Money
The Relationship Between Money and Happiness
Explore the full-size version of this chart by clicking here.
Charting the Relationship Between Money and Happiness
Today’s chart is best viewed full-screen. Explore the high resolution version by clicking here.
Can money buy you happiness?
It’s a longstanding question that has many different answers, depending on who you ask.
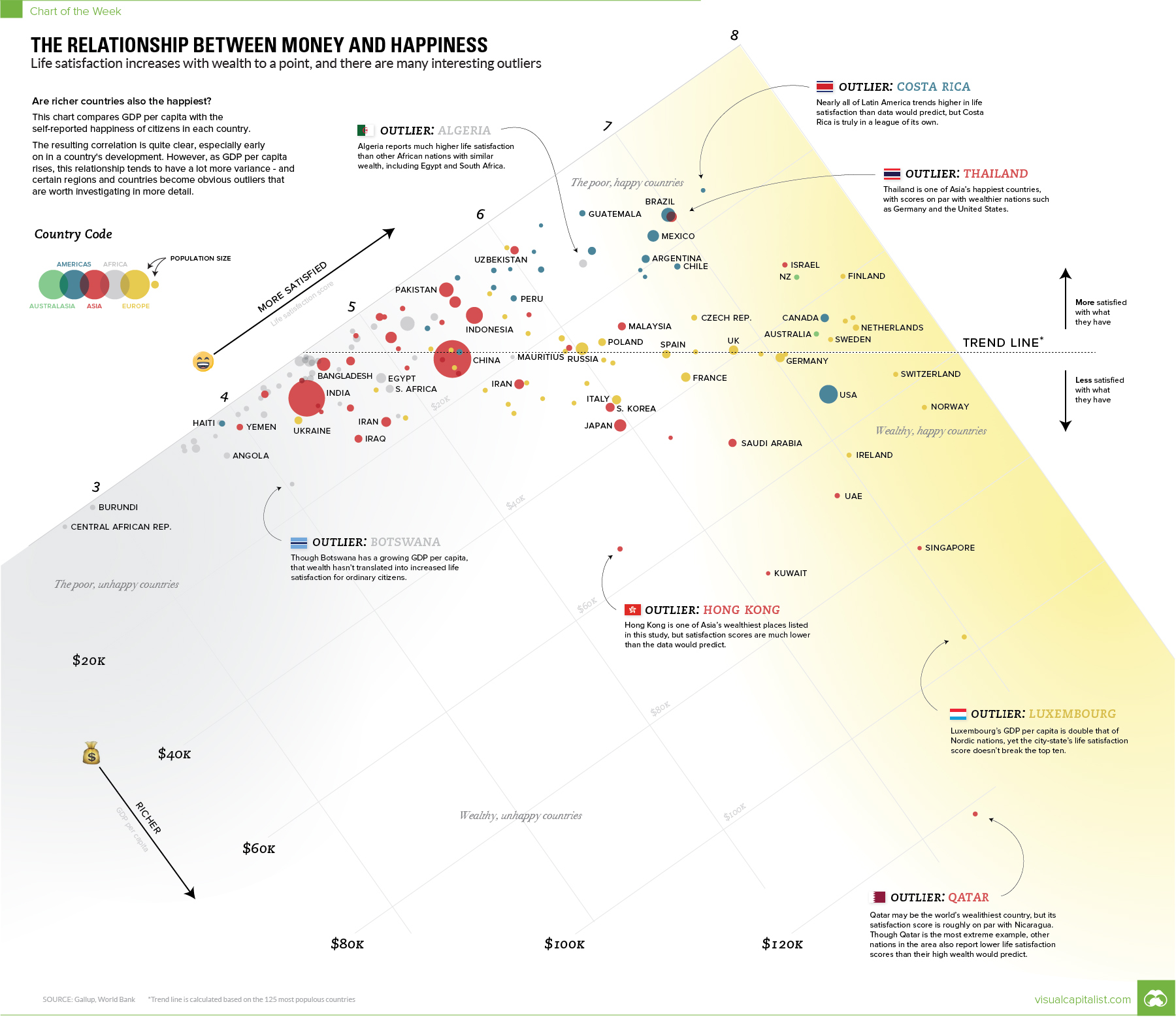
Today’s chart approaches this fundamental question from a data-driven perspective, and it provides one potential solution: money does buy some happiness, but only to a limited extent.
Money and Happiness
First, a thinking exercise.
Let’s say you have two hypothetical people: one of them is named Beff Jezos and he’s a billionaire, and the other is named Jill Smith and she has a more average net worth. Who do you think would be happiest if their wealth was instantly doubled?
Beff might be happy that he’s got more in the bank, but materially his life is unlikely to change much – after all, he’s a billionaire. On the flipside, Jill also has more in the bank and is likely able to use those additional resources to provide better opportunities for her family, get out of debt, or improve her work-life balance.
These resources translate to real changes for Jill, potentially increasing her level of satisfaction with life.
Just like these hypotheticals, the data tells a similar story when we look at countries.
The Data-Driven Approach
Today’s chart looks at the relationship between GDP per capita (PPP) and the self-reported levels of happiness of each country. Sources for data are the World Bank and the World Happiness Report 2017.
According to the numbers, the relationship between money and happiness is strong early on for countries. Then later, when material elements of Maslow’s hierarchy are met, the relationship gets harder to predict.
In general, this means that as a country’s wealth increases from $10k to $20k per person, it will likely slide up the happiness scale as well. For a double from $30k to $60k, the relationship still holds – but it tends to have far more variance. This variance is where things get interesting.
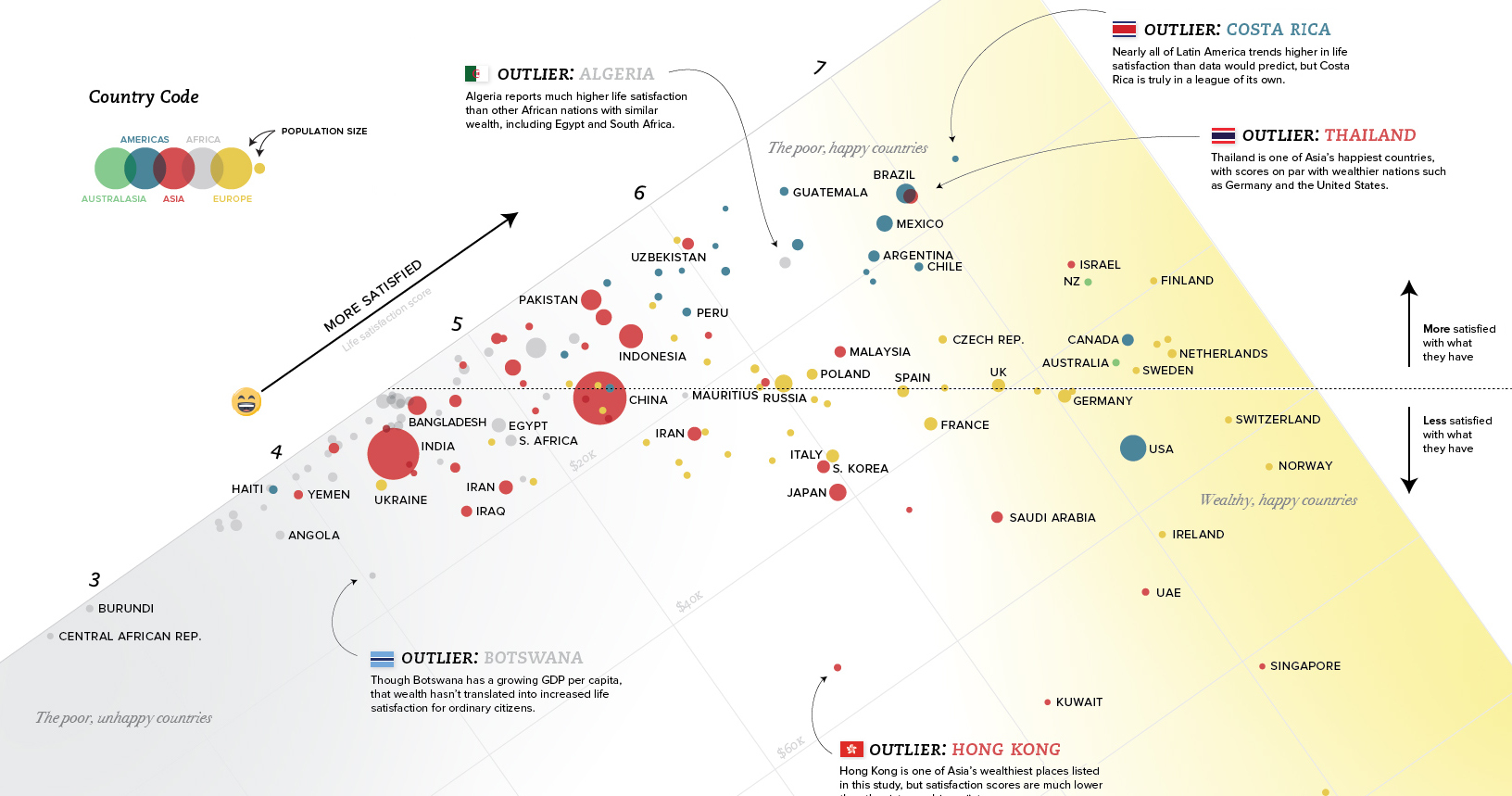
Outlier Regions
Some of the most obvious outliers can be found in Latin America and the Middle East:
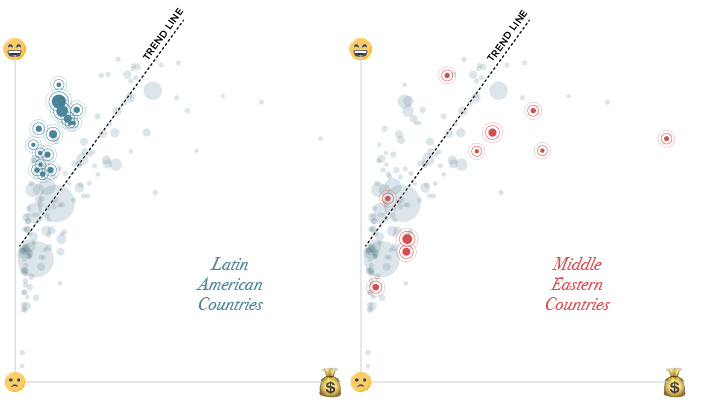
In Latin America, people self-report that they are more satisfied than the trend between money and happiness would predict.
Costa Rica stands out in particular here, with a GDP per capita of $15,400 and a 7.14 rating on the Cantril Ladder (which is a measure of happiness). Whether it’s the country’s rugged coastlines or the local culture that does the trick, Costa Rica has higher happiness ratings than the U.S., Belgium, or Germany – all countries with far higher levels of wealth.
In the Middle East, the situation is mostly reversed. Countries like Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Iran, Iraq, Yemen, Turkey, and the U.A.E. are all on the other side of the trend line.
Outlier Countries
Within regions, there is even plenty of variance.
We just mentioned the Middle East as a place where the wealth-happiness continuum doesn’t seem to hold up as well as it does in other places in the world.
Interestingly, in Qatar, which is actually the wealthiest country in the world on a per capita basis ($127k), things are even more out of whack. Qatar only scores a 6.37 on the Cantril Ladder, making it a big exception even within the context of the already-outlying Middle East.
Nearby Saudi Arabia, U.A.E., and Oman are all poorer than Qatar per capita, yet they are happier places. Oman rates a 6.85 on the satisfaction scale, with less than one-third the wealth per capita of Qatar.
There are other outlier jurisdictions on the list as well: Thailand, Uzbekistan, and Pakistan are all significantly happier than the trend line (or their regional location) would project. Meanwhile, places like Hong Kong, Ireland, Singapore, and Luxembourg are less happy than wealth would predict.
Money
Charted: Who Has Savings in This Economy?
Older, better-educated adults are winning the savings game, reveals a January survey by the National Opinion Research Center at the University of Chicago.
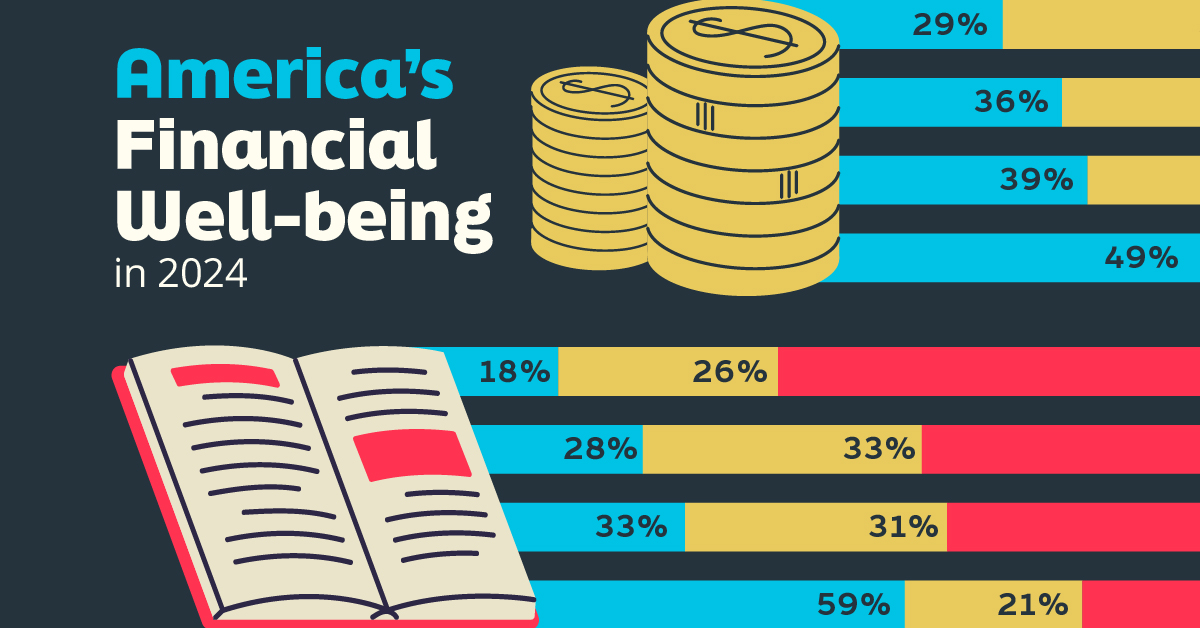
Who Has Savings in This Economy?
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Two full years of inflation have taken their toll on American households. In 2023, the country’s collective credit card debt crossed $1 trillion for the first time. So who is managing to save money in the current economic environment?
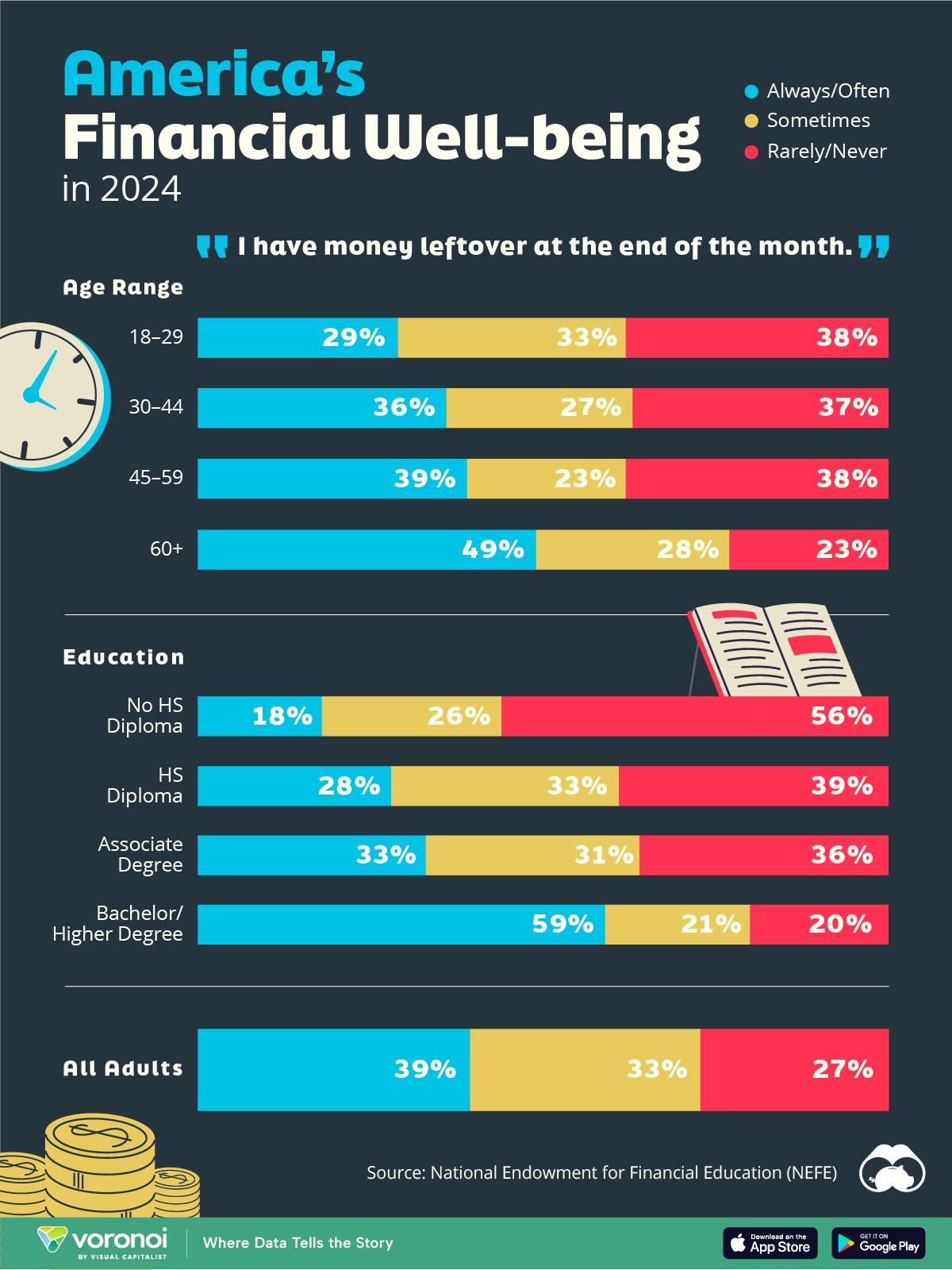
We visualize the percentage of respondents to the statement “I have money leftover at the end of the month” categorized by age and education qualifications. Data is sourced from a National Endowment for Financial Education (NEFE) report, published last month.
The survey for NEFE was conducted from January 12-14, 2024, by the National Opinion Research Center at the University of Chicago. It involved 1,222 adults aged 18+ and aimed to be representative of the U.S. population.
Older Americans Save More Than Their Younger Counterparts
General trends from this dataset indicate that as respondents get older, a higher percentage of them are able to save.
| Age | Always/Often | Sometimes | Rarely/Never |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18–29 | 29% | 33% | 38% |
| 30–44 | 36% | 27% | 37% |
| 45–59 | 39% | 23% | 38% |
| Above 60 | 49% | 28% | 23% |
| All Adults | 39% | 33% | 27% |
Note: Percentages are rounded and may not sum to 100.
Perhaps not surprisingly, those aged 60+ are the age group with the highest percentage saying they have leftover money at the end of the month. This age group spent the most time making peak earnings in their careers, are more likely to have investments, and are more likely to have paid off major expenses like a mortgage or raising a family.
The Impact of Higher Education on Earnings and Savings
Based on this survey, higher education dramatically improves one’s ability to save. Shown in the table below, those with a bachelor’s degree or higher are three times more likely to have leftover money than those without a high school diploma.
| Education | Always/Often | Sometimes | Rarely/Never |
|---|---|---|---|
| No HS Diploma | 18% | 26% | 56% |
| HS Diploma | 28% | 33% | 39% |
| Associate Degree | 33% | 31% | 36% |
| Bachelor/Higher Degree | 59% | 21% | 20% |
| All Adults | 39% | 33% | 27% |
Note: Percentages are rounded and may not sum to 100.
As the Bureau of Labor Statistics notes, earnings improve with every level of education completed.
For example, those with a high school diploma made 25% more than those without in 2022. And as the qualifications increase, the effects keep stacking.
Meanwhile, a Federal Reserve study also found that those with more education tended to make financial decisions that contributed to building wealth, of which the first step is to save.
-

 Green1 week ago
Green1 week agoRanked: The Countries With the Most Air Pollution in 2023
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Travel2 weeks ago
Travel2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue