sponsored by eToro
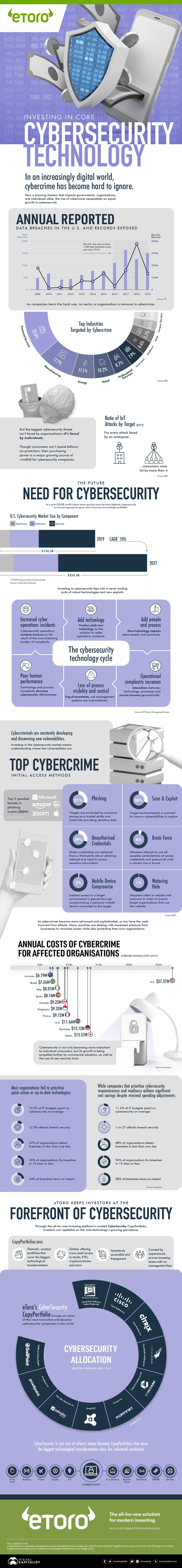
Investing in Core Cybersecurity Technology
The world has become increasingly more digital—with everything from customer data and employee services to entire businesses living on servers—and in recent years cybercrime has become a constant threat.
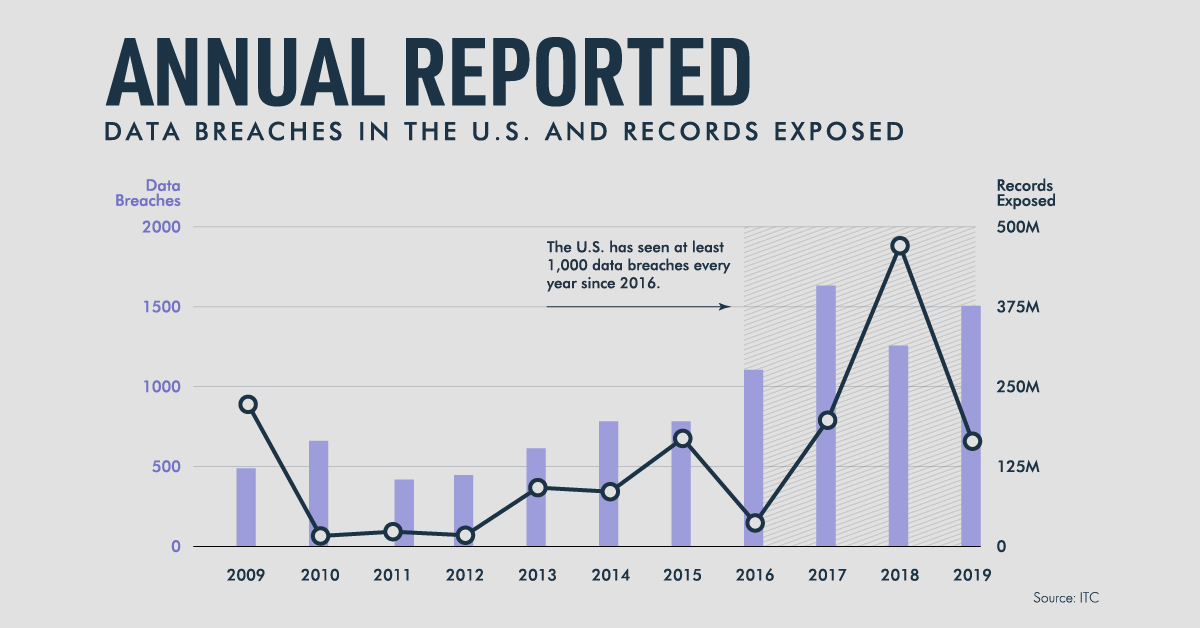
After large-scale breaches in government organisations around the world and huge public companies like Sony, cybersecurity is being taken more seriously. And since 2016, the U.S. has seen at least 1,000 data breaches every single year, exposing billions more records.
But in a field where new exploits are just around the corner, and with COVID-19 driving more employees and services remote than ever before, the need for better cybersecurity technology and investment has reached critical importance.
This infographic from eToro highlights developments in the cybersecurity market and how they affect companies, consumers, and investors.
The Cybersecurity Landscape
No person or organisation is immune to cybercrime, but some are targeted more frequently.
Across businesses, cybercriminals look for exploits in sectors with either the most to lose in terms of financials or data, or they target sectors with the least protection.
Unsurprisingly, the top industry targeted by cybercrime in 2020 was financial services. But cybercriminals also focused on manufacturing, energy, and retail—industries forced to quickly shift to digital channels because of the pandemic, but without the time to adapt and safeguard.
| Top Industries Targeted by Cybercrime | % Targeted (2020) |
|---|---|
| Financial Services | 23.0% |
| Manufacturing | 17.7% |
| Energy | 11.1% |
| Retail | 10.2% |
| Professional Services | 8.7% |
| Government | 7.9% |
| Healthcare | 6.6% |
| Media | 5.7% |
| Transportation | 5.1% |
| Education | 4.0% |
Though targeting is inconsistent across industries, financial impact is significant across the board.
In Europe, the average annual cost inflicted by cybercrime for affected organisations in 2019 ranged from $8 million in Italy to $13 million in Germany. In the U.S., the average annual cost of cybercrime was over $27 million.
| Organisation Base Country | Average Annual Cost of Cybercrime (2019) |
|---|---|
| U.S. | $27.37M |
| Japan | $13.57M |
| Germany | $13.12M |
| UK | $11.46M |
| France | $9.72M |
| Singapore | $9.32M |
| Canada | $9.25M |
| Spain | $8.16M |
| Italy | $8.01M |
| Brazil | $7.24M |
| Australia | $6.79M |
But in terms of volume, the most common cybersecurity threat is faced by individuals instead of companies. In addition to being a common target for cybercriminals attempting to access company data, consumers faced four times as many attacks as enterprises in 2019.
The Future Cybersecurity Need
The growth of cybercrime activity and adjacent cybersecurity investment over the last few decades was already impressive, but a post-COVID world puts the digital market front and center.
In the U.S., the cybersecurity market was valued at $156.5 billion in 2019, with more than half of the market focused on services over software and hardware. In 2027, the market is estimated to be worth $326.4 billion, a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10%, with the focus remaining the same.
The driver of software and hardware usage is consistent with more aspects of business and personal life digitising, but growth in services is aligned with the uncertainty of future cybersecurity issues.
Winning the Fight Against Cybercrime
Cybersecurity and cybercrime grow and build off each other in a never-ending cycle, driving a need for increased investment alongside them.
The Cybersecurity Technology Cycle:
- Increased cyber operations incidents: Cybersecurity operations incidents increase as a result of the overwhelming burden of complexity.
- Add technology: Vendors pitch new technology as the solution to cyber operations incidents.
- Add people and process: New technology requires more people and processes.
- Operational complexity increases: Interactions between technology, processes and people increase geometrically.
- Loss of process visibility and control: Fog of uncertainty develops, old management systems are overwhelmed.
- Poor human performance: Technology and process complexity decrease cybersecurity effectiveness.
- Repeat 1)
As new devices and software come online, old methods used by cybercriminals for infiltration or data gathering are replaced with new ones.
In 2019, the most commonly used initial access methods were phishing (31%), scan & exploit (30%) and unauthorised credential usage (29%), with compromise of mobile devices only accounting for 2%. With more work going offline and onto personal devices post-pandemic, and increasingly so post-digitisation, those numbers are likely to fluctuate.
That’s why the cybersecurity market is expected to keep growing in importance and size over the coming decade. An increasingly digital world is putting more risk online as well, and as many companies have learned the hard way, cybersecurity is a core technology worth investing in.
How Can Investors Take Part?
eToro’s CyberSecurity CopyPortfolio* gives investors direct access to the growing cybersecurity market.
Curated by experienced and proven investment teams, the thematic portfolio offers exposure to a broad range of developers and companies invested in cybersecurity, with no management fees.
*Your capital is at risk.
CopyPortfolios is a portfolio management product, provided by eToro Europe Ltd., which is authorised and regulated by the Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission.
CopyPortfolios should not be considered as exchange traded funds, nor as hedge funds.
-

 Sponsored3 years ago
Sponsored3 years agoMore Than Precious: Silver’s Role in the New Energy Era (Part 3 of 3)
Long known as a precious metal, silver in solar and EV technologies will redefine its role and importance to a greener economy.
-

 Sponsored7 years ago
Sponsored7 years agoThe History and Evolution of the Video Games Market
Everything from Pong to the rise of mobile gaming and AR/VR. Learn about the $100 billion video games market in this giant infographic.
-

 Sponsored8 years ago
Sponsored8 years agoThe Extraordinary Raw Materials in an iPhone 6s
Over 700 million iPhones have now been sold, but the iPhone would not exist if it were not for the raw materials that make the technology...
-

 Sponsored8 years ago
Sponsored8 years agoThe Industrial Internet, and How It’s Revolutionizing Mining
The convergence of the global industrial sector with big data and the internet of things, or the Industrial Internet, will revolutionize how mining works.