Money
Visualizing the Ranking of 100 Common Careers
If you’re like most Americans, you probably spend more than 40 hours a week on the job.
For this reason, your career of choice plays a big role in determining your overall well-being. Not only does your profession have a massive influence on the potential money you make, but it also impacts your stress, work-life balance, happiness, and feeling of accomplishment.
However, it’s well-known that not all careers are created equally – and while some are stress-free with comfortable salaries, others can be high-stress without the compensation to make up for it.
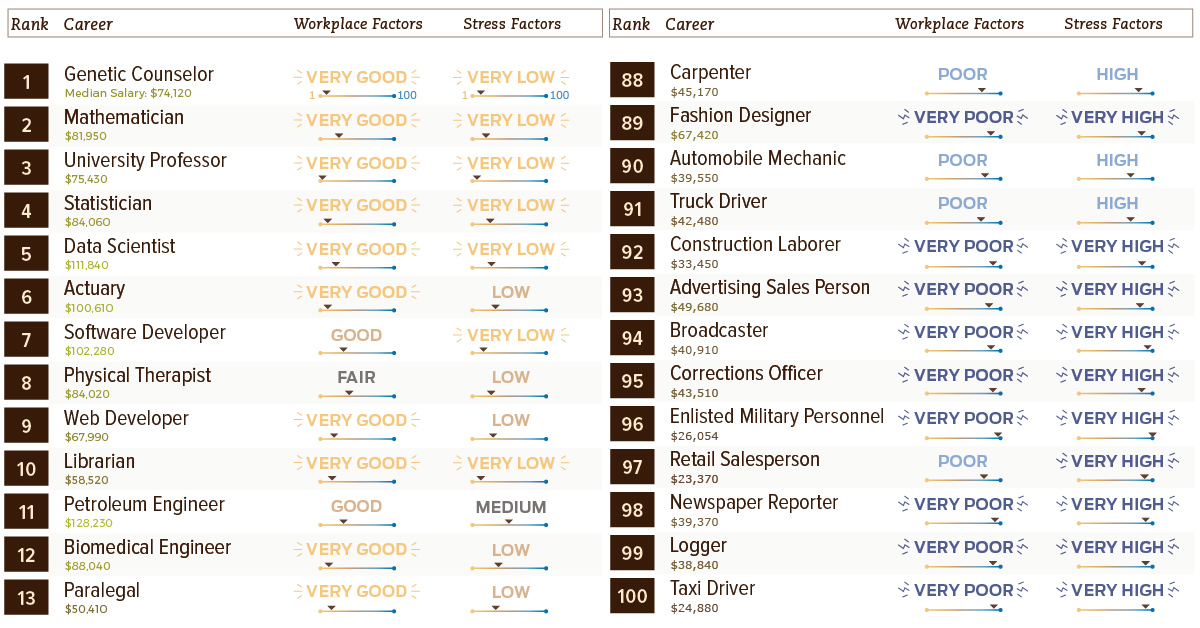
Ranked: 100 Common Careers
Today’s chart uses data from the 2018 Jobs Rated Report by CareerCast.com, and we’ve used it to rank 100 of the most common careers based on median income, as well as three other categories: stress, growth outlook, and workplace environment.
The careers at the top of the list below have the best aggregate score, while the jobs towards the end of the list tend to be high-stress, low-income.
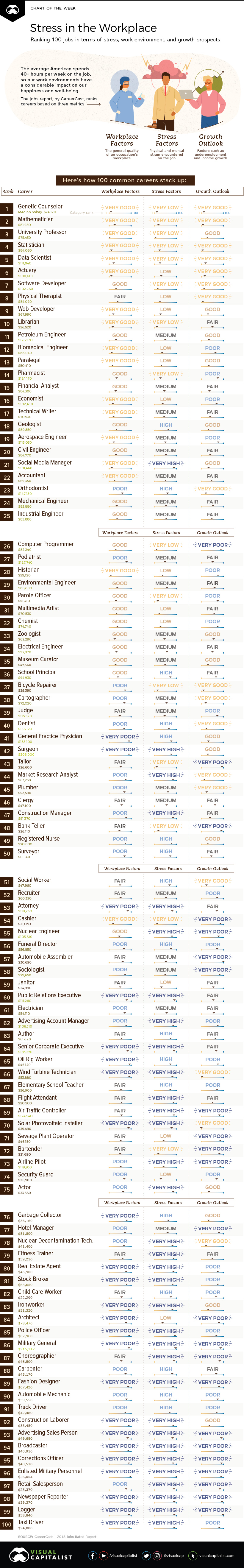
The 2018 Jobs Rated Report uses median income, as well as three other key categories to compile its rankings of common careers:
- Workplace:
A score based on the relative physical and mental demands for the job - Stress:
A weighting of 11 different stress factors, which range from “deadlines” to “own life at risk” - Growth Outlook:
Factors such as employment growth, income growth potential, and unemployment
See the full methodology here, for a more detailed explanation of the above categories.
Choosing the Optimal Career
If your goal is to maximize income, then traditional high-paying careers – like being a lawyer, doctor, investment banker, or senior corporate executive – are a good way to go.
For many people, however, a good career is defined as being more than just having high earning potential. Ideally, it’s also low-stress, while providing a healthy workplace that makes workers look forward to their jobs every day.
For people that think that way, it seems like being a pharmacist or a data scientist might present the best of both worlds:
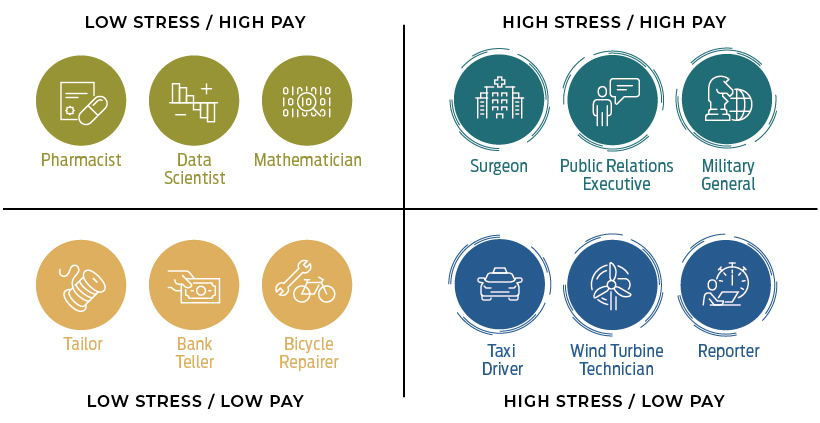
At the same time, it may be safe to say that taxi drivers and reporters get the worst of both worlds: high stress and low pay.
Where does your occupation fall on the money/stress spectrum? Do you feel like the ranking above provides an accurate representation of your career?
Money
How Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
See how much the debt-to-GDP ratios of advanced economies have grown (or shrank) since the year 2000.
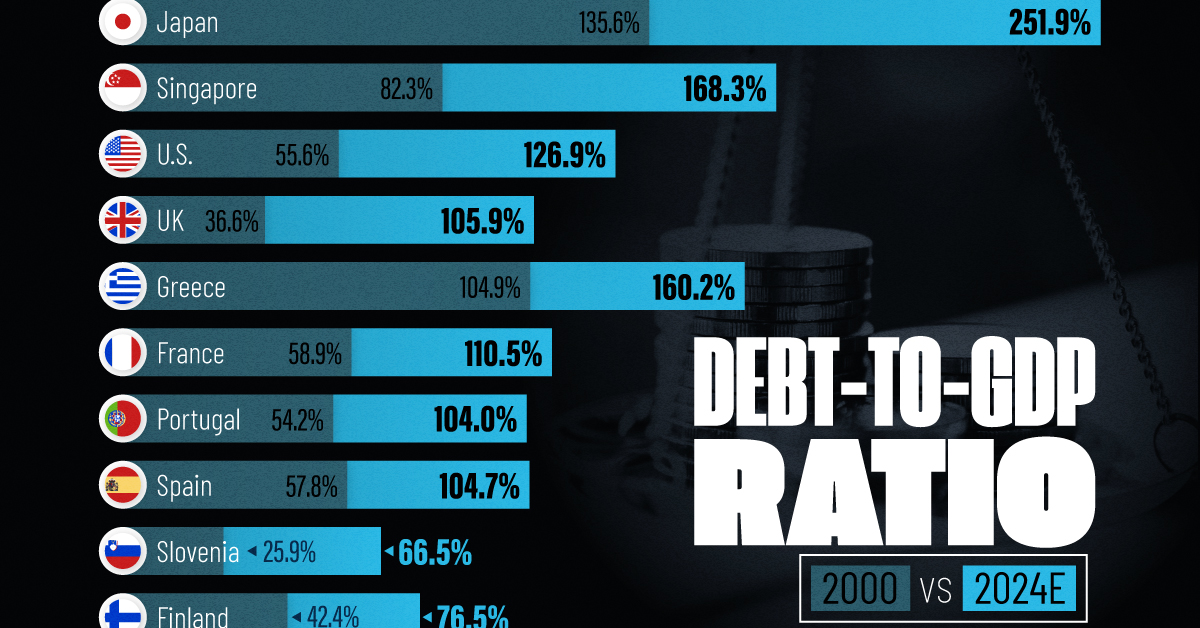
How Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Government debt levels have grown in most parts of the world since the 2008 financial crisis, and even more so after the COVID-19 pandemic.
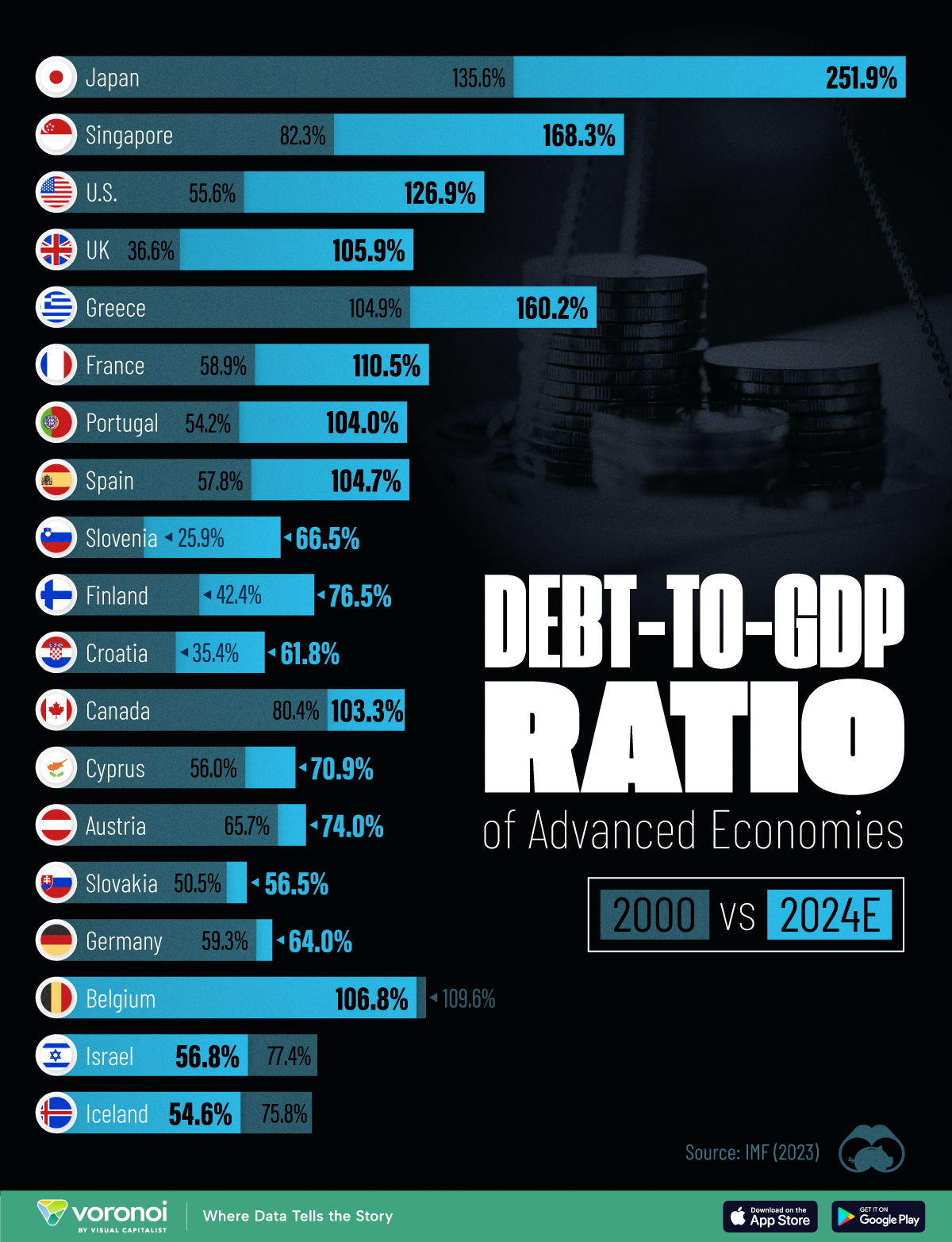
To gain perspective on this long-term trend, we’ve visualized the debt-to-GDP ratios of advanced economies, as of 2000 and 2024 (estimated). All figures were sourced from the IMF’s World Economic Outlook.
Data and Highlights
The data we used to create this graphic is listed in the table below. “Government gross debt” consists of all liabilities that require payment(s) of interest and/or principal in the future.
| Country | 2000 (%) | 2024 (%) | Change (pp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🇯🇵 Japan | 135.6 | 251.9 | +116.3 |
| 🇸🇬 Singapore | 82.3 | 168.3 | +86.0 |
| 🇺🇸 United States | 55.6 | 126.9 | +71.3 |
| 🇬🇧 United Kingdom | 36.6 | 105.9 | +69.3 |
| 🇬🇷 Greece | 104.9 | 160.2 | +55.3 |
| 🇫🇷 France | 58.9 | 110.5 | +51.6 |
| 🇵🇹 Portugal | 54.2 | 104.0 | +49.8 |
| 🇪🇸 Spain | 57.8 | 104.7 | +46.9 |
| 🇸🇮 Slovenia | 25.9 | 66.5 | +40.6 |
| 🇫🇮 Finland | 42.4 | 76.5 | +34.1 |
| 🇭🇷 Croatia | 35.4 | 61.8 | +26.4 |
| 🇨🇦 Canada | 80.4 | 103.3 | +22.9 |
| 🇨🇾 Cyprus | 56.0 | 70.9 | +14.9 |
| 🇦🇹 Austria | 65.7 | 74.0 | +8.3 |
| 🇸🇰 Slovak Republic | 50.5 | 56.5 | +6.0 |
| 🇩🇪 Germany | 59.3 | 64.0 | +4.7 |
| 🇧🇪 Belgium | 109.6 | 106.8 | -2.8 |
| 🇮🇱 Israel | 77.4 | 56.8 | -20.6 |
| 🇮🇸 Iceland | 75.8 | 54.6 | -21.2 |
The debt-to-GDP ratio indicates how much a country owes compared to the size of its economy, reflecting its ability to manage and repay debts. Percentage point (pp) changes shown above indicate the increase or decrease of these ratios.
Countries with the Biggest Increases
Japan (+116 pp), Singapore (+86 pp), and the U.S. (+71 pp) have grown their debt as a percentage of GDP the most since the year 2000.
All three of these countries have stable, well-developed economies, so it’s unlikely that any of them will default on their growing debts. With that said, higher government debt leads to increased interest payments, which in turn can diminish available funds for future government budgets.
This is a rising issue in the U.S., where annual interest payments on the national debt have surpassed $1 trillion for the first time ever.
Only 3 Countries Saw Declines
Among this list of advanced economies, Belgium (-2.8 pp), Iceland (-21.2 pp), and Israel (-20.6 pp) were the only countries that decreased their debt-to-GDP ratio since the year 2000.
According to Fitch Ratings, Iceland’s debt ratio has decreased due to strong GDP growth and the use of its cash deposits to pay down upcoming maturities.
See More Debt Graphics from Visual Capitalist
Curious to see which countries have the most government debt in dollars? Check out this graphic that breaks down $97 trillion in debt as of 2023.
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
-

 Travel1 week ago
Travel1 week agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024